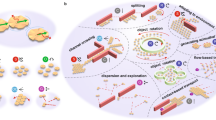
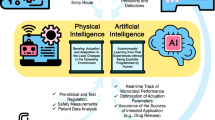
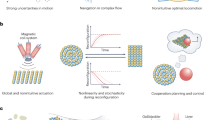
Abstract
Medical microrobotics capitalizes on smart materials to target specific body sites effectively, precisely and locally, thus holding promise to revolutionize precision medicine in the future. Advances in material science and microfabrication or nanofabrication techniques have facilitated the implementation of a myriad of functionalities into microrobots. Efficient navigation and monitoring of microrobots within the highly dynamic and often inaccessible environment of living mammalian tissues is paramount for their effective in vivo applications and eventual clinical translation. This need calls for the deployment of biomedical imaging modalities with adequate sensitivity, penetration depth and spatiotemporal resolution, as well as for efficient integration of biocompatible contrast materials into microrobots. In this Review, we discuss emerging approaches for multiplexed imaging and actuation of microrobots within complex biological environments, focusing on the synergistic combination of responsive and contrasting materials to achieve desired morphological and functional properties, in vivo visibility and biosafety. The convergence between microrobotics and biomedical imaging paves the way for a new generation of medical microrobots enabling the use of energy for both mechanical actuation and efficient monitoring of their activity in vivo.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
27,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
118,99 € per year
only 9,92 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki, T. The history of optical microscope. Mech. Eng. Rev. 4, 16-00242 (2017).
Röntgen, W. K. A new form of radiation. Science 3, 726–729 (1896).
Feynman, R. Electrical Engineering Handbook 3–12 (CRC, 2012).
Lu, W., Yao, J., Zhu, X. & Qi, Y. Nanomedicines: redefining traditional medicine. Biomed. Pharmacother. 134, 111103 (2021).
Iacovacci, V., Diller, E., Ahmed, D. & Menciassi, A. Medical microrobots. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 26, 561–591 (2024).
Del Campo Fonseca, A. & Ahmed, D. Ultrasound robotics for precision therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 205, 115164 (2024).
Nelson, B. J. & Pané, S. Delivering drugs with microrobots. Science 382, 1120–1122 (2023).
Strebhardt, K. & Ullrich, A. Paul Ehrlich’s magic bullet concept: 100 years of progress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 473–480 (2008).
Go, G. et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-based medical microrobot system for knee cartilage regeneration in vivo. Sci. Robot. 5, eaay6626 (2020).
Wrede, P. et al. Real-time 3D optoacoustic tracking of cell-sized magnetic microrobots circulating in the mouse brain vasculature. Sci. Adv. 8, eabm9132 (2022).
Del Campo Fonseca, A. et al. Ultrasound trapping and navigation of microrobots in the mouse brain vasculature. Nat. Commun. 14, 5889 (2023).
Gwisai, T. et al. Engineering living immunotherapeutic agents for improved cancer treatment. Adv. Ther. 7, 2300302 (2024).
Go, G. et al. Multifunctional microrobot with real-time visualization and magnetic resonance imaging for chemoembolization therapy of liver cancer. Sci. Adv. 8, eabq8545 (2022).
Simó, C. et al. Urease-powered nanobots for radionuclide bladder cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 554–564 (2024).
Li, N. et al. Human-scale navigation of magnetic microrobots in hepatic arteries. Sci. Robot. 9, eadh8702 (2024).
Chen, C., Ding, S. & Wang, J. Materials consideration for the design, fabrication and operation of microscale robots. Nat. Rev. Mater. 9, 159–172 (2024).
Soto, F. et al. Smart materials for microrobots. Chem. Rev. 122, 5365–5403 (2022).
Kim, J. et al. Advanced materials for micro/nanorobotics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 53, 9190–9253 (2024).
Xu, H., Medina-Sánchez, M., Maitz, M. F., Werner, C. & Schmidt, O. G. Sperm micromotors for cargo delivery through flowing blood. ACS Nano 14, 2982–2993 (2020).
Alapan, Y., Bozuyuk, U., Erkoc, P., Karacakol, A. C. & Sitti, M. Multifunctional surface microrollers for targeted cargo delivery in physiological blood flow. Sci. Robot. 5, eaba5726 (2020).
Bozuyuk, U., Wrede, P., Yildiz, E. & Sitti, M. Roadmap for clinical translation of mobile microrobotics. Adv. Mater. 36, e2311462 (2024).
Yasa, I. C., Ceylan, H., Bozuyuk, U., Wild, A.-M. & Sitti, M. Elucidating the interaction dynamics between microswimmer body and immune system for medical microrobots. Sci. Robot. 5, eaaz3867 (2020).
Olsen Alstrup, A. K. & Winterdahl, M. Imaging techniques in large animals. Scand. J. Lab. Anim. Sci. 36, 55–66 (2014).
Koba, W. et al. Imaging devices for use in small animals. Semin. Nucl. Med. 41, 151–165 (2011).
Aziz, A. et al. Nanomaterial-decorated micromotors for enhanced photoacoustic imaging. J. Micro Bio Robot. 19, 37–45 (2023).
