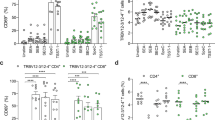
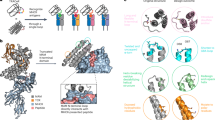
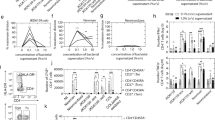
Abstract
Bacterial superantigens are small proteins that have a very potent stimulatory effect on T lymphocytes through their ability to bind to both MHC class II molecules and T-cell receptors. We have determined the three-dimensional structure of a Streptococcal superantigen, SPE-C, at 2.4 Å resolution. The structure shows that SPE-C has the usual superantigen fold, but that the surface that forms a generic, low-affinity MHC-binding site in other superantigens is here used to create a SPE-C dimer. Instead, MHC class II binding occurs through a zinc binding site that is analogous to a similar site in staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Consideration of the SPE-C dimer suggests a novel mechanism for promotion of MHC aggregation and T-cell activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
209,00 € per year
only 17,42 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Germain, R.M. & Margulies, D.H. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 11, 403–450 (1993).
Marrack, P. & Kappler, J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science 248, 705–711 (1990).
Herman, A., Kappler, J.W., Marrack, P. & Pullen, A.M. Superantigens: mechanism of T-cell stimulation and role in immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 9, 745–772 (1991).
Fraser, J.D. High affinity binding of staphylococcal enterotoxins A and B to HLA-DR. Nature 339, 221–223 (1989).
Mollick, J.A., Cook, R.G. & Rich, R.R. Class II MHC molecules are specific receptors for staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Science 244, 817–820 (1989).
White, J. et al. The Vβ-specific superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: stimulation of mature T cells and clonal deletion in neonatal mice. Cell 56, 27–35 (1989).
Kappler, J. et al. Vβ-specific stimulation of human T cells by staphylococcal toxins. Science 244, 811–813 (1989).
Choi, Y.W. et al. Residues of the variable region of the T-cell receptor beta-chain that interact with S. aureus toxin superantigens. Nature 346, 471–473 (1990).
Bohach, G.A., Fast, D.J., Nelson, R.D. & Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins involved in toxic shock syndrome and related illness. Crit. Rev. Microbiol 17, 251–272 (1990).
Kotzin, B.L., Leung, D.Y., Kappler, J. & Marrack, P. Superantigens and their potential role in human disease. Adv. Immunol. 54, 99–166 (1990).
Schad, E.M. et al. Crystal structure of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin type A. EMBO J. 14, 3292–3301 (1995).
Swaminathan, S., Furey, W., Pletcher, J. & Sax, M. Crystal structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin B, a superantigen. Nature 359, 801–806 (1992).
Papageorgiou, A.C. et al. Crystal structure of the superantigen enterotoxin C2 from Staphylococcus aureus reveals a zinc-binding site. Structure, 3, 769–779 (1995).
Swaminathan, S., Furey, W., Pletcher, J. & Sax, M. Residues defining Vβ specificity in staphylococcal enterotoxins. Nature Struct. Biol. 2, 680–686 (1995).
Acharya, K.R. et al. Structural basis of superantigen action inferred from crystal structure of toxic-shock syndrome toxin-1. Nature 367, 94–97 (1994).
Prasad, G.S. et al. Structure of toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. Biochemistry 32, 13761–13766 (1993).
Jardetzky, T.S. et al. Three-dimensional structure of a human class II histocompatibility molecule complexed with superantigen. Nature 368, 711–718 (1994).
Kirn, J., Urban, R.G., Strominger, J.L. & Wiley, D.C. Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 complexed with a class II major histocompatibility molecule HLA-DR1. Science 266, 1870–1874 (1994).
Fraser, J.D., Urban, R.G., Strominger, J.L. & Robinson, H. Zinc regulates the function of two superantigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5507–5511 (1992).
Hudson, K.R. et al. Staphylococcal enterotoxin A has two cooperative binding sites on major histocompatibility complex class-II. J. Exp. Med. 189, 711–720 (1995).
Goshorn, S.C. & Schlievert, P.M. Nucleotide sequence of streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin type C. Infect. Immun. 56, 2518–2520 (1988).
Li, P-L., Teidemann, R.E., Moffat, S.L. & Fraser, J.D. The superantigen streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin C (SPE-C) exhibits a novel mode of action, J. Exp. Med., in the press.
Sundström, M. et al. The crystal structure of staphylococcal enterotoxin type D revealsZn2+-mediated homodimerisation. EMBO J. 15, 6832–6840 (1996).
