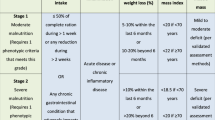
Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to compare three objective nutritional screening tools for identifying GLIM-defined malnutrition in patients with gastric cancer (GC).
Method
Objective nutritional screening tools including geriatric nutritional risk index (GNRI), prognostic nutritional index (PNI), and controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score, were evaluated in patients with GC at our institution. Malnutrition was diagnosed according to the GLIM criteria. The diagnostic value of GNRI, PNI, and COUNT scores in identifying GLIM-defined malnutrition was assessed by conducting Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curves and calculating the area under the curve (AUC). Additionally, sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) were determined. The Kappa coefficient (k) was used to assess agreement between three objective nutritional screening tools and GLIM criteria.
Results
A total of 316 patients were enrolled in this study, and malnutrition was diagnosed in 151 (47.8%) patients based on the GLIM criteria. The GNRI demonstrated good diagnostic accuracy (AUC = 0.805, 95% CI: 0.758–0.852) for detecting GLIM-defined malnutrition, while the PNI and COUNT score showed poor diagnostic accuracy with AUCs of 0.699 (95% CI: 0.641–0.757) and 0.665 (95% CI: 0.605–0.725) respectively. Among these objective nutritional screening tools, the GNRI-based malnutrition risk assessment demonstrated the highest specificity (80.0%), accuracy (72.8%), PPV (74.8%), NPV (71.4%), and consistency (k = 0.452) with GLIM-defined malnutrition.
Conclusions
Compared to PNI and COUNT scores, GNRI demonstrated superior performance as an objective nutritional screening tool for identifying GLIM-defined malnutrition in GC patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 22,42 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Applications for data access for non-commercial use can be submitted to author Junbo Zuo, [email protected].
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
Xu R, Chen XD, Ding Z. Perioperative nutrition management for gastric cancer. Nutrition. 2022;93:111492.
GlobalSurg Collaborative and NIHR Global Health Unit on Global Surgery. Impact of malnutrition on early outcomes after cancer surgery: an international, multicentre, prospective cohort study. Lancet Glob Health. 2023;11:e341–9.
Matsui R, Inaki N, Tsuji T. Effect of malnutrition as defined by the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria on compliance of adjuvant chemotherapy and relapse-free survival for advanced gastric cancer. Nutrition. 2023;109:111958.
Xu LB, Shi MM, Huang ZX, Zhang WT, Zhang HH, Shen X, et al. Impact of malnutrition diagnosed using Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria on clinical outcomes of patients with gastric cancer. JPEN. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2022;46:385–94.
Guo ZQ, Yu JM, Li W, Fu ZM, Lin Y, Shi YY, et al. Survey and analysis of the nutritional status in hospitalized patients with malignant gastric tumors and its influence on the quality of life. Support Care Cancer. 2020;28:373–80.
Cederholm T, Jensen GL, Correia M, Gonzalez MC, Fukushima R, Higashiguchi T, et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition - A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin Nutr. 2019;38:1–9.
Bouillanne O, Morineau G, Dupont C, Coulombel I, Vincent JP, Nicolis I, et al. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index: a new index for evaluating at-risk elderly medical patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;82:777–83.
Lidoriki I, Schizas D, Frountzas M, Machairas N, Prodromidou A, Kapelouzou A, et al. GNRI as a Prognostic Factor for Outcomes in Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Nutr Cancer. 2021;73:391–403.
Sun K, Chen S, Xu J, Li G, He Y. The prognostic significance of the prognostic nutritional index in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140:1537–49.
Kheirouri S, Alizadeh M. Prognostic Potential of the Preoperative Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score in Predicting Survival of Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review. Adv Nutr. 2021;12:234–50.
Onodera T, Goseki N, Kosaki G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai zasshi. 1984;85:1001–5.
Ignacio de Ulíbarri J, González-Madroño A, de Villar NG, González P, González B, Mancha A, et al. CONUT: a tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hospital population. Nutr Hosp. 2005;20:38–45.