Nauber, R., Hoppe, J., Robles, D. C. & Medina-Sánchez, M. Photoacoustics-guided real-time closed-loop control of magnetic microrobots through deep learning. In Int. Conf. Manipul. Autom. Robot. Small Scales (MARSS) 1–5 (IEEE, 2024).
Nothnagel, N. et al. Steering of magnetic devices with a magnetic particle imaging system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63, 2286–2293 (2016).
Park, J., Kim, J.-Y., Pané, S., Nelson, B. J. & Choi, H. Acoustically mediated controlled drug release and targeted therapy with degradable 3D porous magnetic microrobots. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10, e2001096 (2021).
Dogan, N. O. et al. Remotely guided immunobots engaged in anti-tumorigenic phenotypes for targeted cancer immunotherapy. Small 18, e2204016 (2022).
Akolpoglu, M. B. et al. Magnetically steerable bacterial microrobots moving in 3D biological matrices for stimuli-responsive cargo delivery. Sci. Adv. 8, eabo6163 (2022).
Sridhar, V. et al. Designing covalent organic framework-based light-driven microswimmers toward therapeutic applications. Adv. Mater. 35, e2301126 (2023).
Jooss, V. M., Bolten, J. S., Huwyler, J. & Ahmed, D. In vivo acoustic manipulation of microparticles in zebrafish embryos. Sci. Adv. 8, eabm2785 (2022).
Lo, W.-C., Fan, C.-H., Ho, Y.-J., Lin, C.-W. & Yeh, C.-K. Tornado-inspired acoustic vortex tweezer for trapping and manipulating microbubbles. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118, e2023188118 (2021).
Dabbagh, S. R. et al. 3D-printed microrobots from design to translation. Nat. Commun. 13, 5875 (2022).
Wei, K., Tang, C., Ma, H., Fang, X. & Yang, R. 3D-printed microrobots for biomedical applications. Biomater. Sci. 12, 4301–4334 (2024).
Aziz, A. et al. Medical imaging of microrobots: toward in vivo applications. ACS Nano 14, 10865–10893 (2020).
Sitti, M. Physical intelligence as a new paradigm. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 46, 101340 (2021).
Rajabasadi, F., Schwarz, L., Medina-Sánchez, M. & Schmidt, O. G. 3D and 4D lithography of untethered microrobots. Prog. Mater. Sci. 120, 100808 (2021).
Sonmez, U. M., Coyle, S., Taylor, R. E. & LeDuc, P. R. Polycarbonate heat molding for soft lithography. Small 16, e2000241 (2020).
Li, T., Chang, J., Zhu, Y. & Wu, C. 3D printing of bioinspired biomaterials for tissue regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9, e2000208 (2020).
Hirt, L., Reiser, A., Spolenak, R. & Zambelli, T. Additive manufacturing of metal structures at the micrometer scale. Adv. Mater. 29, 1604211 (2017).
Ibrahim, K. et al. Laser‐directed assembly of nanorods of 2D materials. Small 15, e1904415 (2019).
Chung, S. Y. et al. All‐solution‐processed flexible thin film piezoelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 24, 6022–6027 (2012).
Hess-Dunning, A. E., Smith, R. L. & Zorman, C. A. Development of polynorbornene as a structural material for microfluidics and flexible BioMEMS. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 131, 40969 (2014).
Lyu, X. et al. Capillary trapping of various nanomaterials on additively manufactured scaffolds for 3D micro-/nanofabrication. Nat. Commun. 15, 6693 (2024).
Zhang, J. et al. Voxelated three-dimensional miniature magnetic soft machines via multimaterial heterogeneous assembly. Sci. Robot. 6, abf0112 (2021).
Liu, Z. et al. Creating three-dimensional magnetic functional microdevices via molding-integrated direct laser writing. Nat. Commun. 13, 2016 (2022).
Rohtlaid, K. et al. PEDOT:PSS-based micromuscles and microsensors fully integrated in flexible chips. Smart Mater. Struct. 29, 09LT01 (2020).
Pang, W. et al. A soft microrobot with highly deformable 3D actuators for climbing and transitioning complex surfaces. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 119, e2215028119 (2022).
Yuan, S., Jing, W. & Jiang, H. A Deployable tensegrity microrobot for minimally invasive interventions. In Int. Mech. Eng. Congr. Expo. Vol. 5 (ASME, 2021).
Ren, Z. et al. Vertical deployment of multilayered metallic microstructures with high area-to-mass ratios by thermal actuation. J. Micro Nanomanuf. 7, 031002 (2019).
Liu, Y. et al. Responsive magnetic nanocomposites for intelligent shape-morphing microrobots. ACS Nano 17, 8899–8917 (2023).
Mohagheghian, E. et al. Quantifying stiffness and forces of tumor colonies and embryos using a magnetic microrobot. Sci. Robot. 8, eadc9800 (2023).
Dong, M. et al. 3D‐printed soft magnetoelectric microswimmers for delivery and differentiation of neuron‐like cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 1910323 (2020).
