Abstract
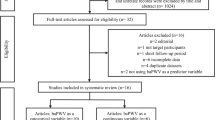
Pulse wave velocity (PWV) is as a reliable marker of arterial stiffness and vascular aging, surpassing traditional risk factors in predicting detrimental cardiovascular events. The present meta-analysis aims to investigate PWV thresholds and assess its prognostic value in outcomes of acute ischemic stroke (AIS). A search was conducted in PubMed, Cochrane, Web of Science, and Scopus for studies published up to January 2024, focusing on patients admitted with AIS, wherein arterial stiffness was assessed through PWV measurements during hospitalization. Identified studies reported PWV values in individuals with both favorable and unfavorable outcomes at the end of follow-up. Initially, 35 eligible studies provided data for weighted mean baPWV (11,953 AIS patients) and cfPWV (2,197 AIS patients) calculations. The average age was 67 years, with approximately 60% male, 67% hypertensive, 30% diabetic and 30% smoker participants. The weighted mean systolic blood pressure was approximately 150 mmHg. In AIS patients, the mean PWV was 10 m/s for standard cfPWV and 20 m/s for baPWV. Nine cohort studies (6,006 AIS patients) were included in the quantitative analysis of clinical outcomes. Higher PWV levels were associated with poorer functional outcomes (2.3 m/s higher, 95%CI:1.2–3.4, p < 0.001; I2 = 87.4%). AIS patients with arterial stiffness/vascular aging (higher PWV) had approximately 46.2% increased risk of poor functional outcome, 12.7% higher risk of mortality, 13.9% greater risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, and 13.9% greater risk of stroke recurrence over the long term compared to those without arterial stiffness. Advanced vascular aging, as indicated by PWV, significantly predicts adverse outcomes in AIS patients. Integrating the assessment of vascular aging into clinical practice can improve risk perception in these patients.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
118,99 € per year
only 9,92 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nilsson PM, Boutouyrie P, Laurent S. Vascular aging: a tale of EVA and ADAM in cardiovascular risk assessment and prevention. Hypertension. 2009;54:3–10.
Boutouyrie P, Bruno RM. The clinical significance and application of vascular stiffness measurements. Am J Hypertens. 2019;32:4–11.
Ben-Shlomo Y, Spears M, Boustred C, May M, Anderson SG, Benjamin EJ, et al. Aortic pulse wave velocity improves cardiovascular event prediction: an individual participant meta-analysis of prospective observational data from 17,635 subjects. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:636–46.
Climie RE, Alastruey J, Mayer CC, Schwarz A, Laucyte-Cibulskiene A, Voicehovska J, et al. Vascular ageing: moving from bench towards bedside. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2023;30:1101–17.
Savopoulos C, Daios S, Kaiafa G. Vascular aging and stroke. Curr Med Chem. 2022;29:5476–7.
Kakaletsis N, Kotsis V, Protogerou AD, Vemmos K, Korompoki E, Kollias A, et al. Early vascular aging in acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2024;33:107800.
Laurent S, Boutouyrie P. Arterial stiffness and hypertension in the elderly. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:544302.
Van Bortel LM, Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Chowienczyk P, Cruickshank JK, De Backer T, et al. Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J Hypertens. 2012;30:445–8.
Lu Y, Pechlaner R, Cai J, Yuan H, Huang Z, Yang G, et al. Trajectories of age-related arterial stiffness in Chinese men and women. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:870–80.
Mancia Chairperson G, Kreutz Co-Chair R, Brunström M, Burnier M, Grassi G, Januszewicz A, et al. 2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension Endorsed by the European Renal Association (ERA) and the International Society of Hypertension (ISH). J Hypertens. 2023;41:1874–2071.
Ohkuma T, Ninomiya T, Tomiyama H, Kario K, Hoshide S, Kita Y, et al. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity and the risk prediction of cardiovascular disease: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Hypertension. 2017;69:1045–52.
Cardoso CRL, Salles GF. Prognostic value of changes in aortic stiffness for cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in resistant hypertension: a cohort study. Hypertension. 2022;79:447–56.
Dorans KS, He H, Chen J, Dobre M, Go AS, Hamm LL, et al. Change in ankle-brachial index and mortality among individuals with chronic kidney disease: findings from the chronic renal insufficiency cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021;36:2224–31.
Ntaios G, Michel P. Temporal distribution and magnitude of the vulnerability period around stroke depend on stroke subtype. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011;32:246–53.
