Fig. 1: Block diagram of closed-loop stimulation: an engineering perspective.
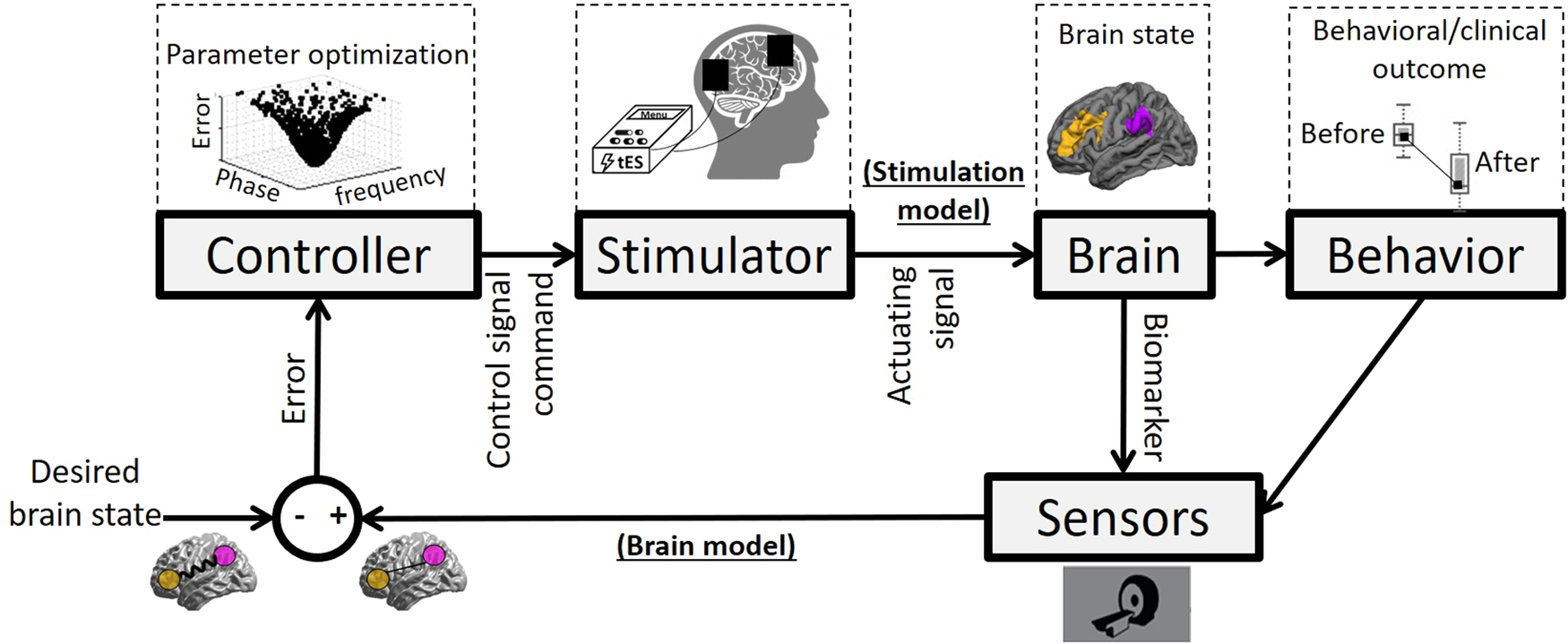
Different parts of this system are constituting the output: brain state or behavior, Desired brain state: a predefined reference. Measured brain state (measurement): measured/quantified brain state known as a biomarker (as an indirect indicator of brain state; e.g., frontoparietal synchronization). Comparator: an algorithm that compares a measured brain state with a predefined desired brain state and sends the comparison result (named Error signal) to the controller. When there is no difference between desired and measured brain states, the comparator output is zero. Therefore, the controller input is also zero, which means that there is no need to change the stimulation parameters. Controller: an optimization algorithm that receives the difference between desired and measured brain states and tries to find optimum values of stimulation parameters based on minimizing differences between the desired and measured brain states. Stimulator: a neurostimulation device such as transcranial electrical stimulator (tES) that adjusts its parameters (e.g., phase and frequency) based on information received from the controller. Brain: the plant under-stimulation. Sensor: a hardware or device that records/quantifies the current brain state (e.g., fMRI system). Control signal/command: signal/command to titrate stimulation dose automatically. Actuating signal: electrical current stimulation signals applied to the brain. Behavior: the loop can be extended to behavior, and instead of target engagement biomarkers, a treatment response biomarker is recorded (e.g., drug craving self-report). Brain model (generated by sensors): A model that links the behavioral and clinical outcome and biomarker to a disease mechanism and defines the dynamic targets for engagement and change. Stimulation model: A model that includes technical properties of the stimulator and its mechanism of action to predict the optimized protocol based on the inputs from the stimulation model.