Noh, S. et al. A biodegradable magnetic microrobot based on gelatin methacrylate for precise delivery of stem cells with mass production capability. Small 18, e2107888 (2022).
Nguyen, K. T. et al. A magnetically guided self-rolled microrobot for targeted drug delivery, real-time X-ray imaging, and microrobot retrieval. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10, e2001681 (2021).
Wei, T. et al. Development of magnet-driven and image-guided degradable microrobots for the precise delivery of engineered stem cells for cancer therapy. Small 16, e1906908 (2020).
Go, G. et al. A soft biodegradable chitosan‐based medical microrobot with optimized structural design and X‐ray visibility for targeted vessel chemoembolization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2305205 (2023).
Wang, B. et al. Endoscopy-assisted magnetic navigation of biohybrid soft microrobots with rapid endoluminal delivery and imaging. Sci. Robot. 6, eabd2813 (2021).
Li, D. et al. Automated in vivo navigation of magnetic-driven microrobots using OCT imaging feedback. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 67, 2349–2358 (2020).
Lee, S. et al. A needle-type microrobot for targeted drug delivery by affixing to a microtissue. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9, e1901697 (2020).
Han, M. et al. Janus microparticles-based targeted and spatially-controlled piezoelectric neural stimulation via low-intensity focused ultrasound. Nat. Commun. 15, 2013 (2024).
Bozuyuk, U., Yildiz, E., Han, M., Demir, S. O. & Sitti, M. Size-dependent locomotion ability of surface microrollers on physiologically relevant microtopographical surfaces. Small 19, e2303396 (2023).
Abbasi, S. A. et al. Autonomous 3D positional control of a magnetic microrobot using reinforcement learning. Nat. Mach. Intell. 6, 92–105 (2024).
Bozuyuk, U. et al. High‐performance magnetic FePt (L10) surface microrollers towards medical imaging‐guided endovascular delivery applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2109741 (2022).
Giltinan, J., Sridhar, V., Bozuyuk, U., Sheehan, D. & Sitti, M. 3D-microprinting of iron platinum nanoparticle-based magnetic mobile microrobots. Adv. Intell. Syst. 3, 2000204 (2020).
Ceylan, H. et al. 3D printed personalized magnetic micromachines from patient blood-derived biomaterials. Sci. Adv. 7, eabh0273 (2021).
Kaynak, M. et al. Acoustic actuation of bioinspired microswimmers. Lab Chip 17, 395–400 (2017).
Wrede, P., Aghakhani, A., Bozuyuk, U., Yildiz, E. & Sitti, M. Acoustic trapping and manipulation of hollow microparticles under fluid flow using a single-lens focused ultrasound transducer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 52224–52236 (2023).
Leibacher, I. et al. Acoustophoresis of hollow and core-shell particles in two-dimensional resonance modes. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 16, 513–524 (2014).
Kim, D. W. et al. Hierarchical nanostructures as acoustically manipulatable multifunctional agents in dynamic fluid flow. Adv. Mater. 36, e2404514 (2024).
Gao, Y., Wang, X. & Chen, Y. Light-driven soft microrobots based on hydrogels and LCEs: development and prospects. RSC Adv. 14, 14278–14288 (2024).
Ye, M. et al. A review of soft microrobots: material, fabrication, and actuation. Adv. Intell. Syst. 5, 2300311 (2023).
Li, D., Liu, C., Yang, Y., Wang, L. & Shen, Y. Micro-rocket robot with all-optic actuating and tracking in blood. Light Sci. Appl. 9, 84 (2020).
Kim, M., Yu, A., Kim, D., Nelson, B. J. & Ahn, S.-H. Multi‐agent control of laser‐guided shape‐memory alloy microrobots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2304937 (2023).
Kim, M.-S., Lee, H.-T. & Ahn, S.-H. Laser controlled 65 micrometer long microrobot made of Ni‐Ti shape memory alloy. Adv. Mater. Technol. 4, 1900583 (2019).
Lu, A. X. et al. Catalytic propulsion and magnetic steering of soft, patchy microcapsules: ability to pick-up and drop-off microscale cargo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 15676–15683 (2016).
Wrede, P., Medina-Sánchez, M., Fomin, V. M. & Schmidt, O. G. Switching propulsion mechanisms of tubular catalytic micromotors. Small 17, e2006449 (2021).
Wilson, D. A., Nolte, R. J. M. & van Hest, J. C. M. Autonomous movement of platinum-loaded stomatocytes. Nat. Chem. 4, 268–274 (2012).
Mirkhani, N., Christiansen, M. G., Gwisai, T., Menghini, S. & Schuerle, S. Spatially selective delivery of living magnetic microrobots through torque-focusing. Nat. Commun. 15, 2160 (2024).
Zhang, F. et al. Gastrointestinal tract drug delivery using algae motors embedded in a degradable capsule. Sci. Robot. 7, eabo4160 (2022).
Zhang, F. et al. Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia. Nat. Mater. 21, 1324–1332 (2022).
Santomauro, G. et al. Incorporation of terbium into a microalga leads to magnetotactic swimmers. Adv. Biosyst. 2, 1800039 (2018).
