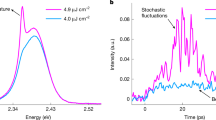
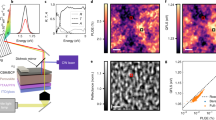
Abstract
Solution-processed colloidal nanocrystals of lead halide perovskites have been intensively investigated in recent years in the context of optoelectronic devices, during which time their quantum properties have also begun to attract attention. Their unmatched ease of synthetic tunability and unique structural, optical and electronic properties, in conjunction with the confinement of carriers in three dimensions, have motivated studies on observing and controlling coherent light–matter interaction in these materials for quantum information technologies. This Review outlines the recent efforts and achievements in this direction. Particularly notable examples are the observation of coherent single-photon emission, evidence for superfluorescence and the realization of room-temperature coherent spin manipulation for ensemble samples, which have not been achieved for prototypical colloidal CdSe nanocrystals that have been under investigation for decades. This Review aims to highlight these results, point out the challenges ahead towards realistic applications and bring together the efforts of multidisciplinary communities in this nascent field.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
27,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 22,42 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loss, D. & DiVincenzo, D. P. Quantum computation with quantum dots. Phys. Rev. A 57, 120–126 (1998).
DiVincenzo, D. P. The physical implementation of quantum computation. Fortschr. Phys. 48, 771–783 (2000).
Gisin, N. & Thew, R. Quantum communication. Nat. Photon. 1, 165–171 (2007).
Zoller, P. et al. Quantum information processing and communication. Eur. Phys. J. D 36, 203–228 (2005).
Yu, C. J. et al. A molecular approach to quantum sensing. ACS Cent. Sci. 7, 712–723 (2021).
Degen, C. L., Reinhard, F. & Cappellaro, P. Quantum sensing. Rev. Mod. Phys. 89, 035002 (2017).
Shields, A. J. Semiconductor quantum light sources. Nat. Photon. 1, 215–223 (2007).
Lu, C.-Y. & Pan, J.-W. Quantum-dot single-photon sources for the quantum internet. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1294–1296 (2021).
Senellart, P., Solomon, G. & White, A. High-performance semiconductor quantum-dot single-photon sources. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 1026–1039 (2017).
Burkard, G. et al. Semiconductor spin qubits. Rev. Mod. Phys. 95, 025003 (2023).
Chatterjee, A. et al. Semiconductor qubits in practice. Nat. Rev. Phys. 3, 157–177 (2021).
Li, X. et al. An all-optical quantum gate in a semiconductor quantum dot. Science 301, 809–811 (2003).
Liu, R.-B., Yao, W. & Sham, L. J. Quantum computing by optical control of electron spins. Adv. Phys. 59, 703–802 (2010).
García de Arquer, F. P. et al. Semiconductor quantum dots: technological progress and future challenges. Science 373, eaaz8541 (2021).
Kagan, C. R. et al. Colloidal quantum dots as platforms for quantum information science. Chem. Rev. 121, 3186–3233 (2020).
Efros, A. L. & Nesbitt, D. J. Origin and control of blinking in quantum dots. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 661–671 (2016).
Nirmal, M. et al. Fluorescence intermittency in single cadmium selenide nanocrystals. Nature 383, 802–804 (1996).
Sun, F. W. & Wong, C. W. Indistinguishability of independent single photons. Phys. Rev. A 79, 013824 (2009).
Berezovsky, J. et al. Picosecond coherent optical manipulation of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Science 320, 349–352 (2008).
Press, D. et al. Complete quantum control of a single quantum dot spin using ultrafast optical pulses. Nature 456, 218–221 (2008).
Zhang, J. et al. Tailoring light–matter–spin interactions in colloidal hetero-nanostructures. Nature 466, 91–95 (2010).
Kovalenko, M. V., Protesescu, L. & Bodnarchuk, M. I. Properties and potential optoelectronic applications of lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. Science 358, 745–750 (2017).
Akkerman, Q. A. et al. Genesis, challenges and opportunities for colloidal lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 17, 394–405 (2018).