Zuo J, Zhou D, Zhang L, Zhou X, Gao X, Hou W, et al. Comparison of bioelectrical impedance analysis and computed tomography for the assessment of muscle mass in patients with gastric cancer. Nutrition. 2024;121:112363.
Zheng HL, Lin J, Shen LL, Yang HB, Xu BB, Xue Z, et al. The GLIM criteria as an effective tool for survival prediction in gastric cancer patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2023;49:964–73.
Xiang Q, Li Y, Xia X, Deng C, Wu X, Hou L, et al. Associations of geriatric nutrition risk index and other nutritional risk-related indexes with sarcopenia presence and their value in sarcopenia diagnosis. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22:327.
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44:837–45.
Xu J, Jie Y, Sun Y, Gong D, Fan Y. Association of Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition with survival outcomes in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2022;41:1874–80.
Matsui R, Rifu K, Watanabe J, Inaki N, Fukunaga T. Impact of malnutrition as defined by the GLIM criteria on treatment outcomes in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2023;42:615–24.
Yin L, Chong F, Huo Z, Li N, Liu J, Xu H. GLIM-defined malnutrition and overall survival in cancer patients: A meta-analysis. JPEN. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2023;47:207–19.
Matsui R, Rifu K, Watanabe J, Inaki N, Fukunaga T. Current status of the association between malnutrition defined by the GLIM criteria and postoperative outcomes in gastrointestinal surgery for cancer: a narrative review. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149:1635–43.
Huang Y, Chen Y, Wei L, Hu Y, Huang L. Comparison of three malnutrition risk screening tools in identifying malnutrition according to Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria in gastrointestinal cancer. Front Nutr. 2022;9:959038.
Chen XY, Lin Y, Yin SY, Shen YT, Zhang XC, Chen KK, et al. The geriatric nutritional risk index is an effective tool to detect GLIM-defined malnutrition in rectal cancer patients. Front Nutr. 2022;9:1061944.
Cohen-Cesla T, Azar A, Hamad RA, Shapiro G, Stav K, Efrati S, et al. Usual nutritional scores have acceptable sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing malnutrition compared to GLIM criteria in hemodialysis patients. Nutr Res. 2021;92:129–38.
Xie H, Tang S, Wei L, Gan J. Geriatric nutritional risk index as a predictor of complications and long-term outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal malignancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:530.
Xu J, Sun Y, Gong D, Fan Y. Predictive Value of Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutr Cancer. 2023;75:24–32.
Yiu CY, Liu CC, Wu JY, Tsai WW, Liu PH, Cheng WJ, et al. Efficacy of the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index for Predicting Overall Survival in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2023;15:4348.
Shen F, Ma Y, Guo W, Li F. Prognostic Value of Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index for Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lung. 2022;200:661–9.
Barazzoni R, Jensen GL, Correia M, Gonzalez MC, Higashiguchi T, Shi HP, et al. Guidance for assessment of the muscle mass phenotypic criterion for the Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM) diagnosis of malnutrition. Clin Nutr. 2022;41:1425–33.
Zhuang CL, Huang DD, Pang WY, Zhou CJ, Wang SL, Lou N, et al. Sarcopenia is an Independent Predictor of Severe Postoperative Complications and Long-Term Survival After Radical Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer: Analysis from a Large-Scale Cohort. Medicine. 2016;95:e3164.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the physicians and nurses in general surgery and patients for their great cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuefeng Bu and Junbo Zuo designed the study. Zhenhua Huang, JingXin Zhang, Wenji Hou, Chen Wang, and Xiuhua Wang collected the data. Junbo Zuo, Yan Huang, and Xuefeng Bu analyzed and interpreted the data. Junbo Zuo and Yan Huang wrote the manuscript. All the authors critically reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, J., Huang, Y., Huang, Z. et al. Comparison of three objective nutritional screening tools for identifying GLIM-defined malnutrition in patients with gastric cancer. Eur J Clin Nutr 79, 64–70 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-024-01514-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-024-01514-9