Sanchis-Gual, R. et al. 3D printed template‐assisted casting of biocompatible polyvinyl alcohol‐based soft microswimmers with tunable stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2212952 (2023).
Chen, S. et al. Biodegradable microrobots for DNA vaccine delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 12, e2202921 (2023).
Darmawan, B. A. et al. Magnetically controlled reversible shape-morphing microrobots with real-time X-ray imaging for stomach cancer applications. J. Mater. Chem. B Mater. Biol. Med. 10, 4509–4518 (2022).
Villa, K. et al. Enzyme‐photocatalyst tandem microrobot powered by urea for Escherichia coli biofilm eradication. Small 18, e2106612 (2022).
Huang, J. et al. Design of light-driven biocompatible and biodegradable microrobots containing Mg-based metallic glass nanowires. ACS Nano 18, 2006–2016 (2024).
Yang, M. et al. MXBOTs: biodegradable Ti3C2 MXene-based microrobots for targeted delivery and synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. ACS Mater. Lett. 6, 1801–1810 (2024).
Liu, D., Wang, T. & Lu, Y. Untethered microrobots for active drug delivery: from rational design to clinical settings. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 11, e2102253 (2022).
Wang, J. et al. Intelligent micro‐/nanorobots for cancer theragnostic. Adv. Mater. 34, e2201051 (2022).
Czeyda-Pommersheim, F., Martin, D. R., Costello, J. R. & Kalb, B. Contrast agents for MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 25, 705–711 (2017).
De La Vega, J. C. et al. Comparison of rhenium and iodine as contrast agents in X-ray imaging. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2021, 1250360 (2021).
Yang, Y. et al. In-vivo programmable acoustic manipulation of genetically engineered bacteria. Nat. Commun. 14, 3297 (2023).
Iacovacci, V. et al. High-resolution SPECT imaging of stimuli-responsive soft microrobots. Small 15, e1900709 (2019).
Lv, J. et al. High-resolution and high-speed 3D tracking of microrobots using a fluorescent light field microscope. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 13, 1426–1439 (2023).
Zhou, Q. et al. Cortex-wide transcranial localization microscopy with fluorescently labeled red blood cells. Nat. Commun. 15, 3526 (2024).
van Moolenbroek, G. T., Patiño, T., Llop, J. & Sánchez, S. Engineering intelligent nanosystems for enhanced medical imaging. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2, 2000087 (2020).
Chen, Z. et al. Multimodal optoacoustic imaging: methods and contrast materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 53, 6068–6099 (2024).
Maksimova, E. A. et al. Multilayer polymer shell perfluoropentane nanodroplets for multimodal ultrasound, magnetic resonance, and optoacoustic imaging. Laser Photon. Rev. 17, 2300137 (2023).
Senthilnathan, N., Oral, C. M., Novobilsky, A. & Pumera, M. Intelligent magnetic microrobots with fluorescent internal memory for monitoring intragastric acidity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 34, 2401463 (2024).
Li, Z. et al. Self-sensing intelligent microrobots for noninvasive and wireless monitoring systems. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 9, 102 (2023).
Chen, S. et al. Reversibly photoswitchable protein assemblies with collagen affinity for in vivo photoacoustic imaging of tumors. Sci. Adv. 10, eadn8274 (2024).
Dubey, D. et al. Engineering responsive ultrasound contrast agents through crosslinked networks on lipid-shelled microbubbles. Small 18, e2107143 (2022).
Wang, Q. et al. Ultrasound Doppler-guided real-time navigation of a magnetic microswarm for active endovascular delivery. Sci. Adv. 7, eabe5914 (2021).
Aziz, A. et al. Real‐time IR tracking of single reflective micromotors through scattering tissues. Adv. Funct. Mater. 29, 1905272 (2019).
Nguyen, V. D. et al. Primary macrophage-based microrobots: an effective tumor therapy in vivo by dual-targeting function and near-infrared-triggered drug release. ACS Nano 15, 8492–8506 (2021).
Zhang, Y. et al. Real-time tracking of fluorescent magnetic spore-based microrobots for remote detection of C. diff toxins. Sci. Adv. 5, eaau9650 (2019).
Alapan, Y. et al. Soft erythrocyte-based bacterial microswimmers for cargo delivery. Sci. Robot. 3, eaar4423 (2018).
Wang, Y. & Kohane, D. S. External triggering and triggered targeting strategies for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 17020 (2017).
Tao, Y., Chan, H. F., Shi, B., Li, M. & Leong, K. W. Light: a magical tool for controlled drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 30, 2005029 (2020).
Ceylan, H. et al. 3D-printed biodegradable microswimmer for theranostic cargo delivery and release. ACS Nano 13, 3353–3362 (2019).
Wu, Z., Lin, X., Zou, X., Sun, J. & He, Q. Biodegradable protein-based rockets for drug transportation and light-triggered release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 250–255 (2015).
Pacheco, M. et al. Microrobotic carrier with enzymatically encoded drug release in the presence of pancreatic cancer cells via programmed self-destruction. Appl. Mater. Today 27, 101494 (2022).
