Abstract
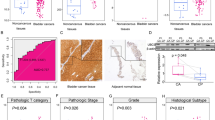
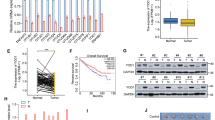
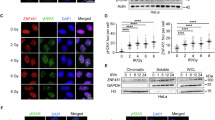
Zinc finger protein 24 (ZNF24) is a conserved multifunctional transcription factor associated with tumorigenesis, but its function in bladder carcinogenesis remains unclear. Herein, the expression of ZNF24 was decreased in bladder cancer (BC) cells and tissues, and patients with higher expression of ZNF24 had a better prognosis. Doxycycline-induced overexpression and knockdown of ZNF24 identified its anti-proliferative and anti-metastasis role in BC in vitro and in vivo. The potential genes for the anti-cancer role of ZNF24, involving transcriptional regulation of several factors, such as dual-specificity phosphatase 1 and squalene epoxidase. E2 conjugating enzyme UBC9 and small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) 1 were found to interact with ZNF24, suggesting that ZNF24 may be SUMOylated. Consistent with the expression, ZNF24 SUMOylation levels were decreased in BC cells and tissues. Pan-SUMOylation inhibition promoted protein degradation of ZNF24. UBC9 SUMOylated ZNF24 at Lys-27 (K27) site with SUMO1 modification and the K27 mutation of ZNF24 greatly damaged the protein stability of ZNF24. Cullin 3 (CUL3), a E3 ubiquitin ligase, was responsible for the degradation of ZNF24. ZNF24 SUMOylation prevented CUL3-mediated protein degradation of ZNF24. Overall, the crosstalk between the SUMOylation and ubiquitination of ZNF24 may be a novel regulatory mechanism to block tumorigenesis and development of BC.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 5,38 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Lenis AT, Lec PM, Chamie K, Mshs MD. Bladder cancer: a review. JAMA. 2020;324:1980–91.
Bladder cancer: diagnosis and management of bladder cancer: (c) NICE (2015) Bladder cancer: diagnosis and management of bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2017;120:755-65.
Smith AB, Jaeger B, Pinheiro LC, Edwards LJ, Tan HJ, Nielsen ME, et al. Impact of bladder cancer on health-related quality of life. BJU Int. 2018;121:549–57.
Sahin U, de H, Lallemand-Breitenbach V. Sumoylation in physiology, pathology and therapy. Cells. 2022;11:814.
Seeler JS, Dejean A. SUMO and the robustness of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:184–97.
Xia QD, Sun JX, Xun Y, Xiao J, Liu CQ, Xu JZ, et al. SUMOylation pattern predicts prognosis and indicates tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in bladder cancer. Front Immunol. 2022;13:864156.
Li Z, Liu J, Fu H, Li Y, Liu Q, Song W, et al. SENP3 affects the expression of PYCR1 to promote bladder cancer proliferation and EMT transformation by deSUMOylation of STAT3. Aging. 2022;14:8032–45.
Huang X, Tao Y, Gao J, Zhou X, Tang S, Deng C, et al. UBC9 coordinates inflammation affecting development of bladder cancer. Sci Rep. 2020;10:20670.
Chen C, Zheng H, Luo Y, Kong Y, An M, Li Y, et al. SUMOylation promotes extracellular vesicle-mediated transmission of lncRNA ELNAT1 and lymph node metastasis in bladder cancer. J Clin Investig. 2021;131:e146431.
An M, Zheng H, Huang J, Lin Y, Luo Y, Kong Y, et al. Aberrant nuclear export of circNCOR1 underlies SMAD7-mediated lymph node metastasis of bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2022;82:2239–53.
Zhao Y, Chen J, Zheng H, Luo Y, An M, Lin Y, et al. SUMOylation-driven mRNA circularization enhances translation and promotes lymphatic metastasis of bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2024;84:434–48.
Yuce K, Ozkan AI. The kruppel-like factor (KLF) family, diseases, and physiological events. Gene. 2024;895:148027.
Han ZG, Zhang QH, Ye M, Kan LX, Gu BW, He KL, et al. Molecular cloning of six novel Krüppel-like zinc finger genes from hematopoietic cells and identification of a novel transregulatory ___domain KRNB. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:35741–8.
Jia D, Hasso SM, Chan J, Filingeri D, D’Amore PA, Rice L, et al. Transcriptional repression of VEGF by ZNF24: mechanistic studies and vascular consequences in vivo. Blood. 2013;121:707–15.
Liu G, Jiang S, Wang C, Jiang W, Liu Z, Liu C, et al. Zinc finger transcription factor 191, directly binding to beta-catenin promoter, promotes cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;55:1830–9.
Eifler K, Vertegaal ACO. SUMOylation-mediated regulation of cell cycle progression and cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015;40:779–93.
Zhang T, Yang H, Zhou Z, Bai Y, Wang J, Wang W. Crosstalk between SUMOylation and ubiquitylation controls DNA end resection by maintaining MRE11 homeostasis on chromatin. Nat Commun. 2022;13:5133.