Strambo D, Zachariadis A, Lambrou D, Schwarz G, Sirimarco G, Aarnio K, et al. A score to predict one-year risk of recurrence after acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke. 2021;16:602–12.
Ntaios G, Papavasileiou V, Makaritsis K, Milionis H, Michel P, Vemmos K. Association of ischaemic stroke subtype with long-term cardiovascular events. Eur J Neurol. 2014;21:1108–14.
Wang Y. Residual recurrence risk of ischaemic cerebrovascular events: concept, classification and implications. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2021;6:155–7.
Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.4 (updated August 2023). www.training.cochrane.org/handbook: Cochrane; 2023.
Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n160.
Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, Tong T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:135.
Van Bortel LM, De Backer T, Segers P. Standardization of arterial stiffness measurements make them ready for use in clinical practice. Am J Hypertens. 2016;29:1234–6.
Chirinos JA, Segers P, Hughes T, Townsend R. Large-artery stiffness in health and disease: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:1237–63.
Wells G, B Shea B, O’Connell D, Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses [Available from: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
Modesti PA, Reboldi G, Cappuccio FP, Agyemang C, Remuzzi G, Rapi S, et al. Panethnic differences in blood pressure in europe: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0147601.
Saji N, Murotani K, Shimizu H, Uehara T, Kita Y, Toba K, et al. Increased pulse wave velocity in patients with acute lacunar infarction doubled the risk of future ischemic stroke. Hypertens Res. 2017;40:371–5.
Tziomalos K, Bouziana SD, Spanou M, Giampatzis V, Papadopoulou M, Kazantzidou P, et al. Increased augmentation index is paradoxically associated with lower in-hospital mortality in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis. 2014;236:150–3.
Rojek A, Gąsecki D, Fijałkowski M, Kowalczyk K, Kwarciany M, Wolf J, et al. Left ventricular ejection fraction and aortic stiffness are independent predictors of neurological outcome in acute ischemic stroke. J Hypertens. 2016;34:2441–8.
Samara S, Vemmou A, Kyrkou A, Papamichael C, Korompoki E, Ntaios G, et al. Prediction of long-term outcomes by arterial stiffness and pressure wave reflections in patients with acute stroke: the Athens Stroke Registry. J Hypertens. 2022;40:2192–9.
Lee YB, Park JH, Kim E, Kang CK, Park HM. Arterial stiffness and functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2014;16:11–9.
Kim J, Song TJ, Kim EH, Lee KJ, Lee HS, Nam CM, et al. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity for predicting functional outcome in acute stroke. Stroke. 2014;45:2305–10.
Ishizuka KH, T Shimizu S. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity is associated with 3-month functional prognosis after ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis. 2016;255:1–5.
Han M, Kim YD, Lee I, Lee H, Heo J, Lee HS, et al. Low toe-brachial index is associated with stroke outcome despite normal ankle-brachial index. Front Neurol. 2021;12:754258.
Ahn KT, Jeong JO, Jin SA, Kim M, Oh JK, Choi UL, et al. Brachial-ankle PWV for predicting clinical outcomes in patients with acute stroke. Blood Press. 2017;26:204–10.
Seo WK, Lee JM, Park MH, Park KW, Lee DH. Cerebral microbleeds are independently associated with arterial stiffness in stroke patients. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008;26:618–23.
Song TJ, Kim J, Kim YD, Nam HS, Lee HS, Nam CM, et al. The distribution of cerebral microbleeds determines their association with arterial stiffness in non-cardioembolic acute stroke patients. Eur J Neurol. 2014;21:463–9.
De Silva DA, Woon FP, Manzano JJ, Liu EY, Chang HM, Chen C, et al. The relationship between aortic stiffness and changes in retinal microvessels among Asian ischemic stroke patients. J Hum Hypertens. 2012;26:716–22.
Kwarciany M, Gąsecki D, Kowalczyk K, Rojek A, Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, et al. Acute hypertensive response in ischemic stroke is associated with increased aortic stiffness. Atherosclerosis. 2016;251:1–5.
Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, Di Sciacca R, Pecoraro R, Arnao V, Buttà C, et al. Arterial stiffness and ischemic stroke in subjects with and without metabolic syndrome. Atherosclerosis. 2012;225:216–9.
Huang J, Tang J, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Tan Z, Shi S. Association between ankle brachial index, brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity, and mild cognitive impairment in patients with acute lacunar infarction. Eur Neurol. 2020;83:147–53.