Zheng, Z. et al. Ionic shape-morphing microrobotic end-effectors for environmentally adaptive targeting, releasing, and sampling. Nat. Commun. 12, 411 (2021).
Li, H., Go, G., Ko, S. Y., Park, J.-O. & Park, S. Magnetic actuated pH-responsive hydrogel-based soft micro-robot for targeted drug delivery. Smart Mater. Struct. 25, 027001 (2016).
Tu, L. et al. Ultrasound-controlled drug release and drug activation for cancer therapy. Exploration 1, 20210023 (2021).
Jeon, S. et al. Magnetically actuated microrobots as a platform for stem cell transplantation. Sci. Robot. 4, eaav4317 (2019).
Dogan, N. O. et al. Immune cell-based microrobots for remote magnetic actuation, antitumor activity, and medical imaging. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13, e2400711 (2024).
Gwisai, T. et al. Magnetic torque-driven living microrobots for increased tumor infiltration. Sci. Robot. 7, eabo0665 (2022).
Milosavljevic, V., Kosaristanova, L., Dolezelikova, K., Adam, V. & Pumera, M. Microrobots with antimicrobial peptide nanoarchitectonics for the eradication of antibiotic‐resistant biofilms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2112935 (2022).
Mayorga-Martinez, C. C. et al. Swarming magnetic photoactive microrobots for dental implant biofilm eradication. ACS Nano 16, 8694–8703 (2022).
Cao, W. et al. Ultrasound-propelled Janus rod-shaped micromotors for site-specific sonodynamic thrombolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 58411–58421 (2021).
Soon, R. H. et al. Pangolin-inspired untethered magnetic robot for on-demand biomedical heating applications. Nat. Commun. 14, 3320 (2023).
Iványi, G. T. et al. Optically actuated soft microrobot family for single-cell manipulation. Adv. Mater. 36, e2401115 (2024).
Ceylan, H., Yasa, I. C., Kilic, U., Hu, W. & Sitti, M. Translational prospects of untethered medical microrobots. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 1, 012002 (2019).
Ju, Y. et al. Impact of anti-PEG antibodies induced by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 23, 135–136 (2023).
Cabanach, P. et al. Zwitterionic 3D-printed non-immunogenic stealth microrobots. Adv. Mater. 32, e2003013 (2020).
Mitchell, M. J. et al. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20, 101–124 (2021).
Fullerton, J. N. & Gilroy, D. W. Resolution of inflammation: a new therapeutic frontier. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 15, 551–567 (2016).
Li, Z. et al. Biohybrid microrobots regulate colonic cytokines and the epithelium barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. Sci. Robot. 9, eadl2007 (2024).
Zhu, Y.-X. et al. A red blood cell‐derived bionic microrobot capable of hierarchically adapting to five critical stages in systemic drug delivery. Exploration 4, 20230105 (2024).
Li, T. et al. Bioinspired claw-engaged and biolubricated swimming microrobots creating active retention in blood vessels. Sci. Adv. 9, eadg4501 (2023).
Weissleder, R. & Nahrendorf, M. Advancing biomedical imaging. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 14424–14428 (2015).
Ussia, M. et al. Magnetically driven self-degrading zinc-containing cystine microrobots for treatment of prostate cancer. Small 19, e2208259 (2023).
Dekanovsky, L. et al. Fully programmable collective behavior of light‐powered chemical microrobotics: pH‐dependent motion behavior switch and controlled cancer cell destruction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2205062 (2022).
Huang, D. et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science 254, 1178–1181 (1991).
Aumann, S., Donner, S., Fischer, J. & Müller, F. in High Resolution Imaging in Microscopy and Ophthalmology (ed. Bille, J. F.) 59–85 (Springer, 2019).
Herman, B. Fluorescence Microscopy (Garland Science, 2020).
Paddock, S. W. Confocal Microscopy: Methods and Protocols (Humana, 2013).
König, K. Multiphoton microscopy in life sciences. J. Microsc. 200, 83–104 (2000).
Stelzer, E. H. K. et al. Light sheet fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 1, 1–25 (2021).
Levoy, M., Ng, R., Adams, A., Footer, M. & Horowitz, M. Light field microscopy. ACM Trans. Graph. 25, 924–934 (2006).
Withers, P. J. et al. X-ray computed tomography. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 1, 18 (2021).
Weiskopf, N., Edwards, L. J., Helms, G., Mohammadi, S. & Kirilina, E. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of brain anatomy and in vivo histology. Nat. Rev. Phys. 3, 570–588 (2021).
Gleich, B. & Weizenecker, J. Tomographic imaging using the nonlinear response of magnetic particles. Nature 435, 1214–1217 (2005).
Wang, F. et al. Flexible Doppler ultrasound device for the monitoring of blood flow velocity. Sci. Adv. 7, eabi9283 (2021).
Cui, X.-W. et al. Ultrasound elastography. Endosc. Ultrasound 11, 252–274 (2022).
Wells, P. N. T. Ultrasound imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 51, R83–R98 (2006).
Townsend, D. W., Carney, J. P. J., Yap, J. T. & Hall, N. C. PET/CT today and tomorrow. J. Nucl. Med. 45, 4S–14S (2004).
