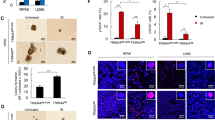
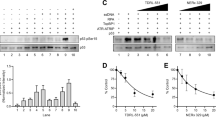
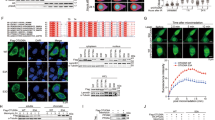
Abstract
RPA2, a key component of the RPA complex, is essential for single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) binding and DNA repair. However, the regulation of RPA2-ssDNA interaction and the recruitment of repair proteins following DNA damage remain incompletely understood. Our study uncovers a novel mechanism by which phosphorylated TRIM21 (Phospho-TRIM21) regulates RPA2 ubiquitination, thereby modulating homologous recombination and tumor radio/chemo-resistance. In the absence of DNA damage, TRIM21 mediates K63-linked ubiquitination of RPA2, countering K6-linked ubiquitination. Upon DNA damage, ubiquitination-modified RPA2 binds ssDNA, stabilizing the DNA structure and facilitating ATRIP/ATR recruitment. ATR subsequently phosphorylates TRIM21 at Ser41, leading to the dissociation of the TRIM21-RPA2 complex and a shift in RPA2 ubiquitination from K63 to K6 linkage. This shift maintains RPA2 ubiquitination homeostasis and stabilizes the RPA2-ATRIP complex, which is crucial for efficient homologous recombination (HR) repair and enhanced tumor radio/chemo-resistance. We also demonstrate that TRIM21 is frequently upregulated in cancers, and its depletion sensitizes cancer cells to radio/chemotherapy, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target. This study provides novel insights into TRIM21’s role in the DNA damage response and its implications for cancer treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 5,38 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Other data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abad E, Graifer D, Lyakhovich A. DNA damage response and resistance of cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2020;474:106–17.
Wei W, Ba Z, Gao M, Wu Y, Ma Y, Amiard S, et al. A role for small RNAs in DNA double-strand break repair. Cell. 2012;149:101–12.
Jackson SP, Bartek J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature. 2009;461:1071–8.
Sutcu HH, Montagne B, Ricchetti M. DNA-PKcs regulates myogenesis in an Akt-dependent manner independent of induced DNA damage. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30:1900–15.
Lou J, Chen H, Han J, He H, Huen MSY, Feng XH, et al. AUNIP/C1orf135 directs DNA double-strand breaks towards the homologous recombination repair pathway. Nat Commun. 2017;8:985.
Zhou X, Sekino Y, Li HT, Fu G, Yang Z, Zhao S, et al. SETD2 deficiency confers sensitivity to dual inhibition of DNA methylation and PARP in kidney cancer. Cancer Res. 2023;83:3813–26.
Tilgner K, Neganova I, Moreno-Gimeno I, AL-Aama JY, Burks D, Yung S, et al. A human iPSC model of Ligase IV deficiency reveals an important role for NHEJ-mediated-DSB repair in the survival and genomic stability of induced pluripotent stem cells and emerging haematopoietic progenitors. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20:1089–100.
Yuan J, Chen J. FIGNL1-containing protein complex is required for efficient homologous recombination repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2013;110:10640–5.
Shahar OD, Ram EVSR, Shimshoni E, Hareli S, Meshorer E, Goldberg M. Live imaging of induced and controlled DNA double-strand break formation reveals extremely low repair by homologous recombination in human cells. Oncogene. 2012;31:3495–504.
Cao K, Wang R, Li L, Liao Y, Hu X, Li R, et al. Targeting DDX11 promotes PARP inhibitor sensitivity in hepatocellular carcinoma by attenuating BRCA2-RAD51 mediated homologous recombination. Oncogene. 2024;43:35–46.
Anantha RW, Sokolova E, Borowiec JA. RPA phosphorylation facilitates mitotic exit in response to mitotic DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008;105:12903–8.
Zhang B, Tang Z, Li L, Lu LY. NBS1 is required for SPO11-linked DNA double-strand break repair in male meiosis. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27:2176–90.
Her J, Bunting SF. How cells ensure correct repair of DNA double-strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 2018;293:10502–11.
Li J, Zhao J, Gan X, Wang Y, Jiang D, Chen L, et al. The RPA-RNF20-SNF2H cascade promotes proper chromosome segregation and homologous recombination repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2023;120:e2303479120.
Weisshart K, Pestryakov P, Smith RWP, Hartmann H, Kremmer E, Lavrik O, et al. Coordinated regulation of replication protein A activities by its subunits p14 and p32. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:35368–76.
Zhu X, Xue J, Jiang X, Gong Y, Gao C, Cao T, et al. TRIM21 suppresses CHK1 activation by preferentially targeting CLASPIN for K63-linked ubiquitination. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:1517–30.
Huang N, Li P, Sun X, Tong L, Dong X, Zhang X, et al. TRIM21 mediates the synergistic effect of Olaparib and Sorafenib by degrading BRCA1 through ubiquitination in TNBC. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2023;9:85.
Foss S, Watkinson R, Sandlie I, James LC, Andersen JT. TRIM21: a cytosolic Fc receptor with broad antibody isotype specificity. Immunol Rev. 2015;268:328–39.
Li JY, Zhao Y, Gong S, Wang MM, Liu X, He QM, et al. TRIM21 inhibits irradiation-induced mitochondrial DNA release and impairs antitumour immunity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumour models. Nat Commun. 2023;14:865.