Dey, A. et al. State of the art and prospects for halide perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Nano 15, 10775–10981 (2021).
Even, J. Pedestrian guide to symmetry properties of the reference cubic structure of 3D all-inorganic and hybrid perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6, 2238–2242 (2015).
Odenthal, P. et al. Spin-polarized exciton quantum beating in hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites. Nat. Phys. 13, 894–899 (2017).
Labeau, O., Tamarat, P. & Lounis, B. Temperature dependence of the luminescence lifetime of single CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 257404 (2003).
Efros, A. L. et al. Band-edge exciton in quantum dots of semiconductors with a degenerate valence band: dark and bright exciton states. Phys. Rev. B 54, 4843–4856 (1996).
Becker, M. A. et al. Bright triplet excitons in caesium lead halide perovskites. Nature 553, 189–193 (2018).
Rainò, G. et al. Single cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals at low temperature: fast single-photon emission, reduced blinking, and exciton fine structure. ACS Nano 10, 2485–2490 (2016).
Utzat, H. et al. Coherent single-photon emission from colloidal lead halide perovskite quantum dots. Science 363, 1068–1072 (2019).
Fu, M. et al. Neutral and charged exciton fine structure in single lead halide perovskite nanocrystals revealed by magneto-optical spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 17, 2895–2901 (2017).
Kaplan, A. E. et al. Hong–Ou–Mandel interference in colloidal CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals. Nat. Photon. 17, 775–780 (2023).
Li, Y. et al. Strong spin-selective optical Stark effect in lead halide perovskite quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11, 3594–3600 (2020).
Lin, X. et al. Room-temperature coherent optical manipulation of hole spins in solution-grown perovskite quantum dots. Nat. Nanotechnol. 18, 124–130 (2023).
Rainò, G. et al. Superfluorescence from lead halide perovskite quantum dot superlattices. Nature 563, 671–675 (2018).
Dai, D. & Monkman, A. Observation of superfluorescence from a quantum ensemble of coherent excitons in a ZnTe crystal: evidence for spontaneous Bose–Einstein condensation of excitons. Phys. Rev. B 84, 115206 (2011).
Timothy Noe, I. I. et al. Giant superfluorescent bursts from a semiconductor magneto-plasma. Nat. Phys. 8, 219–224 (2012).
Cao, Z. et al. Optical studies of semiconductor perovskite nanocrystals for classical optoelectronic applications and quantum information technologies: a review. Adv. Photon. 2, 054001 (2020).
Lv, Y. et al. Magneto-optical effects in lead halide perovskites. Adv. Phys. X 8, 2258951 (2023).
Aharonovich, I., Englund, D. & Toth, M. Solid-state single-photon emitters. Nat. Photon. 10, 631–641 (2016).
Browne, D. et al. From quantum optics to quantum technologies. Prog. Quantum Electron. 54, 2–18 (2017).
Michler, P. et al. A quantum dot single-photon turnstile device. Science 290, 2282–2285 (2000).
Tomm, N. et al. A bright and fast source of coherent single photons. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 399–403 (2021).
Zhai, L. et al. Quantum interference of identical photons from remote GaAs quantum dots. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 829–833 (2022).
Empedocles, S. A. & Bawendi, M. G. Quantum-confined Stark effect in single CdSe nanocrystallite quantum dots. Science 278, 2114–2117 (1997).
Hu, F. et al. Slow Auger recombination of charged excitons in nonblinking perovskite nanocrystals without spectral diffusion. Nano Lett. 16, 6425–6430 (2016).
Park, Y.-S. et al. Room temperature single-photon emission from individual perovskite quantum dots. ACS Nano 9, 10386–10393 (2015).
Hu, F. et al. Superior optical properties of perovskite nanocrystals as single photon emitters. ACS Nano 9, 12410–12416 (2015).
Fu, M. et al. Unraveling exciton–phonon coupling in individual FAPbI3 nanocrystals emitting near-infrared single photons. Nat. Commun. 9, 3318 (2018).