De Silva DA, Woon FP, Gan HY, Chen CP, Chang HM, Koh TH, et al. Arterial stiffness is associated with intracranial large artery disease among ethnic Chinese and South Asian ischemic stroke patients. J Hypertens. 2009;27:1453–8.
Li X, Du H, Gao Q, Chen J, Chen X. Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity is associated with intracranial artery calcification in acute stroke patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2023;233:107918.
Chang YM, Lee TL, Su HC, Chien CY, Lin TY, Lin SH, et al. The association between ankle-brachial index/pulse wave velocity and cerebral large and small vessel diseases in stroke patients. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023;13:1455.
De Silva DA, Woon FP, Gan HY, Cameron J, Kingwell B, Koh TH, et al. Arterial stiffness, metabolic syndrome and inflammation amongst Asian ischaemic stroke patients. Eur J Neurol. 2008;15:872–5.
Karaszewski B, Kwarciany M, Gąsecki D. Reply to: “Arterial stiffness, central blood pressures, wave reflections, and acute hypertensive response in stroke”. Atherosclerosis. 2016;252:197–8.
Spronck B, Terentes-Printzios D, Avolio AP, Boutouyrie P, Guala A, Jerončić A, et al. 2024 recommendations for validation of noninvasive arterial pulse wave velocity measurement devices. Hypertension. 2024;81:183–92.
Soureti A, Hurling R, Murray P, van Mechelen W, Cobain M. Evaluation of a cardiovascular disease risk assessment tool for the promotion of healthier lifestyles. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010;17:519–23.
Lin B, Zhang Z, Mei Y, Wang C, Xu H, Liu L, et al. Cumulative risk of stroke recurrence over the last 10 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci. 2021;42:61–71.
Chen Y, Wright N, Guo Y, Turnbull I, Kartsonaki C, Yang L, et al. Mortality and recurrent vascular events after first incident stroke: a 9-year community-based study of 0·5 million Chinese adults. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8:e580–90.
Xu J, Zhang X, Jin A, Pan Y, Li Z, Meng X, et al. Trends and risk factors associated with stroke recurrence in China, 2007–2018. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:e2216341.
Boulanger M, Béjot Y, Rothwell PM, Touzé E. Long-term risk of myocardial infarction compared to recurrent stroke after transient ischemic attack and ischemic stroke: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7:e007267.
Striepe K, Jumar A, Ott C, Karg MV, Schneider MP, Kannenkeril D, et al. Effects of the selective sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor empagliflozin on vascular function and central hemodynamics in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2017;136:1167–9.
Batzias K, Antonopoulos AS, Oikonomou E, Siasos G, Bletsa E, Stampouloglou PK, et al. Effects of newer antidiabetic drugs on endothelial function and arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Diabetes Res. 2018;2018:1232583.
Adamou A, Barkas F, Milionis HJ, Ntaios G. Glucagon-like receptor-1 agonists and stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Int J Stroke. 2024;19:876–87.
Milionis H, Ntaios G, Korompoki E, Vemmos K, Michel P. Statin-based therapy for primary and secondary prevention of ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis and critical overview. Int J Stroke. 2020;15:377–84.
Sagris D, Ntaios G, Georgiopoulos G, Pateras K, Milionis H. Proprotein convertase subtilisin-kexin type 9 inhibitors and stroke prevention: a meta-analysis. Eur J Intern Med. 2021;85:130–2.
Sagris D, Ntaios G, Milionis H. Beyond antithrombotics: recent advances in pharmacological risk factor management for secondary stroke prevention. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2024;95:264–72.
Ntaios G, Baumgartner H, Doehner W, Donal E, Edvardsen T, Healey JS, et al. Embolic strokes of undetermined source: a clinical consensus statement of the ESC Council on Stroke, the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging and the European Heart Rhythm Association of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2024;45:1701–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors significantly contributed to the manuscript and approved the final version for publication. NK, AP, VK, and CS designed the study. NK, AP, VK contributed to data acquisition and performed the statistical analysis. NK, AP, KV, EK, AK, HM, and GN contributed to the interpretation of data. NK wrote the first manuscript draft. All authors edited the final manuscript draft. NK is the guarantor of this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kakaletsis, N., Protogerou, A.D., Kotsis, V. et al. Advanced vascular aging and outcomes after acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hum Hypertens 38, 676–686 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-024-00961-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41371-024-00961-y
This article is cited by
-
Early vascular aging ambulatory score in acute ischemic stroke
npj Aging (2025)