Abstract
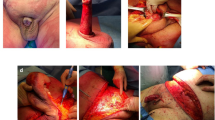
This study evaluates the use of acellular dermal matrix (ADM) in conjunction with negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) and delayed split-thickness skin graft (STSG) application as an alternative to free tissue transfer for defect coverage of the penile shaft. Five patients with genital lymphedema and one with penile skin deficiency underwent penile shaft reconstruction with a two-stage surgical procedure. The first procedure aimed to the correction of skin defect and to neodermis regeneration through the use of an ADM (Integra®, Integra Lifesciences Corp., Plainsboro, NJ, USA) and NPWT. The second procedure 3 weeks later aimed to the covering of the skin defect with an unmeshed STSG. Both the Integra and skin graft showed completely taking at 7 days postop. No major complications occurred. At 6 months grafts gained sufficient elasticity to allow the sliding of the epidermis over the dermal layer, similarly the physiological penile shaft skin. Our results suggest that combined therapy might be an alternative to free tissue transfer for defect coverage of the penile shaft, leading to a good esthetic result, an optimal shaft coverage and providing adequate extensibility during erections. For best results we advise that in these cases urologists should collaborate with plastic surgeons.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 22,42 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castro RB, Oliveira AB, Favorito LA. Utilization of skin flap for reconstruction of the genitalia after an electric burn. Int Braz J Urol. 2006;32:68–9.
Ludolph I, Titel T, Beier JP, Dragu A, Schmitz M, Wullich B, et al. Penile reconstruction with dermal template and vacuum therapy in severe skin and soft tissue defects caused by Fournier’s gangrene and hidradenitis suppurativa. Int Wound J. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1111/iwj.12235.
Tang SH, Kamat D, Santucci RA. Modern management of adult-acquired buried penis. Urology. 2008;72:124–7.
Garaffa G, Sansalone S, Ralph DJ. Penile reconstruction. Asian J Androl. 2013;15:16–9.
Garaffa G, Christopher N, Ralph DJ. The management of genital lymphoedema. BJU Int. 2008;102:480–4.
Malloy TR, Wein AJ, and Gross P. Scrotal and penile lymphedema: surgical considerations and management. J Urol. 1983. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(17)51097-6.
Djedovic G, Matiasek J, Morandi E, Pierer G and Rieger UM. Use of an acellular dermal template for defect coverage on the penile shaft. Eur J Plast Surg. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-015-1096-z.
Rosenstein DI, Morey AF and McAnich JW. Penile traumas. In Graham S, Keane T (eds.). Glenn’s urologic surgery. 7th edn. (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2010. p 516)
Bryk DJ, Yamaguchi Y and Zhao LC. Tissue transfer techniques in reconstructive urology. Korean J Urol. 2015. https://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2015.56.7.478.
Ballaro A, Webster JJ and Ralph DJ. Penile resurfacing for extensive genital warts. Int J Impot Res. 2001. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900640.
Fuller TW, Theisen KM, Shah A and Rusilko PJ. Surgical management of adult acquired buried penis. Curr Urol Rep. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-018-0768-1.
Weinfeld AB, Kelley P, Yuksel E, Tiwari P, Hsu P, Choo J, et al. Circumferential negative-pressure dressing (VAC) to bolster skin grafts in the reconstruction of the penile shaft and scrotum. Ann Plast Surg. 2005. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sap.0000143606.39693.3f.
Stokes TC, Follmar KE, Silverstein AD, Weizer AZ, Donatucci CF, Anderson EE, et al. Use of negative-pressure dressings and split-thickness skin grafts following penile shaft reduction and reduction scrotoplasty in the management of penoscrotal elephantiasis. Ann Plast Surg. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sap.0000202826.61782.c9.
G Papa, M Pangos, N Renzi, V Ramella, N Panizzo and Marij AZ. Five years of experience using a dermal substitute: Indications, histologic studies, and first results: using a new single-layer tool. Dermatologic Surg. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2011.02156.x.
Triana Junco P, Fore M, Nuñez Cerezo V, Jimenez Gomez J, Miguel Ferrero M, Díaz González M, et al. Penile reconstruction with skin grafts and dermal matrices: indications and management. Eur J Pediatr Surg Rep. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1606282.
Kristinsson S, Johnson M and Ralph D Review of penile reconstructive techniques. Int J Impot Res. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-020-0246-4.
De Stefani S, Liguori G, Ciampalini S, Trombetta C, Pascone M, Bertolotto M, et al. Radial fascio-cutaneous flap of the forearm and myocutaneous gracilis muscle flap in urologic surgery: surgical anatomy and techniques. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2000;72:37–43.
Lee S, Bang C, Kim J. Penoscrotal reconstruction using groin and bilateral superomedial thigh flaps: a case of penile vaselinoma causing Fournier’s gangrene. Yonsei Med J. 2007;48:723–6. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.4.723.
Arnež ZM, Ramella V, Papa G, Novati FC, Manca E, Leuzzi S, et al. Is the LICOX® PtO2 system reliable for monitoring of free flaps? Comparison between two cohorts of patients. Microsurgery. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/micr.30396.
Fakin R, Zimmermann S, Jindarak S, Lindenblatt N, Giovanoli P and Suwajo P. Reconstruction of penile shaft defects following silicone injection by bipedicled anterior scrotal flap. J Urol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2016.11.093.
Argenta LC and Morykwas MJ. Vacuum-assisted closure: a new method for wound control and treatment: clinical experience. Ann Plast Surg. 1997. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-199706000-00002.
Alwaal A, McAninch JW, Harris CR and Breyer BN. Utilities of split-thickness skin grafting for male genital reconstruction. Urology. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2015.07.005.
Dantzer E, Queruel P, Salinier L, Palmier B and Quinot JF. Dermal regeneration template for deep hand burns: clinical utility for both early grafting and reconstructive surgery. Br J Plast Surg. 2003. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1226(03)00366-7.
Alei G, Letizia P, Ricotilli F, Simone P, Alei L, Massoni F, et al. Original technique for penile girth augmentation through porcine dermal acellular grafts: results in a 69-patient series. J Sex Med. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2012.02744.x.
Nguyen DQ, Potokar TS, Price P. An objective long-term evaluation of Integra (a dermal skin substitute) and split thickness skin grafts, in acute burns and reconstructive surgery. Burns. 2010;36:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2009.07.011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liguori, G., Papa, G., Boltri, M. et al. Reconstruction of penile skin loss using a combined therapy of negative pressure wound therapy, dermal regeneration template, and split-thickness skin graft application. Int J Impot Res 33, 854–859 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-020-00343-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-020-00343-1
This article is cited by
-
The use of Matriderm for penile reconstruction: a case series
European Journal of Plastic Surgery (2022)