Abstract
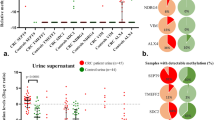
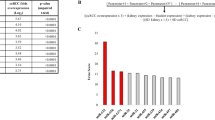
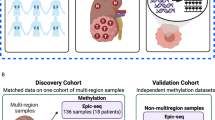
Renal cancer (RC) is the most lethal urological malignancy with 30% late diagnosis. Over 50% RCs are asymptomatic and discovered incidentally. Current RC detection relies on imaging while it lacks satisfactory sensitivity for detecting small-size tumors. A sensitive and robust diagnostic tool is needed to facilitate standardized RC early detection. Herein, we performed genome-wide methylation sequencing on both tissues and urine samples for RC DNA methylation makers discovery and developed a PCR-based RC early detector (RED) using a cohort of 93 RC and 35 non-RC urine samples. RED further achieved sensitivities of 82.2% and 80.7%, and specificities of 77.1% and 75% in a testing cohort (90 RC vs. 35 non-RC) and a validation cohort (119 RC vs. 48 non-RC), respectively. Importantly, RED exhibited 89.5% sensitivity for tumors in diameter <2 cm. It can detect 83.6% clear cell renal cell carcinoma, 75.0% of translocational renal cell carcinoma, 100% of primitive neuroectodermal tumors, renal malignant masenchymomas and mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma. RED showed promising performance for RC detection with early stage and small size and have potential to be used in conjunction with imaging.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 5,38 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48.
Usher-Smith J, Simmons RK, Rossi SH, Stewart GD. Current evidence on screening for renal cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2020;17:637–42.
Rabjerg M, Mikkelsen MN, Walter S, Marcussen N. Incidental renal neoplasms: is there a need for routine screening? A Danish single-center epidemiological study. APMIS. 2014;122:708–14.
Selby PJ, Banks RE, Gregory W, Hewison J, Rosenberg W, Altman DG, et al. Methods for the evaluation of biomarkers in patients with kidney and liver diseases: multicentre research programme including ELUCIDATE RCT. Southampton (UK). 2018; https://doi.org/10.3310/pgfar06030.
Bhatt JR, Finelli A. Landmarks in the diagnosis and treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Urol. 2014;11:517–25.
Kubiliute R, Zukauskaite K, Zalimas A, Ulys A, Sabaliauskaite R, Bakavicius A, et al. Clinical significance of novel DNA methylation biomarkers for renal clear cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022;148:361–75.
Mizuma Y, Watanabe Y, Ozasa K, Hayashi K, Kawai K. Validity of sonographic screening for the detection of abdominal cancers. J Clin Ultrasound. 2002;30:408–15.
Filipas D, Spix C, Schulz-Lampel D, Michaelis J, Hohenfellner R, Roth S, et al. Screening for renal cell carcinoma using ultrasonography: a feasibility study. BJU Int. 2003;91:595–9.
Rossi SH, Prezzi D, Kelly-Morland C, Goh V. Imaging for the diagnosis and response assessment of renal tumours. World J Urol. 2018;36:1927–42.
Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bedke J, Capitanio U, Dabestani S, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2022 Update. Eur Urol. 2022;82:399–410.
Laird PW. The power and the promise of DNA methylation markers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:253–66.
Das PM, Singal R. DNA methylation and cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:4632–42.
Koch A, Joosten SC, Feng Z, de Ruijter TC, Draht MX, Melotte V, et al. Analysis of DNA methylation in cancer: ___location revisited. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15:459–66.
de Martino M, Klatte T, Haitel A, Marberger M. Serum cell-free DNA in renal cell carcinoma: a diagnostic and prognostic marker. Cancer. 2012;118:82–90.
Hoque MO, Begum S, Topaloglu O, Jeronimo C, Mambo E, Westra WH, et al. Quantitative detection of promoter hypermethylation of multiple genes in the tumor, urine, and serum DNA of patients with renal cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5511–7.
Nuzzo PV, Berchuck JE, Korthauer K, Spisak S, Nassar AH, Abou Alaiwi S, et al. Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes. Nat Med. 2020;26:1041–3.
Rydzanicz M, Wrzesinski T, Bluyssen HA, Wesoly J. Genomics and epigenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: recent developments and potential applications. Cancer Lett. 2013;341:111–26.
Jobling P, Pundavela J, Oliveira SM, Roselli S, Walker MM, Hondermarck H. Nerve-Cancer Cell Cross-talk: A Novel Promoter of Tumor Progression. Cancer Res. 2015;75:1777–81.
Pan C, Winkler F. Insights and opportunities at the crossroads of cancer and neuroscience. Nat Cell Biol. 2022;24:1454–60.
Mancusi R, Monje M. The neuroscience of cancer. Nature. 2023;618:467–79.
Chen S, Yu Y, Li T, Ruan W, Wang J, Peng Q, et al. A novel DNA methylation signature associated with lymph node metastasis status in early gastric cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 2022;14:18.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82273412); Special Funding of Department of Finance of Guangdong Province (Grant No. KS0120220267, KS0120220268, KS0120220269, KS0120220270, KS0120220271, KS0120220272); Guangzhou Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 202201011030); Scheme of Guangzhou Economic and Technological Development District for Leading Talents in Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Grant No. 2017-L152); Scheme of Guangzhou for Leading Talents in Innovation and Entrepreneurship (Grant No. 2016007); Scheme of Guangzhou for Leading Team in Innovation (Grant No.201909010010); Guangzhou Development Zone International Science and Technology Cooperation Project (Grant No. 2020GH15, 2021GH17); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou (Grant No. 202206080013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X Zhang, Q Huang, J Liu, D Ding and J Fan conceived, designed and directed the study. W Ruan, H Wang, Z Liang developed the methodology. T Shi, H Chen, Z Wang, C Peng, S Huang collected patient samples and acquired the patient information. H Wang, J Zhong perform data analysis and interpretation of data. W Ruan, Z Liang, X Liang, and J Chen performed sample testing and provided technical or material support. T Shi and W Ruan wrote the manuscript. X Pu, L Wang, W Wei and T Li coordinated in patient recruitments. Y Wen and Z Chen reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. The co-first authors T Shi, H Chen, Z Wang, H Wang, C Peng, S Huang and Y Wen contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
HW, YW, ZL, JZ, XL, JC, ZC, WR and J-BF are/were employees of AnchorDx Medical Co, Ltd. or AnchorDx, Inc. All other authors declare no competing financial interest.
Ethics approval
The study was performed in compliance with ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was conducted under the approval of the Ethics Committees of the Chinese PLA General Hospital, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital and Henan Provincial People’s Hospital. The written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, T., Chen, H., Wang, Z. et al. A urine DNA methylation assay for early detection of renal cancer. Oncogene 44, 1709–1717 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-03268-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-03268-x