Abstract
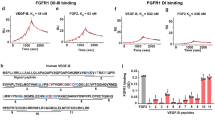
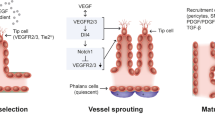
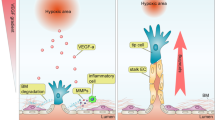
Until recently, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was the only growth factor proven to be specific and critical for blood vessel formation. Other long-known factors, such as the fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), platelet-derived growth factor, or transforming growth factor-β, had profound effects in endothelial cells. But such factors were nonspecific, in that they could act on many other cells, and it seemed unlikely that these growth factors would be effective targets for treatment of endothelial cell diseases. A recently discovered endothelial cell specific growth factor, angiopoietin, has greatly contributed to our understanding of the development, physiology, and pathology of endothelial cells (Davis et al., 1996; Yancopoulos et al., 2000). The recent studies that identified and characterized the physiological and pathological roles of angiopoietin have allowed us to widen and deepen our knowledge about blood vessel formation and vascular endothelial function. Therefore, in this review, we describe the biomedical significance of these endothelial cell growth factors, the angiopoietins, in the vascular system under normal and pathological states.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Koh, G., Kim, I., Kwak, H. et al. Biomedical significance of endothelial cell specific growth factor, angiopoietin. Exp Mol Med 34, 1–11 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2002.1
This article is cited by
-
Genetic variants in the angiopoietin-2 gene are associated with increased risk of ARDS
Intensive Care Medicine (2009)
-
Peritoneal morphologic changes in a peritoneal dialysis rat model correlate with angiopoietin/Tie-2
Pediatric Nephrology (2009)
-
Effects of estradiol-17β on expression of mRNA for seven angiogenic factors and their receptors in the endometrium of ovariectomized (OVX) ewes
Endocrine (2006)
-
Increased angiopoietin2 expression is associated with endothelial apoptosis and blood–brain barrier breakdown
Laboratory Investigation (2005)
-
Influence of Inflammatory Cytokines on Arteriogenesis
Microcirculation (2003)