Yuan, J. et al. Single‐photon emission from single microplate MAPbI3 nanocrystals with ultranarrow photoluminescence linewidths and exciton fine structures. Adv. Opt. Mater. 10, 2200606 (2022).
Zhu, C. et al. Room-temperature, highly pure single-photon sources from all-inorganic lead halide perovskite quantum dots. Nano Lett. 22, 3751–3760 (2022).
Li, Y. et al. Size- and halide-dependent Auger recombination in lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 14292–14295 (2020).
Lv, Y. et al. Quantum interference in a single perovskite nanocrystal. Nano Lett. 19, 4442–4447 (2019).
Rainò, G. et al. Ultra-narrow room-temperature emission from single CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 13, 2587 (2022).
Sun, W. et al. Elastic phonon scattering dominates dephasing in weakly confined cesium lead bromide nanocrystals at cryogenic temperatures. Nano Lett. 23, 2615–2622 (2023).
Zhu, C. et al. Quantifying the size‐dependent exciton–phonon coupling strength in single lead‐halide perovskite quantum dots. Adv. Opt. Mater. 12, 2301534 (2024).
Ginterseder, M. et al. Lead halide perovskite nanocrystals with low inhomogeneous broadening and high coherent fraction through dicationic ligand engineering. Nano Lett. 23, 1128–1134 (2023).
Tamarat, P. et al. The dark exciton ground state promotes photon-pair emission in individual perovskite nanocrystals. Nat. Commun. 11, 6001 (2020).
Zhu, C. et al. Single-photon superradiance in individual caesium lead halide quantum dots. Nature 626, 535–541 (2024).
Dicke, R. H. Coherence in spontaneous radiation processes. Phys. Rev. 93, 99–110 (1954).
Cherniukh, I. et al. Perovskite-type superlattices from lead halide perovskite nanocubes. Nature 593, 535–542 (2021).
Krieg, F. et al. Monodisperse long-chain sulfobetaine-capped CsPbBr3 nanocrystals and their superfluorescent assemblies. ACS Cent. Sci. 7, 135–144 (2020).
Bonifacio, R. & Lugiato, L. Cooperative radiation processes in two-level systems: superfluorescence. Phys. Rev. A 11, 1507–1521 (1975).
Findik, G. et al. High-temperature superfluorescence in methyl ammonium lead iodide. Nat. Photon. 15, 676–680 (2021).
Biliroglu, M. et al. Room-temperature superfluorescence in hybrid perovskites and its origins. Nat. Photon. 16, 324–329 (2022).
Tao, W., Zhang, Y. & Zhu, H. Dynamic exciton polaron in two-dimensional lead halide perovskites and implications for optoelectronic applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 55, 345–353 (2022).
Thouin, F. et al. Phonon coherences reveal the polaronic character of excitons in two-dimensional lead halide perovskites. Nat. Mater. 18, 349–356 (2019).
Han, Y. et al. Lattice distortion inducing exciton splitting and coherent quantum beating in CsPbI3 perovskite quantum dots. Nat. Mater. 21, 1282–1289 (2022).
Cai, R. et al. Zero-field quantum beats and spin decoherence mechanisms in CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals. Nat. Commun. 14, 2472 (2023).
Sercel, P. C. et al. Exciton fine structure in perovskite nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 19, 4068–4077 (2019).
Sercel, P. C. et al. Quasicubic model for metal halide perovskite nanocrystals. J. Chem. Phys. 151, 234106 (2019).
Nestoklon, M. et al. Optical orientation and alignment of excitons in ensembles of inorganic perovskite nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. B 97, 235304 (2018).
Aich, R. B. et al. Bright-exciton splittings in inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. Appl. 11, 034042 (2019).
Gao, K. et al. Manipulating coherent exciton dynamics in CsPbI3 perovskite quantum dots using magnetic field. Adv. Mater. 36, 2309420 (2024).
Tamarat, P. et al. The ground exciton state of formamidinium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals is a singlet dark state. Nat. Mater. 18, 717–724 (2019).
Isarov, M. et al. Rashba effect in a single colloidal CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystal detected by magneto-optical measurements. Nano Lett. 17, 5020–5026 (2017).
