Abstract
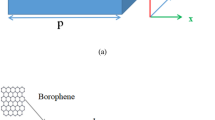
A tunable and switchable plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) effect in the near-infrared region (NIR) is achieved in a borophene-based metasurface, which consists of a periodic array of parallel double-layer borophene nanoribbons (BNRs). The upper- and lower-layer BNRs fulfill two plasmonic bright modes exciting and coupling for PIT phenomenon generation. By changing borophene electron density, the PIT window can be not only tuned to varying resonance frequency, but also adjusted for switching modulation. The calculation results reveal that as the electron density increases from 2.4 × 1019 to 5.6 × 1019 m−2, the PIT resonance frequency correspondingly shifts from 150 to 220 THz, and a maximum amplitude modulation depth (MD) of the PIT window reaches 98.3% at 193.55 THz (\(\lambda =1.55\;\mu \mathrm{m}\)). Moreover, the slow light characteristics of the proposed metasurface are analyzed in detail using the well-controlled group delay. Such a switchable and broadband tunable metadevice can expand the applications for PIT effect in active slow light, plasmonic sensing, and optical modulator areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data Availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available in the present article.
References
Boiler KJ, Imamoglu A, Harris SE (1991) Observation of electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys Rev Lett 66(20):2593–2596
Hau LV, Harris SE, Dutton Z, Behroozi CH (1999) Light speed reduction to 17 metres per second in an ultracold atomic gas. Nature 397(6720):594–598
Kash MM, Sautenkov VA, Zibrov AS, Hollberg L, Welch GR, Lukin MD, Rostovtsev Y, Fry ES, Scully MO (1999) Ultraslow group velocity and enhanced nonlinear optical effects in a coherently driven hot atomic gas. Phys Rev Lett 82(26):5229–5232
Fleischhauer M, Imamoglu A, Marangos JP (2005) Electromagnetically induced transparency: optics in coherent media. Rev Mod Phys 77(2):633–673
Liu CE, Dutton Z, Behroozi CH, Hau LV (2001) Observation of coherent optical information storage in an atomic medium using halted light pulses. Nature 409(6819):490–493
Liu YC, Li BB, Xiao YF (2017) Electromagnetically induced transparency in optical microcavities. Nanophotonics-Berlin 6(5):789–811
Alzar C, Martinez M, Nussenzveig P (2002) Classical analog of electromagnetically induced transparency. Am J Phys 70(1):37–41
Chen Y, Zhu K, Li Y, Fang Y, Wu Q, Sun Y, Chen H (2017) Nonlinear properties of photonic crystal cavity with embedded electromagnetic-induced-transparency-like meta-atoms. Opt Mater Express 7(8):3034
Zhang S, Genov DA, Wang YU, Liu M, Zhang X (2008) Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys Rev Lett 101(4):047401
Liu N, Langguth L, Weiss T, Kästel J, Fleischhauer M, Pfau T, Giessen H (2009) Plasmonic analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency at the Drude damping limit. Nat Mater 8(9):758–762
Liu N, Weiss T, Mesch M, Langguth L, Eigenthaler U, Hirscher M, Sönnichsen C, Giessen H (2010) Planar metamaterial analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency for plasmonic sensing. Nano Lett 10(4):1103–1107
Fan YC, Qiao T, Zhang FL, Fu QH, Dong JJ, Kong BT, Li HQ (2017) An electromagnetic modulator based on electrically controllable metamaterial analogue to electromagnetically induced transparency. Sci Rep 7(1):40441
Ren K, Zhang Y, Ren XB, He YM, Han Q (2021) Polarization-sensitive and active controllable electromagnetically induced transparency in U-shaped terahertz metamaterials. Front Optoelectron 14(2):221–228
Jin XR, Park J, Zheng HY, Lee S, Lee Y, Rhee JY, Kim KW, Cheong HS, Jang WH (2011) Highly-dispersive transparency at optical frequencies in planar metamaterials based on two-bright-mode coupling. Opt Express 19(22):21652–21657
Manjappa M, Turaga SP, Srivastava YK, Bettiol AA, Singh R (2017) Magnetic annihilation of the dark mode in a strongly coupled bright-dark terahertz metamaterial. Opt Lett 42(11):2106–2109
Wang ZF, Fu JH, Zeng QS, Song MX, Denidni TA (2019) High-transmittance absorptive structure based on effect of electromagnetically induced transparency. Ieee Antenn Wirel Pr 18(12):2463–2467
Wan ML, Zhai WQ, Song YL, Li Y, Ji PF, Zhou FQ (2015) Actively controllable EIT-like resonance between localized and propagating surface plasmons for optical switching. J Mod Optic 62(15):1264–1269
Zhang L, Dong ZG, Wang YM, Liu YJ, Zhang S, Kwang J, Yang W, Qiu CW (2018) Polarization-controlled dynamically switchable plasmon-induced transparency in plasmonic metamaterial. Nanoscale 1(41):19517–19523
