Abstract
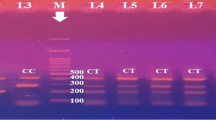
The risk of cerebral infarction (CI) in an individual is dependent on the interplay between genetic risk factors and environmental influences. Binding of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) to its receptor (TP) modulates thrombosis/hemostasis and plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of CI. The aim of the present study was to investigate the relationship between human TP gene single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and haplotypes and CI in a Japanese population. A genetic association study was performed in 194 CI patients and 365 non-CI subjects by specifically characterizing 6 SNPs in the human TP gene (rs2271875, rs768963, rs2238634, rs11085026, rs4523 and rs4806942). Analysis demonstrated that there were significant differences in the overall distribution of genotypes and dominant or recessive models of rs2271875 and rs768963 between the CI and the non-CI groups. Multiple logistic regression analysis revealed that the C allele of rs768963 was significantly associated with CI (p=0.029), even after adjusting for confounding factors (odds ratio: 2.41). Further, the C-T-C haplotype of rs768963-rs2238634-rs4806942 was significantly more frequent in the CI group (23.0%) than in the non-CI group (17.7%). These results suggest that specific SNPs and haplotypes may have utility as genetic markers for the risk of CI and that TP or a neighboring gene is associated with the increased susceptibility to CI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Hassan A, Markus HS : Genetics and ischaemic stroke. Brain 2000; 123: 1784–1812.
Gorelick PB, Sacco RL, Smith DB, et al: Prevention of a first stroke: a review of guidelines and a multidisciplinary consensus statement from the National Stroke Association. JAMA 1999; 281: 1112–1120.
Yamagishi K, Iso H, Kitamura A, et al: Smoking raises the risk of total and ischemic strokes in hypertensive men. Hypertens Res 2003; 26: 209–217.
Coyle AT, Miggin SM, Kinsella BT : Characterization of the 5′ untranslated region of alpha and beta isoforms of the human thromboxane A2 receptor (TP). Differential promoter utilization by the TP isoforms. Eur J Biochem 2002; 269: 4058–4073.
Nusing RM, Hirata M, Kakizuka A, Eki T, Ozawa K, Narumiya S : Characterization and chromosomal mapping of the human thromboxane A2 receptor gene. J Biol Chem 1993; 268: 25253–25259.
Turek JW, Halmos T, Sullivan NL, Antonakis K, Le Breton GC : Mapping of a ligand-binding site for the human thromboxane A2 receptor protein. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 16791–16797.
Huang JS, Ramamurthy SK, Lin X, Le Breton GC : Cell signalling through thromboxane A2 receptors. Cell Signal 2004; 16: 521–533.
Aoi N, Soma M, Nakayama T, et al: Variable number of tandem repeat of the 5′-flanking region of Type-C human natriuretic peptide receptor gene influences blood pressure levels in obesity-associated hypertension. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 711–716.
Baird PN, Richardson AJ, Craig JE, Mackey DA, Rochtchina E, Mitchell P : Analysis of optineurin (OPTN) gene mutations in subjects with and without glaucoma: the Blue Mountains Eye Study. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2004; 32: 518–522.
Nakayama T, Soma M, Kanmatsuse K, Kokubun S : The microsatellite alleles on chromosome 1 associated with essential hypertension and blood pressure levels. J Hum Hypertens 2004; 18: 823–828.
Nakayama T, Soma M, Sato N, et al: An association study in essential hypertension using functional polymorphisms in lymphotoxin-α gene. Am J Hypertens 2004; 17: 1045–1049.
Maruyama A, Nakayama T, Sato N, Mizutani Y, Furuya K, Yamamoto T : Association study using single nucleotide polymorphisms in the estrogen receptor β (ESR2) gene for preeclampsia. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 903–909.
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB : Maximum likelihood from in complete data via the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc 1977; 39: 1–22.
Kobayashi Y, Nakayama T, Sato N, et al: Haplotype-based case-control study of adrenomedullin genes on proteinuria in the subjects with essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 229–236.
Nakayama T, Soma M, Rahmutula D, Izumi Y, Kanmatsuse K : Nonsense mutation of prostacyclin synthase gene in a family. Lancet 1997; 349: 1887–1888.
Nakayama T, Soma M, Rehemudula D, et al: Association of 5′ upstream promoter region of prostacyclin synthase gene variant with cerebral infarction. Am J Hypertens 2000; 13: 1263–1267.
Unoki M, Furuta S, Onouchi Y, et al: Association studies of 33 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 29 candidate genes for bronchial asthma: positive association a T924C polymorphism in the thromboxane A2 receptor gene. Hum Genet 2000; 106: 440–446.
Boehringer S, Epplen JT, Krawczak M : Genetic association studies of bronchial asthma—a need for Bonferroni correction? Hum Genet 2000; 107: 197.
Nyholt DR : Genetic case-control association studies—correcting for multiple testing. Hum Genet 2001; 109: 564–567.
Hirata T, Kakizuka A, Ushikubi F, Fuse I, Okuma M, Narumiya S : Arg60 to Leu mutation of the human thromboxane A2 receptor in a dominantly inherited bleeding disorder. J Clin Invest 1994; 94: 1662–1667.
Francois H, Athirakul K, Mao L, Rockman H, Coffman TM : Role for thromboxane receptors in angiotensin-II–induced hypertension. Hypertension 2004; 43: 364–369.
Thomas DW, Mannon RB, Mannon PJ, et al: Coagulation defects and altered hemodynamic responses in mice lacking receptors for thromboxane A2. J Clin Invest 1998; 102: 1994–2001.
Satoh K, Imaizumi T, Yoshida H, Hiramoto M, Konta A, Takamatsu S : Plasma 11-dehydrothromboxane B2: a reliable indicator of platelet hyperfunction in patients with ischemic stroke. Acta Neurol Scand 1991; 83: 99–102.
Koudstaal PJ, Ciabattoni G, van Gijn J, et al: Increased thromboxane biosynthesis in patients with acute cerebral ischemia. Stroke 1993; 24: 219–223.
Imamura T, Kiguchi S, Kobayashi K, Ichikawa K, Yamazaki Y, Kojima M : Effect of ozagrel, a selective thromboxane A2−synthetase inhibitor, on cerebral infarction in rats. Comparative study with norphenazone, a free-radical scavenger. Arzneimittelforschung 2003; 53: 688–694.
Cambria-Kiely JA, Gandhi PJ : Aspirin resistance and genetic polymorphisms. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2002; 14: 51–58.
Schork NJ, Fallin D, Lanchbury JS : Single nucleotide polymorphisms and the future of genetic epidemiology. Clin Genet 2000; 58: 250–264.
Morris RW, Kaplan NL : On the advantage of haplotype analysis in the presence of multiple disease susceptibility alleles. Genet Epidemiol 2002; 23: 221–233.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaneko, Y., Nakayama, T., Saito, K. et al. Relationship between the Thromboxane A2 Receptor Gene and Susceptibility to Cerebral Infarction. Hypertens Res 29, 665–671 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.665
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.665
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors and Ischemic Stroke: a Focus on Molecular Function and Therapeutic Potential
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Association of thromboxane A2 receptor gene polymorphisms with cerebral infarction in a Chinese population
Neurological Sciences (2013)
-
Purinergic receptor P2Y, G-protein coupled, 2 (P2RY2) gene is associated with cerebral infarction in Japanese subjects
Hypertension Research (2009)