Badr, C. E. & Tannous, B. A. Bioluminescence imaging: progress and applications. Trends Biotechnol. 29, 624–633 (2011).
Ebrahimi, N. et al. Magnetic actuation methods in bio/soft robotics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2005137 (2021).
Sitti, M. & Wiersma, D. S. Pros and cons: magnetic versus optical microrobots. Adv. Mater. 32, e1906766 (2020).
Jamil, M. F., Pokharel, M. & Park, K. Light-controlled microbots in biomedical application: a review. Appl. Sci. 12, 11013 (2022).
Hou, Y. et al. A review on microrobots driven by optical and magnetic fields. Lab Chip 23, 848–868 (2023).
Maragò, O. M., Jones, P. H., Gucciardi, P. G., Volpe, G. & Ferrari, A. C. Optical trapping and manipulation of nanostructures. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 807–819 (2013).
Yang, W., Wang, X., Wang, Z., Liang, W. & Ge, Z. Light-powered microrobots: recent progress and future challenges. Opt. Lasers Eng. 161, 107380 (2023).
Aghakhani, A. et al. High shear rate propulsion of acoustic microrobots in complex biological fluids. Sci. Adv. 8, eabm5126 (2022).
Mahkam, N. et al. Acoustic streaming-induced multimodal locomotion of bubble-based microrobots. Adv. Sci. 10, e2304233 (2023).
Deng, Y., Paskert, A., Zhang, Z., Wittkowski, R. & Ahmed, D. An acoustically controlled helical microrobot. Sci. Adv. 9, eadh5260 (2023).
Wu, Z. et al. A microrobotic system guided by photoacoustic computed tomography for targeted navigation in intestines in vivo. Sci. Robot. 4, eaax0613 (2019).
Ricotti, L. et al. Biohybrid actuators for robotics: a review of devices actuated by living cells. Sci. Robot. 2, eaaq0495 (2017).
Mestre, R., Patiño, T. & Sánchez, S. Biohybrid robotics: from the nanoscale to the macroscale. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 13, e1703 (2021).
Alapan, Y. et al. Microrobotics and microorganisms: biohybrid autonomous cellular robots. Annu. Rev. Control Robot. Auton. Syst. 2, 205–230 (2019).
Sridhar, V. et al. Light-driven carbon nitride microswimmers with propulsion in biological and ionic media and responsive on-demand drug delivery. Sci. Robot. 7, eabm1421 (2022).
Serra-Casablancas, M. et al. Catalase-powered nanobots for overcoming the mucus barrier. ACS Nano 18, 16701–16714 (2024).
Fraire, J. C. et al. Swarms of enzymatic nanobots for efficient gene delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 16, 47192–47205 (2024).
Li, Z. et al. Inhalable biohybrid microrobots: a non-invasive approach for lung treatment. Nat. Commun. 16, 666 (2025).
Andreou, C., Weissleder, R. & Kircher, M. F. Multiplexed imaging in oncology. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 6, 527–540 (2022).
Bakenecker, A. C. et al. Actuation and visualization of a magnetically coated swimmer with magnetic particle imaging. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 473, 495–500 (2019).
Kósa, G., Jakab, P., Székely, G. & Hata, N. MRI driven magnetic microswimmers. Biomed. Microdevices 14, 165–178 (2012).
Vonthron, M., Lalande, V., Bringout, G., Tremblay, C. & Martel, S. A MRI-based integrated platform for the navigation of micro-devices and microrobots. In IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intell. Robots Syst. 1285–1290 (IEEE, 2011).
Belharet, K., Folio, D. & Ferreira, A. MRI-based microrobotic system for the propulsion and navigation of ferromagnetic microcapsules. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 19, 157–169 (2010).
Xu, Z. et al. X-ray-powered micromotors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 15727–15732 (2019).
Pane, S., Iacovacci, V., Sinibaldi, E. & Menciassi, A. Real-time imaging and tracking of microrobots in tissues using ultrasound phase analysis. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118, 014102 (2021).
Dillinger, C., Knipper, J., Nama, N. & Ahmed, D. Steerable acoustically powered starfish-inspired microrobot. Nanoscale 16, 1125–1134 (2024).
Aziz, A., Holthof, J., Meyer, S., Schmidt, O. G. & Medina-Sánchez, M. Dual ultrasound and photoacoustic tracking of magnetically driven micromotors: from in vitro to in vivo. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10, e2101077 (2021).
Sitti, M. Mobile Microrobotics (MIT Press, 2017).
Liu, Y. et al. A low-cost and shielding-free ultra-low-field brain MRI scanner. Nat. Commun. 12, 7238 (2021).
Arnold, T. C., Freeman, C. W., Litt, B. & Stein, J. M. Low-field MRI: clinical promise and challenges. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 57, 25–44 (2023).
Nelson, B. J. An electromagnetic robot for navigating medical devices. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2, 370–371 (2024).
Gervasoni, S. et al. A human-scale clinically ready electromagnetic navigation system for magnetically responsive biomaterials and medical devices. Adv. Mater. 36, e2310701 (2024).
