Abstract
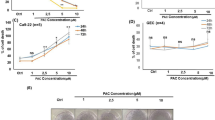
Honokiol (HNK) is a small organic molecule purified from magnolia species and has demonstrated anticancer activities in a variety of cancer cell lines; however, its effect on oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells is unknown. We investigated the antitumor activities of HNK on OSCC cells in vitro for the first time. The inhibitory effects of HNK on the growth and proliferation of OSCC cells were demonstrated via in vitro 3‐(4,5‐dimethyl thiazol‐2‐yl)‐2,5‐diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and propidium iodide (PI) assays, and the apoptotic cells were investigated by the observation of morphological changes and detection of DNA fragmentation via PI, TdT‐mediated dUTP‐biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL), and DNA ladder assays, as well as flow cytometry assay. The results showed that HNK inhibited the growth and proliferation of OSCC cells in vitro in a time and dose‐dependent manner. The inhibitory effect was associated with the cell apoptosis induced by HNK, evidenced by the morphological features of apoptotic cells, TUNEL‐positive cells and a degradation of chromosomal DNA into small internucleosomal fragments. The study also demonstrated here that the inhibition or apoptosis mediated by 15 μg·mL−1 or 20 μg·mL−1 of HNK were more stronger compared with those of 20 μg·mL−1 5‐fluorouracil (5‐Fu, the control) applied to OSCC cells, when the ratio of OSCC cell numbers were measured between the treatment of different concentrations of HNK to the 5‐Fu treatment for 48 h. HNK is a promising compound that can be potentially used as a novel treatment agent for human OSCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Lu, R., Dan, H. et al. Honokiol: a promising small molecular weight natural agent for the growth inhibition of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int J Oral Sci 3, 34–42 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4248/IJOS11014
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4248/IJOS11014
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular pathways modulated by phytochemicals in head and neck cancer
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Biotin-modified oligochitosan-F127 micelles for honokiol’s encapsulation
Journal of Nanoparticle Research (2021)
-
Phyto-polyphenols as potential inhibitors of breast cancer metastasis
Molecular Medicine (2018)
-
Honokiol inhibits sphere formation and xenograft growth of oral cancer side population cells accompanied with JAK/STAT signaling pathway suppression and apoptosis induction
BMC Cancer (2016)
-
Honokiol blocks and reverses cardiac hypertrophy in mice by activating mitochondrial Sirt3
Nature Communications (2015)