Liu, A. et al. Multidimensional coherent spectroscopy reveals triplet state coherences in cesium lead-halide perovskite nanocrystals. Sci. Adv. 7, eabb3594 (2021).
Liu, A. Measuring exciton fine-structure in randomly oriented perovskite nanocrystal ensembles using nonlinear optical spectroscopy: theory. Nanomaterials 12, 801 (2022).
Seiler, H. et al. Two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy reveals liquid-like lineshape dynamics in CsPbI3 perovskite nanocrystals. Nat. Commun. 10, 4962 (2019).
Brosseau, P. et al. Exciton–polaron interactions in metal halide perovskite nanocrystals revealed via two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 159, 184711 (2023).
Yin, C. et al. Bright-exciton fine-structure splittings in single perovskite nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 026401 (2017).
Li, Y. et al. Size- and composition-dependent exciton spin relaxation in lead halide perovskite quantum dots. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 1701–1708 (2020).
Tao, W., Zhou, Q. & Zhu, H. Dynamic polaronic screening for anomalous exciton spin relaxation in two-dimensional lead halide perovskites. Sci. Adv. 6, eabb7132 (2020).
Dey, A. et al. Fast electron and slow hole spin relaxation in CsPbI3 nanocrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 121, 201106 (2022).
Crane, M. J. et al. Coherent spin precession and lifetime-limited spin dephasing in CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 20, 8626–8633 (2020).
Grigoryev, P. S. et al. Coherent spin dynamics of electrons and holes in CsPbBr3 colloidal nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 21, 8481–8487 (2021).
Kirstein, E. et al. Mode locking of hole spin coherences in CsPb(Cl,Br)3 perovskite nanocrystals. Nat. Commun. 14, 699 (2023).
Belykh, V. V. et al. Coherent spin dynamics of electrons and holes in CsPbBr3 perovskite crystals. Nat. Commun. 10, 673 (2019).
Fumani, A. K. & Berezovsky, J. Spin-pumping efficiency in room-temperature CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 28202–28206 (2014).
Cheng, H. et al. Dopant-induced slow spin relaxation in CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 4325–4332 (2022).
Koppens, F. H. et al. Driven coherent oscillations of a single electron spin in a quantum dot. Nature 442, 766–771 (2006).
De La Giroday, A. B. et al. All-electrical coherent control of the exciton states in a single quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 82, 241301 (2010).
Nowack, K. C. et al. Coherent control of a single electron spin with electric fields. Science 318, 1430–1433 (2007).
De Greve, K. et al. Ultrafast coherent control and suppressed nuclear feedback of a single quantum dot hole qubit. Nat. Phys. 7, 872–878 (2011).
Greilich, A. et al. Optical control of one and two hole spins in interacting quantum dots. Nat. Photon. 5, 702–708 (2011).
Foletti, S. et al. Universal quantum control of two-electron spin quantum bits using dynamic nuclear polarization. Nat. Phys. 5, 903–908 (2009).
Economou, S. E. & Reinecke, T. Theory of fast optical spin rotation in a quantum dot based on geometric phases and trapped states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 217401 (2007).
Greilich, A. et al. Ultrafast optical rotations of electron spins in quantum dots. Nat. Phys. 5, 262–266 (2009).
Yang, Y. et al. Large polarization-dependent exciton optical Stark effect in lead iodide perovskites. Nat. Commun. 7, 12613 (2016).
Shrivastava, M. et al. Room-temperature anomalous coherent excitonic optical Stark effect in metal halide perovskite quantum dots. Nano Lett. 22, 808–814 (2022).
Ramsay, A. et al. Fast optical preparation, control, and readout of a single quantum dot spin. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 197401 (2008).
Kroutvar, M. et al. Optically programmable electron spin memory using semiconductor quantum dots. Nature 432, 81–84 (2004).
Widmann, M. et al. Coherent control of single spins in silicon carbide at room temperature. Nat. Mater. 14, 164–168 (2015).
Morello, A. Single spins in silicon carbide. Nat. Mater. 14, 135–136 (2015).