Xu Q, Su XQ, Ouyang CM, Xu NN, Cao W, Zhang YP, Li Q, Hu C, Gu JQ, Tian Z (2016) Frequency-agile electromagnetically induced transparency analogue in terahertz metamaterials. Opt Lett 41(19):4562–4565
Yahiaoui R, Manjappa M, Srivastava YK, Singh R (2017) Active control and switching of broadband electromagnetically induced transparency in symmetric metadevices. Appl Phys Lett 111(2):021101
Mao LB, Li Y, Li GX, Zhang S, Cao T (2020) Reversible switching of electromagnetically induced transparency in phase change metasurfaces. Adv Photonics 2(5):056004–056004
Li C, Zhu W, Liu Z, Pan RH, Hu S, Du S, Li JJ, Gu CZ (2020) Independent tuning of bright and dark meta-atoms with phase change materials on EIT metasurfaces. Nanoscale 12(18):165–171
Wang DC, Sun S, Feng Z (2020) Enabling switchable and multifunctional terahertz metasurfaces with phase-change material. Opt Mater Express 10(9):2054
Xiao SY, Wang T, Liu TT, Yan XC, Li Z, Xu C (2018) Active modulation of electromagnetically induced transparency analogue in terahertz hybrid metal-graphene metamaterials. Carbon 126:271–278
Shu C, Chen QG, Mei JS, Yin JH (2019) Analogue of tunable electromagnetically induced transparency in terahertz metal-graphene metamaterial. Mater Res Express 6(5):55808
Jia ZP, Huang L, Su JB, Tang B (2021) Tunable electromagnetically induced transparency-like in graphene metasurfaces and its application as a refractive index sensor. J Lightwave Technol 39(5):1544–1549
Xiao BG, Tong SJ, Fyffe A, Shi ZM (2020) Tunable electromagnetically induced transparency based on graphene metamaterials. Opt Express 28(3):4048
Jia ZP, Huang L, Su JB, Tang B (2020) Tunable plasmon-induced transparency based on monolayer black phosphorus by bright-dark mode coupling. Appl Phys Express 13(7):72006
Lian C, Hu SQ, Zhang J, Cheng C, Yuan Z, Gao SW, Meng S (2020) Integrated plasmonics: broadband Dirac plasmons in borophene. Phys Rev Lett 125(11):116802
Dereshgi SA, Liu ZZ, Aydin K (2020) Anisotropic localized surface plasmons in borophene. Opt Express 28(11):16725
Ruan QY, Wang LQ, Bets KV, Yakobson BI (2021) Step-edge epitaxy for borophene growth on insulators. ACS Nano 15(11):18347–18353
Feng BJ, Zhang J, Zhong Q, Li WB, Li S, Li H, Cheng P, Meng S, Chen L, Wu KH (2016) Experimental realization of two-dimensional boron sheets. Nat Chem 8(6):563–568
Zhang CH, Zhang ZZ, Yan WJ, Qin XM (2021) Effect of doping on the photoelectric properties of borophene. Adv Cond Matter Phys 2021:1–7
Zhang JJ, Zhang ZJ, Song XX, Zhang HT, Yang JB (2021) Infrared plasmonic sensing with anisotropic two-dimensional material borophene. Nanomaterials-Basel 11(5):1165
Nong JP, Feng F, Gan JA, Min CJ, Yuan XC, Somekh M (2022) Active modulation of graphene near-infrared electroabsorption employing borophene plasmons in a wide waveband. Adv Opt Mater 10(6):2102131
Nong J, Wei W, Wang W, Lan G, Shang Z, Yi J, Tang L (2018) Strong coherent coupling between graphene surface plasmons and anisotropic black phosphorus localized surface plasmons. Opt Express 26(2):1633
Sensale-Rodriguez B, Yan RS, Kelly MM, Fang T, Tahy K, Hwang WS, Jena D, Liu L, Xing HG (2012) Broadband graphene terahertz modulators enabled by intraband transitions. Nat Commun 3(1):780
Kafaie Shirmanesh G, Sokhoyan R, Pala RA, Atwater HA (2018) Dual-gated active metasurface at 1550 nm with wide (>300°) phase tunability. Nano Lett 18(5):2957–2963
Sabri R, Forouzmand A, Mosallaei H (2020) Multi-wavelength voltage-coded metasurface based on indium tin oxide: independently and dynamically controllable near-infrared multi-channels. Opt Express 28(3):3464
Sabri R, Mosallaei H (2022) Inverse design of perimeter-controlled InAs-assisted metasurface for two-dimensional dynamic beam steering. Nanophotonics 11(20):4515–4530
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12004080, 61705046) and Science and Technology Project of Guangzhou (202201010540).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.Z.: model design, investigation, methodology, and writing—revision and editing. A.W.: data curation, software handling, and original draft writing. K.X.: validation and data analysis. X.H.: conceptualization, comment, and revision. H.J. and W. Z.: reviewing, editing, and supervision. All authors read and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Wu, A., Xiao, K. et al. Dual-controllable Plasmon-induced Transparency Based on Active Borophene Metasurface in the Near-infrared Region. Plasmonics 18, 761–768 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01801-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-023-01801-4