Abstract
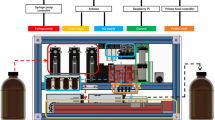
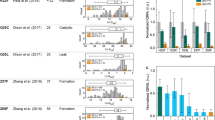
The oligonucleotide microarray, a high-throughput polymorphism detection technology, holds great promise for the characterization of complex genetic variance. To achieve greater sensitivity and specificity for it to be an effective platform technology we present results and discuss some of the factors influencing signal intensities and single-mismatch discrimination in array-based mutation/SNP detection. Probes with a series of concentrations were spotted onto the slide in order to find the optimal concentration with the identifiable satisfying signals and the stable ratios between matched and mismatched probes. It was found that under our experimental conditions, when the initial probe concentration is higher than the maximum immobilization capability of the slide (7.5 µM), the hybridization signal will be saturated and the ratio between matched and mismatched probes will be more stable than at a lower probe concentration. Considering the cost of probes and the systematic stability, a constant spotting concentration of 10 µM was selected. The stability of different types of mismatched oligo-DNA duplexes on the glass surface was also confirmed. The results show that the order of stability of mismatched oligo-DNA duplexes on a glass surface is in general agreement with previous reports conducted using liquid and polyacrylamide gel pads. This suggests that the influence of the mismatched base pair on the stability of the duplex in a solid hybridization system is similar to that in the solution hybridization environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Li, Y., Fu, X. et al. Analysis of the factors affecting the accuracy of detection for single base alterations by oligonucleotide microarray. Exp Mol Med 37, 71–77 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.10
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2005.10