Laskowski, R.A., MacArthur, M.W., Moss, D.S. & Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 26, 283–291 (1993).
Overington, J.P. Comparison of the three-dimensional structures of homologous proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct Biol. 2, 394–401 (1992).
Vallee, B.L. & Auld, D.S. Zinc coordination, function and structure of zinc enzymes and other proteins. Biochemistry 29, 5647–5659 (1990).
Jones, S. & Thornton, J.M. Protein-protein interactions — a review of protein dimer interactions. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 63, 31–65 (1995).
Wilson, I.A. & Stanfield, R.L. Antibody-antigen interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 3, 113–118 (1993).
Kappler, J.W., Herman, A., Clements, J. & Marrack, P. Mutations defining functional regions of the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J. Exp. Med. 175, 387–396 (1992).
Abrahmsen, L. et al. Characterisation of two distinct MHC class II binding sites in the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A. EMBO J. 14, 2978–2986 (1995).
Ulrich, R.G., Bavari, S. & Olson, M.A. Staphylococcal enterotoxins A and B share a common structural motif for binding class II major histocompatibility complex molecules. Nature Struct. Biol. 2, 554–560 (1995).
Fraser, J.D., Lowe, S., Irwin, M.J., Gascoigne, N.R. & Hudson, K.R. Structural model of staphylococcal enterotoxin A interaction with MHC class II antigens. In Superantigens: A pathogen's view of the immune system 7 (eds Huber, B.T. & Palmer, E.) 7–29 (Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York; 1993).
Herman, A. et al. Identification of the staphylococcal enterotoxin A superantigen binding site in the beta 1 ___domain of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 9954–9958 (1991).
Karp, D.R. & Long, E.O. Identification of HLA-DR1 beta chain residues critical for binding staphylococcal enterotoxins A and E. J. Exp. Med. 175, 415–424 (1992).
Fields, B.A. et al. Crystal structure of a T-cell receptor β-chain complexed with a superantigen. Nature 384, 188–192 (1996).
Blanco, L., Choi, E.M., Connolly, K., Thompson, M.R. & Bonventre, P.F. Mutants of staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1: mitogenicity and recognition by a neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Infect. Immun. 58, 3020–3028 (1990).
Bonventre, P.F., Heeg, H., Cullen, C.M. & Lian, C-J. Toxicity of recombinant toxic shock syndrome toxin and mutant toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus in a rabbit infection model of toxic shock syndrome. Infect. Immun 61, 793–799 (1993).
Hurley, J.M. et al. Identification of class II major histocompatibility complex and T cell receptor binding sites in the superantigen toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. J. Exp. Med. 181, 2229–2235 (1995).
Tiedemann, R.E. & Fraser, J.D. Cross-linking of MHC class II molecules by staphylococcal enterotoxin A is essential for antigen-presenting cell and T cell activation. J. Immunol. 157, 3958–3966 (1996).
Ullrich, A. & Schlessinger, J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 61, 203–212 (1990).
Sakabe, N. X-ray diffraction data collection system for modern protein crystallography with a Weissenberg camera and an imaging plate using Synchrotron radiation. Nucl. Instr. and Methods in Phys. Res. A303, 448–463 (1991).
Otwinowski, Z. Oscillation data reduction program. In Data Collection and Processing (eds Sawyer, L., Isaacs N. & Bailey, S.) 56–62 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, UK; 1993).
Collaborative Computational Project No.4. The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Cowtan, K. An automated procedure for phase improvement by density modification. Joint CCP4 and ESF-EACBM Newsletter in Protein Crystallography 31, 34–38 (1994).
Brunger, A.T. X-PLOR version 3.1, a system for X-ray crystallography and NMR.(Yale University Press, New Haven, Connecticut; 1992).
Tronrud, D.E. Conjugate-direction minimization: an improved method for refinement of macromolecules. Acta Crystallogr. A48, 912–916 (1992).
Engh, R.A. & Huber, R. Accurate bond and angle parameters for X-ray protein structure refinement. Acta Cryst. A47, 392–400 (1991).
Bernstein, F.C. et al. The Protein Data Bank: a computer based archival file for macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Biol. 112, 535–542 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roussel, A., Anderson, B., Baker, H. et al. Crystal structure of the streptococcal superantigen SPE-C: dimerization and zinc binding suggest a novel mode of interaction with MHC class II molecules. Nat Struct Mol Biol 4, 635–643 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0897-635
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0897-635
This article is cited by
-
Zinc in innate and adaptive tumor immunity
Journal of Translational Medicine (2010)
-
B-Cell Epitopes of Intracellular Autoantigens: Myth and Reality
Molecular Medicine (2000)