Ranieri M, Vivo M, De Simone M, Guerrini L, Pollice A, La Mantia G, et al. Sumoylation and ubiquitylation crosstalk in the control of ΔNp63α protein stability. Gene. 2018;645:34–40.
Edelstein LC, Collins T. The SCAN ___domain family of zinc finger transcription factors. Gene. 2005;359:1–17.
Wang H, Sun R, Liu G, Yao M, Fei J, Shen H. Characterization of the target DNA sequence for the DNA-binding ___domain of zinc finger protein 191. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sin. 2008;40:704–10.
Liu Y, Wu D, Cheng H, Chen L, Zhang W, Zou L, et al. Wnt8B, transcriptionally regulated by ZNF191, promotes cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma via Wnt signaling. Cancer Sci. 2021;112:629–40.
Zeng Q, Liu J, Cao P, Li J, Liu X, Fan X, et al. Inhibition of REDD1 sensitizes bladder urothelial carcinoma to paclitaxel by inhibiting autophagy. Clin Cancer Res : J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2018;24:445–59.
Du L, Fakih MG, Rosen ST, Chen Y. SUMOylation of E2F1 regulates expression of EZH2. Cancer Res. 2020;80:4212–23.
Hou G, Zhao X, Li L, Yang Q, Liu X, Huang C, et al. SUMOylation of YTHDF2 promotes mRNA degradation and cancer progression by increasing its binding affinity with m6A-modified mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:2859–77.
Du L, Liu W, Aldana-Masangkay G, Pozhitkov A, Pichiorri F, Chen Y, et al. SUMOylation inhibition enhances dexamethasone sensitivity in multiple myeloma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41:8.
Bettermann K, Benesch M, Weis S, Haybaeck J. SUMOylation in carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2012;316:113–25.
Li J, Chen X, Gong X, Liu Y, Feng H, Qiu L, et al. A transcript profiling approach reveals the zinc finger transcription factor ZNF191 is a pleiotropic factor. BMC Genomics. 2009;10:241.
Liu G, Jiang S, Wang C, Jiang W, Liu Z, Liu C, et al. Zinc finger transcription factor 191, directly binding to β-catenin promoter, promotes cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol (Balt, Md). 2012;55:1830–9.
Rousseau-Merck MF, Huebner K, Berger R, Thiesen HJ. Chromosomal localization of two human zinc finger protein genes, ZNF24 (KOX17) and ZNF29 (KOX26), to 18q12 and 17p13-p12, respectively. Genomics. 1991;9:154–61.
Harper J, Yan L, Loureiro RM, Wu I, Fang J, D’Amore PA, et al. Repression of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by the zinc finger transcription factor ZNF24. Cancer Res. 2007;67:8736–41.
Meng F, Ai C, Yan G, Wang G. Tumor-suppressive zinc finger protein 24 (ZNF24) sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil by inhibiting the Wnt pathway and activating the p53 signaling. Exp cell Res. 2023;433:113796.
Liu L, Lei Y, Chen W, Zhou Q, Zheng Z, Zeng G, et al. In vivo genome-wide CRISPR screening identifies ZNF24 as a negative NF-κB modulator in lung cancer. Cell Biosci. 2022;12:193.
Zhang R, Cheung CY, Seo SU, Liu H, Pardeshi L, Wong KH, et al. RUVBL1/2 complex regulates pro-inflammatory responses in macrophages via regulating histone H3K4 trimethylation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:679184.
Ye S, Ding YF, Jia WH, Liu XL, Feng JY, Zhu Q, et al. SET ___domain-containing protein 4 epigenetically controls breast cancer stem cell quiescence. Cancer Res. 2019;79:4729–43.
Shrestha S, Adhikary G, Xu W, Kandasamy S, Eckert RL. ACTL6A suppresses p21(Cip1) expression to enhance the epidermal squamous cell carcinoma phenotype. Oncogene. 2020;39:5855–66.
Shangguan X, He J, Ma Z, Zhang W, Ji Y, Shen K, et al. SUMOylation controls the binding of hexokinase 2 to mitochondria and protects against prostate cancer tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1812.
Garcia-Caballero A, Zhang FX, Chen L, M’Dahoma S, Huang J, Zamponi GW. SUMOylation regulates USP5-Cav3.2 calcium channel interactions. Mol Brain. 2019;12:73.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82373077 and 82373947) and the Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province (Grant No. 242102310115 and 242102310397).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Writing—original draft, and Writing—review and editing: XW, BW, XY, and DS; Data curation, Methodology, and Validation: XW, BW, YY, ZF, and CY; Software and Formal analysis: XW, BW, LZ, XF, DT, and LZ; Supervision, Project administration, and Funding acquisition: XW, XY, and DS.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The informed consents were obtained from all participants. All human experiments were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University. All animal experiments were conducted following the guidelines of the Institutional Committee for Animal Care and Use and the ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, X., Wang, B., Yang, Y. et al. Crosstalk between SUMOylation and ubiquitination controls the stability of transcription factor zinc finger protein 24: a novel antitumor mechanism in bladder cancer. Oncogene (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03450-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03450-9