Wang, B. et al. tPA-anchored nanorobots for in vivo arterial recanalization at submillimeter-scale segments. Sci. Adv. 10, eadk8970 (2024).
Wallyn, J., Anton, N., Akram, S. & Vandamme, T. F. Biomedical imaging: principles, technologies, clinical aspects, contrast agents, limitations and future trends in nanomedicines. Pharm. Res. 36, 78 (2019).
Bozuyuk, U., Ozturk, H. & Sitti, M. Microrobotic locomotion in blood vessels: a computational study on the performance of surface microrollers in the cardiovascular system. Adv. Intell. Syst. 5, 2300099 (2023).
Bozuyuk, U. et al. Reduced rotational flows enable the translation of surface-rolling microrobots in confined spaces. Nat. Commun. 13, 6289 (2022).
Thangaraju, P. & Varthya, S. B. in Medical Device Guidelines and Regulations Handbook (eds Shanmugam, P. S. T. et al.) 163–187 (Springer, 2022).
Darrow, J. J., Avorn, J. & Kesselheim, A. S. FDA regulation and approval of medical devices: 1976–2020. JAMA 326, 420–432 (2021).
Dreyfus, R. et al. Dexterous helical magnetic robot for improved endovascular access. Sci. Robot. 9, eadh0298 (2024).
Yan, X. et al. Multifunctional biohybrid magnetite microrobots for imaging-guided therapy. Sci. Robot. 2, eaaq1155 (2017).
Lunney, J. K. et al. Importance of the pig as a human biomedical model. Sci. Transl Med. 13, eabd5758 (2021).
Chowdhury, A. M. M. B., Abbasi, S. A., Gharamaleki, N. L., Kim, J.-Y. & Choi, H. Virtual reality‐enabled intuitive magnetic manipulation of microrobots and nanoparticles. Adv. Intell. Syst. 6, 2300793 (2024).
Zhang, H. et al. Dual-responsive biohybrid neutrobots for active target delivery. Sci. Robot. 6, eaaz9519 (2021).
Marshall, L. J., Bailey, J., Cassotta, M., Herrmann, K. & Pistollato, F. Poor translatability of biomedical research using animals — a narrative review. Altern. Lab. Anim. 51, 102–135 (2023).
Van Norman, G. A. Limitations of animal studies for predicting toxicity in clinical trials. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 4, 845–854 (2019).
Younis, M. A., Tawfeek, H. M., Abdellatif, A. A. H., Abdel-Aleem, J. A. & Harashima, H. Clinical translation of nanomedicines: challenges, opportunities, and keys. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 181, 114083 (2022).
Kuhlman, B. et al. Design of a novel globular protein fold with atomic-level accuracy. Science 302, 1364–1368 (2003).
Medany, M., Mukkavilli, S. K. & Ahmed, D. AI-driven autonomous microrobots for targeted medicine. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2, 914–915 (2024).
Tiryaki, M. E., Demir, S. O. & Sitti, M. Deep learning-based 3D magnetic microrobot tracking using 2D MR images. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 7, 6982–6989 (2022).
Demir, S. O. et al. Task space adaptation via the learning of gait controllers of magnetic soft millirobots. Int. J. Rob. Res. 40, 1331–1351 (2021).
Zhou, Y. & Han, Y. Engineered bacteria as drug delivery vehicles: principles and prospects. Eng. Microbiol. 2, 100034 (2022).
Liu, L. et al. Cell membrane coating integrity affects the internalization mechanism of biomimetic nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 12, 1–12 (2021).
World Health Organization. Handbook: Good Laboratory Practice (GLP): Quality Practices for Regulated Non-Clinical Research and Development (WHO, 2010).
Hegyi, P., Erőss, B., Izbéki, F., Párniczky, A. & Szentesi, A. Accelerating the translational medicine cycle: the Academia Europaea pilot. Nat. Med. 27, 1317–1319 (2021).
Martin, L., Hutchens, M., Hawkins, C. & Radnov, A. How much do clinical trials cost? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 16, 381–382 (2017).
McNamee, L. M., Walsh, M. J. & Ledley, F. D. Timelines of translational science: from technology initiation to FDA approval. PLoS ONE 12, e0177371 (2017).
Nozdriukhin, D. et al. Multifunctional microflowers for precise optoacoustic localization and intravascular magnetic actuation in vivo. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 14, e2404242 (2025).
Law, J. et al. Microrobotic swarms for selective embolization. Sci. Adv. 8, eabm5752 (2022).
Renaudin, N. et al. Functional ultrasound localization microscopy reveals brain-wide neurovascular activity on a microscopic scale. Nat. Methods 19, 1004–1012 (2022).
Zhou, Q. et al. Three-dimensional wide-field fluorescence microscopy for transcranial mapping of cortical microcirculation. Nat. Commun. 13, 7969 (2022).
Deán-Ben, X. L. et al. Deep optoacoustic localization microangiography of ischemic stroke in mice. Nat. Commun. 14, 3584 (2023).
Jeong, S. et al. Penetration of an artificial arterial thromboembolism in a live animal using an intravascular therapeutic microrobot system. Med. Eng. Phys. 38, 403–410 (2016).
