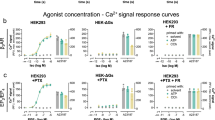
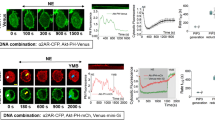
Abstract
Phospholipase C (PLC)1 hydrolyzes phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate to generate the second messengers, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP3 induces a transient increase in intracellular free Ca2+, while DAG directly activates protein kinase C. Upon stimulation of cells with growth factors, PLC-γ1 is activated upon their association with and phosphorylation by receptor and non-receptor tyrosine kinases. In this review, we will focus on the activation mechanism and regulatory function of PLC-γ1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M., Kim, E., Ryu, S. et al. The mechanism of phospholipase C-γ1 regulation. Exp Mol Med 32, 101–109 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2000.18
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2000.18
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Excitatory and inhibitory synaptic dysfunction in mania: an emerging hypothesis from animal model studies
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2018)
-
HMGB1 release by H2O2-induced hepatocytes is regulated through calcium overload and 58-F interference
Cell Death Discovery (2017)
-
ADAM17/EGFR axis promotes transglutaminase-dependent skin barrier formation through phospholipase C γ1 and protein kinase C pathways
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
PIKE mediates EGFR proliferative signaling in squamous cell carcinoma cells
Oncogene (2012)
-
The death receptor CD95 activates the cofilin pathway to stimulate tumour cell invasion
EMBO reports (2011)