Abstract
Aim:
To provide experimental data for further research on the signal transduction of apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells, we examined the effects of exogenous C2-ceramide administration on several members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) superfamily and caspase-3 in A549 cells.
Methods:
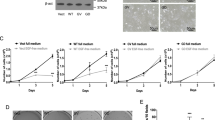
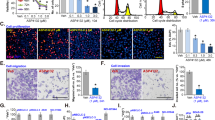
Cell viability and apoptosis were analyzed by cell counting kit-8 assay and flow cytometry. Various MAPK and caspase-3 proteins were detected by Western blotting.
Results:
C2-ceramide selectively altered the phosphorylation state of members of the MAPK superfamily, causing hyperphosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) 1/2 and the p38 MAPK, but not affecting the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase. SB-203580 (a p38 MAPK inhibitor) and p38 siRNA, but not U0126 (a MEK inhibitor), partially rescued cell death induced by C2-ceramide. C2-ceramide promoted the activation of caspase-3.
Conclusion:
Exogenous C2-ceramide induced apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. The activation of MAPK and caspase-3 were involved in the mechanisms of C2-ceramide-induced apoptosis in A549 cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Wang J, Hu XS, Shi JP . Sphingolipid and apoptosis. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan 2003; 34: 217–21.
Chan C, Goldkorn T . Ceramide path in human lung cell death. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2000; 22: 460–8.
Kolesnick R, Hannun YA . Ceramide and apoptosis. Trends Biochem Sci 1999; 24: 224–5.
Perry DK . Ceramide and apoptosis. Biochem Soc Trans 1999; 27: 399–404.
Kurinna SM, Tsao CC, Nica AF, Jiffar T, Ruvolo PP . Ceramide promotes apoptosis in lung cancer-derived A549 cells by a mechanism involving c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 7852–6.
Ravid T, Tsaba A, Gee P, Rasooly R, Medina EA, Goldkorn T . Ceramide accumulation precedes caspase-3 activation during apoptosis of A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2003; 284: L1082–92.
Newton R, Hart L, Chung KF, Barnes PJ . Ceramide induction of COX-2 and PGE(2) in pulmonary A549 cells does not involve activation of NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2000; 277: 675–9.
Morrison DK, Davis RJ . Regulation of MAP kinase signaling modules by scaffold proteins in mammals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2003; 19: 91–118.
Shin CY, Lee YP, Lee TS, Song HJ, Sohn UD . C(2)-ceramide-induced circular smooth muscle cell contraction involves PKC-epsilon and p44/p42 MAPK activation in cat oesophagus. Mito-gen-activated protein kinase. Cell Signal 2002; 14: 925–32.
Willaime S, Vanhoutte P, Caboche J, Lemaigre-Dubreuil Y, Mariani J, Brugg B . Ceramide-induced apoptosis in cortical neurons is mediated by an increase in p38 phosphorylation and not by the decrease in ERK phosphorylation. Eur J Neurosci 2001; 13: 2037–46.
Smyth MJ, Perry DK, Zhang J, Poirier GG, Hannun YA, Obeid LM . prICE: a downstream target for ceramide-induced apoptosis and for the inhibitory action of Bcl-2. Biochem J 1996; 316: 25–8.
Sawada M, Nakashima S, Banno Y, Yamakawa H, Hayashi K, Takenaka K, et al. Ordering of ceramide formation, caspase activation, and Bax/ Bcl-2 expression during etoposide-induced apoptosis in C6 glioma cells. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 761–72.
Stoica BA, Movsesyan VA, Knoblach SM, Faden AI . Ceramide induces neuronal apoptosis through mitogen-activated protein kinases and causes release of multiple mitochondrial proteins. Mol Cell Neurosci 2005; 29: 355–71.
Willaime-Morawek S, Brami-Cherrier K, Mariani J, Caboche J, Brugg B . C-Jun N-terminal kinases/c-Jun and p38 pathways cooperate in ceramide-induced neuronal apoptosis. Neuroscience 2003; 119: 387–97.
Ravid T, Avner R, Polak-Charcon S, Faust JR, Roitelman J . Impaired regulation of 3–hydroxy-3–methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase degradation in lovastatin-resistant cells. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 29341–51.
Goldkorn T, Balaban N, Shannon M, Chea V, Matsukuma K, Gilchrist D, et al. H2O2 acts on cellular membranes to generate ceramide signaling and initiate apoptosis in tracheobronchial epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 1998; 111: 3209–20.
Lavrentiadou SN, Chan C, Kawcak TN, Ravid T, Tsaba, A, van der Vliet, A, et al. Ceramide-mediated apoptosis in lung epithelial cells is regulated by glutathione. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001; 25: 676–84.
Padron JM . Sphingolipids in anticancer therapy. Curr Med Chem 2006; 13: 755–70.
Modrak DE, Gold DV, Goldenberg DM . Sphingolipid targets in cancer therapy. Mol Cancer Ther 2006; 5: 200–8.
Siskind LJ . Mitochondrial ceramide and the induction of apoptosis. J Bioenerg Biomembr 2005; 37: 143–53.
Sawai H, Domae N, Okazaki T . Current status and perspectives in ceramide-targeting molecular medicine. Curr Pharm Des 2005; 11: 2479–87.
Jaffrezou JP, Laurent G . Ceramide: a new target in anticancer research? Bull Cancer 2004; 91: E133–61.
Ogretmen B, Hannun YA . Biologically active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Cancer 2004; 4: 604–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Th., Liu, Jf., Zhang, Y. et al. Ceramide induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells through mitogen-activated protein kinases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 28, 439–445 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00505.x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2007.00505.x
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of mitochondrial Bax, caspases, and MAPKs for ceramide-induced apoptosis in renal proximal tubular cells
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2013)
-
Genipin inhibits endothelial exocytosis via nitric oxide in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2009)