Yan, Y. et al. Programming structural and magnetic anisotropy for tailored interaction and control of soft microrobots. Commun. Eng. 3, 1–11 (2024).
Cui, J. et al. Nanomagnetic encoding of shape-morphing micromachines. Nature 575, 164–168 (2019).
Ren, Z. et al. Soft-bodied adaptive multimodal locomotion strategies in fluid-filled confined spaces. Sci. Adv. 7, eabh2022 (2021).
Hu, W., Lum, G. Z., Mastrangeli, M. & Sitti, M. Small-scale soft-bodied robot with multimodal locomotion. Nature 554, 81–85 (2018).
Guo, Y., Zhang, J., Hu, W., Khan, M. T. A. & Sitti, M. Shape-programmable liquid crystal elastomer structures with arbitrary three-dimensional director fields and geometries. Nat. Commun. 12, 5936 (2021).
Zhang, J., Guo, Y., Hu, W. & Sitti, M. Wirelessly actuated thermo- and magneto-responsive soft bimorph materials with programmable shape-morphing. Adv. Mater. 33, 2100336 (2021).
Zhang, J. et al. Liquid crystal elastomer-based magnetic composite films for reconfigurable shape-morphing soft miniature machines. Adv. Mater. 33, e2006191 (2021).
Alapan, Y., Karacakol, A. C., Guzelhan, S. N., Isik, I. & Sitti, M. Reprogrammable shape morphing of magnetic soft machines. Sci. Adv. 6, eabc6414 (2020).
Gu, H. et al. Self-folding soft-robotic chains with reconfigurable shapes and functionalities. Nat. Commun. 14, 1263 (2023).
Jin, Q., Yang, Y., Jackson, J. A., Yoon, C. & Gracias, D. H. Untethered single cell grippers for active biopsy. Nano Lett. 20, 5383–5390 (2020).
Yu, Y. et al. Microfluidic lithography of bioinspired helical micromotors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 12127–12131 (2017).
Wang, J. et al. Microfluidic generation of porous microcarriers for three-dimensional cell culture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 27035–27039 (2015).
Ceylan, H., Yasa, I. C. & Sitti, M. 3D chemical patterning of micromaterials for encoded functionality. Adv. Mater. 29, 1605072 (2017).
Park, J., Jin, C., Lee, S., Kim, J.-Y. & Choi, H. Magnetically actuated degradable microrobots for actively controlled drug release and hyperthermia therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 8, e1900213 (2019).
Hu, X. et al. Magnetic soft micromachines made of linked microactuator networks. Sci. Adv. 7, eabe8436 (2021).
Hortelao, A. C. et al. Swarming behavior and in vivo monitoring of enzymatic nanomotors within the bladder. Sci. Robot. 6, eabd2823 (2021).
Ahmad, B., Chambon, H., Tissier, P. & Bolopion, A. Laser actuated microgripper using optimized chevron-shaped actuator. Micromachines 12, 1487 (2021).
Bakenecker, A. C. et al. Navigation of a magnetic micro-robot through a cerebral aneurysm phantom with magnetic particle imaging. Sci. Rep. 11, 14082 (2021).
Sadeghi-Tarakameh, A. et al. In vivo human head MRI at 10.5 T: a radiofrequency safety study and preliminary imaging results. Magn. Reson. Med. 84, 484–496 (2020).
Jung, K. O. et al. Whole-body tracking of single cells via positron emission tomography. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 4, 835–844 (2020).
Pirmoazen, A. M. et al. Diagnostic performance of 9 quantitative ultrasound parameters for detection and classification of hepatic steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Invest. Radiol. 57, 23–32 (2022).
Ivankovic, I. et al. Multispectral optoacoustic tomography enables in vivo anatomical and functional assessment of human tendons. Adv. Sci. 11, e2308336 (2024).
Levy, J. et al. High-frequency ultrasound in clinical dermatology: a review. Ultrasound J. 13, 24 (2021).
Wong, M. D., Spring, S. & Henkelman, R. M. Structural stabilization of tissue for embryo phenotyping using micro-CT with iodine staining. PLoS ONE 8, e84321 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge grant support from the Swiss National Science Foundation (310030_192757), US National Institutes of Health (RF1-NS126102), Innosuisse — Swiss Innovation Agency (51767.1 IP-LS), Swiss Cancer Research (KFS-5234-02-2021), Personalized Health and Related Technologies of the ETH Domain (PHRT-582), EU Joint Programme — Neurodegenerative Disease Research (JPND022-083), European Horizon RIA Digital and Emerging Technologies (101135053), European Horizon MSCA Doctoral Networks (101119924) and European Research Council (ERC) Advanced Grant SoMMoR project (grant no. 834531). P.W. and E.R. thank the Max Planck and ETH Center for Learning Systems (CLS) for financial support. The authors thank V.E. Fulford from Alar Illustration for her scientific illustrations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to all aspects of the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Materials thanks Wei Gao and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wrede, P., Remlova, E., Chen, Y. et al. Synergistic integration of materials in medical microrobots for advanced imaging and actuation. Nat Rev Mater (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-025-00811-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41578-025-00811-4