Brauner S, Ivanchenko M, Thorlacius GE, Ambrosi A, Wahren-Herlenius M. The Sjögren’s syndrome-associated autoantigen Ro52/TRIM21 modulates follicular B cell homeostasis and immunoglobulin production. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194:315–26.
Alomari M. TRIM21 - A potential novel therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2021;165:105443.
Guha A, Ahuja D, Das Mandal S, Parasar B, Deyasi K, Roy D, et al. Integrated regulation of HuR by translation repression and protein degradation determines pulsatile expression of p53 Under DNA damage. iScience. 2019;15:342–59.
Wang H, Zhou Y, Oyang L, Han Y, Xia L, Lin J, et al. LPLUNC1 stabilises PHB1 by counteracting TRIM21-mediated ubiquitination to inhibit NF-κB activity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene. 2019;38:5062–75.
James LC, Keeble AH, Khan Z, Rhodes DA, Trowsdale J. Structural basis for PRYSPRY-mediated tripartite motif (TRIM) protein function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:6200–5.
Dickson C, Fletcher AJ, Vaysburd M, Yang JC, Mallery DL, Zeng J, et al. Intracellular antibody signalling is regulated by phosphorylation of the Fc receptor TRIM21. Elife. 2018;7:e32660.
Sun Y, McCorvie TJ, Yates LA, Zhang X. Structural basis of homologous recombination. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77:3–18.
Feldkamp MD, Mason AC, Eichman BF, Chazin WJ. Structural analysis of replication protein A recruitment of the DNA damage response protein SMARCAL1. Biochemistry. 2014;53:3052–61.
Maréchal A, Zou L. RPA-coated single-stranded DNA as a platform for post-translational modifications in the DNA damage response. Cell Res. 2015;25:9–23.
Hsu CH, Yu YL. The interconnected roles of TRIM21/Ro52 in systemic lupus erythematosus, primary Sjögren’s syndrome, cancers, and cancer metabolism. Cancer Cell Int. 2023;23:289.
Wang F, Zhang Y, Shen J, Yang B, Dai W, Yan J, et al. The ubiquitin E3 Ligase TRIM21 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by suppressing the p62-Keap1-Nrf2 antioxidant pathway. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;11:1369–85.
Ball HL, Myers JS, Cortez D. ATRIP binding to replication protein A-single-stranded DNA promotes ATR-ATRIP localization but is dispensable for Chk1 phosphorylation. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:2372–81.
Zou L, Elledge SJ. Sensing DNA damage through ATRIP recognition of RPA-ssDNA complexes. Science. 2003;300:1542–8
Gan X, Zhang Y, Jiang D, Shi J, Zhao H, Xie C, et al. Proper RPA acetylation promotes accurate DNA replication and repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51:5565–83.
Lin YC, Wang Y, Hsu R, Giri S, Wopat S, Arif MK, et al. PCNA-mediated stabilization of E3 ligase RFWD3 at the replication fork is essential for DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2018;115:13282–7.
Inano S, Sato K, Katsuki Y, Kobayashi W, Tanaka H, Nakajima K, et al. RFWD3-Mediated Ubiquitination Promotes Timely Removal of Both RPA and RAD51 from DNA damage sites to facilitate homologous recombination. Mol Cell. 2017;66:622–634.e8.
Chen B, Xu F, Gao Y, Hu G, Zhu K, Lu H, et al. DNA damage-induced translocation of mitochondrial factor HIGD1A into the nucleus regulates homologous recombination and radio/chemo-sensitivity. Oncogene. 2022;41:1918–30.
Lee AYS. A review of the role and clinical utility of anti-Ro52/TRIM21 in systemic autoimmunity. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37:1323–33.
Holwek E, Opinc-Rosiak A, Sarnik J, Makowska J. Ro52/TRIM21 - From host defense to autoimmunity. Cell Immunol. 2023;393-394:104776.
Rajsbaum R, Stoye JP, O’Garra A. Type I interferon-dependent and -independent expression of tripartite motif proteins in immune cells. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38:619–30.
Hatakeyama S. TRIM family proteins: roles in autophagy, immunity, and carcinogenesis. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42:297–311.
Hatakeyama S. TRIM proteins and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:792–804.
Wold MS. Replication protein A: a heterotrimeric, single-stranded DNA-binding protein required for eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1997;66:61–92.
Chen R, Wold MS. Replication protein A: single-stranded DNA’s first responder: dynamic DNA-interactions allow replication protein A to direct single-strand DNA intermediates into different pathways for synthesis or repair. Bioessays. 2014;36:1156–61.
Choi JH, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Kemp M, Mason AC, Wold MS, Sancar A. Reconstitution of RPA-covered single-stranded DNA-activated ATR-Chk1 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010;107:13660–5.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars (12122510), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32171240), the HFIPS Director’s Fund (BJPY2021B07 and BJPY2023A010), National Postdoctoral Researcher Assistance Program (GZC20232718) and Youth Project of the President’s Fund of Hefei Institutes of Physical Science(E36CGG2F).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.Zhang: Conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, validation, investigation, visualization, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing. B.Chen, F.Xu, R.Wang, X.Zhao, Z.Yao, J.Zhang, S.Zhou: investigation. A.Xu, L.Wu: Project administration, supervision. G.Zhao: Conceptualization, resources, data curation, formal analysis, supervision, funding acquisition, investigation, project administration, writing-review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Chen, B., Xu, F. et al. Phospho-TRIM21 orchestrates RPA2 ubiquitination switch to promote homologous recombination and tumor radio/chemo-resistance. Oncogene 44, 1106–1117 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03288-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03288-1