Abstract
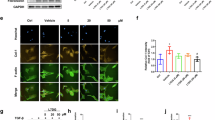
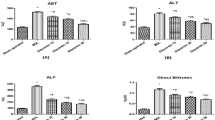
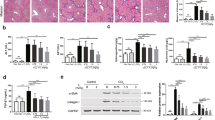
Chronic tissue injury with fibrosis results in the disruption of tissue architecture, organ dysfunction, and eventual organ failure. Therefore, the development of effective antifibrotic drugs is urgently required. IMB-S7 is novel biphenyl compound derived from bifendate (biphenyldicarboxylate) that is used for the treatment of chronic hepatitis in China. In the current study we investigated the potential of IMB-S7 as an antihepatic fibrosis agent. In bile duct ligation (BDL) rat model, oral administration of IMB-S7 (400 mg· kg−1· d−1, for 14 days) significantly ameliorated BDL-induced liver necrosis, bile duct proliferation, and collagen accumulation. We then showed that IMB-S7 treatment markedly suppressed the TGF-β/Smad pathway in human hepatic stellate cell line LX2 and mouse primary HSCs, as well as in liver samples of BDL rats, thus inhibiting the transcription of most fibrogenesis-associated genes, including TGF-β1, COL1A1, and ACTA2. Furthermore, IMB-S7 treatment significantly suppressed the expression of integrin αv at the mRNA and protein levels in TGF-β-treated LX2 cells and liver samples of BDL rats. Using integrin αv overexpression and silencing, we demonstrated that integrin αv activity correlated positively with the activation of TGF-β/Smad pathway. Based on dual luciferase assay and DNA affinity precipitation assay, we revealed that IMB-S7 inactivated integrin αv through competitively inhibiting the binding of Sp1, a transcription factor, to the integrin αv (ITGAV) promoter (−173/−163 bp). These results suggest that IMB-S7 inhibits HSCs activation and liver fibrosis through Sp1-integrin αv signaling, and IMB-S7 may be a promising candidate to combat hepatic fibrosis in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Login or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Investig. 2005;115:209–18.
Schuppan D, Afdhal NH. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 2008;371:838–51.
Hasan IH, El-Desouky MA, Hozayen WG, Abd el Aziz GM. Protective effect of zingiber officinale against CCl4-induced liver fibrosis is mediated through downregulating the TGF-beta1/Smad3 and NF-κB/IκB pathways. Pharmacology. 2016;97:1–9.
Zhang Y, Meng XM, Huang XR, Wang XJ, Yang L, Lan HY. Transforming growth factor-beta1 mediates psoriasis-like lesions via a Smad3-dependent mechanism in mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2014;41:921–32.
Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110:673–87.
Pellicoro A, Ramachandran P, Iredale JP, Fallowfield JA. Liver fibrosis and repair: immune regulation of wound healing in a solid organ. Nat Rev Immunol 2014;14:181–94.
Munger JS, Huang X, Kawakatsu H, Griffiths MJ, Dalton SL, Wu J, et al. The integrin alpha v beta 6 binds and activates latent TGF beta 1: a mechanism for regulating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Cell. 1999;96:319–28.
Wang B, Dolinski BM, Kikuchi N, Leone DR, Peters MG, Weinreb PH, et al. Role of alphavbeta6 integrin in acute biliary fibrosis. Hepatology. 2007;46:1404–12.
Hahm K, Lukashev ME, Luo Y, Yang WJ, Dolinski BM, Weinreb PH, et al. Alphav beta6 integrin regulates renal fibrosis and inflammation in Alport mouse. Am J Pathol 2007;170:110–25.
Popov Y, Patsenker E, Stickel F, Zaks J, Bhaskar KR, Niedobitek G, et al. Integrin alphavbeta6 is a marker of the progression of biliary and portal liver fibrosis and a novel target for antifibrotic therapies. J Hepatol 2008;48:453–64.
Conroy KP, Kitto LJ, Henderson NC. Alphav integrins: key regulators of tissue fibrosis. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;365:511–9.
Henderson NC, Arnold TD, Katamura Y, Giacomini MM, Rodriguez JD, McCarty JH, et al. Targeting of alphav integrin identifies a core molecular pathway that regulates fibrosis in several organs. Nat Med 2013;19:1617–24.
Wipff PJ, Rifkin DB, Meister JJ, Hinz B. Myofibroblast contraction activates latent TGF-beta1 from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol 2007;179:1311–23.
Zhao SS, Wang JX, Wang YC, Shao RG, He HW. [Establishment and application of a high-throughput drug screening model based on COL1A1 promoter for anti-liver fibrosis]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2015;50:169–73.
Cui S, Wang M, Fan G. Anti-HBV efficacy of bifendate in treatment of chronic hepatitis B, a primary study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2002;82:538–40.
Wu T, Roger H, Xie L, Liu G, Hao B. Bicyclol for chronic hepatitis B. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;4:CD004480.
Mederacke I, Dapito DH, Affo S, Uchinami H, Schwabe RF. High-yield and high-purity isolation of hepatic stellate cells from normal and fibrotic mouse livers. Nat Protoc 2015;10:305–15.
Walker GE, Wilson EM, Powell D, Oh Y. Butyrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, activates the human IGF binding protein-3 promoter in breast cancer cells: molecular mechanism involves an Sp1/Sp3 multiprotein complex. Endocrinology. 2001;142:3817–27.
Ellis EL, Mann DA. Clinical evidence for the regression of liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 2012;56:1171–80.
El-Beshbishy HA. The effect of dimethyl dimethoxy biphenyl dicarboxylate (DDB) against tamoxifen-induced liver injury in rats: DDB use is curative or protective. J Biochem Mol Biol 2005;38:300–6.
Kim SG, Kim HJ, Choi SH, Ryu JY. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced I-kappaB degradation and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression by dimethyl-4,4’-dimethoxy-5,6,5’,6’-dimethylene dioxybiphenyl-2,2’-dicarboxylate (DDB): minor role in hepatic detoxifying enzyme expression. Liver. 2000;20:319–29.
Akhurst RJ, Hata A. Targeting the TGFbeta signalling pathway in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2012;11:790–811.
Kang Y. Pro-metastasis function of TGFbeta mediated by the Smad pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98:1380–90.
Shi M, Zhu J, Wang R, Chen X, Mi L, Walz T, et al. Latent TGF-beta structure and activation. Nature. 2011;474:343–9.
Wu W, Dong YW, Shi PC, Yu M, Fu D, Zhang CY, et al. Regulation of integrin alphaV subunit expression by sulfatide in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Lipid Res 2013;54:936–52.
Garcia-Ruiz I, Gomez-Izquierdo E, Diaz-Sanjuan T, Grau M, Solis-Munoz P, Munoz-Yague T, et al. Sp1 and Sp3 transcription factors mediate leptin-induced collagen alpha1(I) gene expression in primary culture of male rat hepatic stellate cells. Endocrinology. 2012;153:5845–56.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (3332019083), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81673497, 81903695),the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (No. 2019-I2M-1–001),and the National Science & Technology Major Project "Key New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program",China(No.2019ZX09201001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HWH and RGS designed the experiments. SSZ performed animal experiments. YXZ and NZ performed the experiments on the cell model. JXW and YCW acquired and analyzed all data. NZ and SSZ wrote and revised the paper. Every author read and approved the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Zhao, Ss., Zhang, Yx. et al. A novel biphenyl compound IMB-S7 ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in BDL rats by suppressing Sp1-mediated integrin αv expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41, 661–669 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0325-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-019-0325-6