Press, D. et al. Ultrafast optical spin echo in a single quantum dot. Nat. Photon. 4, 367–370 (2010).
Biadala, L. et al. Magnetic polaron on dangling-bond spins in CdSe colloidal nanocrystals. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12, 569–574 (2017).
Shornikova, E. V. et al. Surface spin magnetism controls the polarized exciton emission from CdSe nanoplatelets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 277–282 (2020).
Urbaszek, B. et al. Nuclear spin physics in quantum dots: an optical investigation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 79–133 (2013).
Merkulov, I., Efros, A. L. & Rosen, M. Electron spin relaxation by nuclei in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 65, 205309 (2002).
Farrow, T. et al. Ultranarrow line width room-temperature single-photon source from perovskite quantum dot embedded in optical microcavity. Nano Lett. 23, 10667–10673 (2023).
Boyle, S. et al. Two-qubit conditional quantum-logic operation in a single self-assembled quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 78, 075301 (2008).
Zajac, D. M. et al. Resonantly driven CNOT gate for electron spins. Science 359, 439–442 (2018).
Petta, J. R. et al. Coherent manipulation of coupled electron spins in semiconductor quantum dots. Science 309, 2180–2184 (2005).
Koley, S. et al. Coupled colloidal quantum dot molecules. Acc. Chem. Res. 54, 1178–1188 (2021).
Ouyang, M. & Awschalom, D. D. Coherent spin transfer between molecularly bridged quantum dots. Science 301, 1074–1078 (2003).
Wasielewski, M. R. et al. Exploiting chemistry and molecular systems for quantum information science. Nat. Rev. Chem. 4, 490–504 (2020).
Bertolotti, F. et al. Coherent nanotwins and dynamic disorder in cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Nano 11, 3819–3831 (2017).
Stoumpos, C. C. & Kanatzidis, M. G. The renaissance of halide perovskites and their evolution as emerging semiconductors. Acc. Chem. Res. 48, 2791–2802 (2015).
Steele, J. A. et al. Thermal unequilibrium of strained black CsPbI3 thin films. Science 365, 679–684 (2019).
Zhao, Q. et al. Size-dependent lattice structure and confinement properties in CsPbI3 perovskite nanocrystals: negative surface energy for stabilization. ACS Energy Lett. 5, 238–247 (2019).
Cottingham, P. & Brutchey, R. L. On the crystal structure of colloidally prepared CsPbBr3 quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 52, 5246–5249 (2016).
Schmitz, A. et al. Optical probing of crystal lattice configurations in single CsPbBr3 nanoplatelets. Nano Lett. 21, 9085–9092 (2021).
Boyer-Richard, S. et al. Symmetry-based tight binding modeling of halide perovskite semiconductors. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7, 3833–3840 (2016).
Giovanni, D. et al. Tunable room-temperature spin-selective optical Stark effect in solution-processed layered halide perovskites. Sci. Adv. 2, e1600477 (2016).
Ramade, J. et al. Fine structure of excitons and electron–hole exchange energy in polymorphic CsPbBr3 single nanocrystals. Nanoscale 10, 6393–6401 (2018).
Amara, M.-R. et al. Spectral fingerprint of quantum confinement in single CsPbBr3 nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 23, 3607–3613 (2023).
Tamarat, P. et al. Universal scaling laws for charge-carrier interactions with quantum confinement in lead-halide perovskites. Nat. Commun. 14, 229 (2023).
Acknowledgements
K.W. acknowledges financial support from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (YSBR-007), Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP I202106) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (20720220009). K.W. also acknowledges the New Cornerstone Science Foundation through the XPLORER PRIZE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.W. proposed the topic and main organization of the paper, with help from J.Z. and Y.L. J.Z., Y.L., X.L., Y.H. and K.W. participated in writing and discussions. J.Z. and Y.L. contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Materials thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Li, Y., Lin, X. et al. Coherent phenomena and dynamics of lead halide perovskite nanocrystals for quantum information technologies. Nat. Mater. 23, 1027–1040 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-024-01922-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-024-01922-z