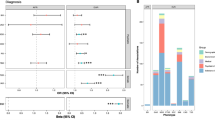
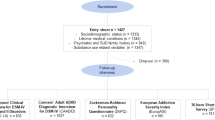
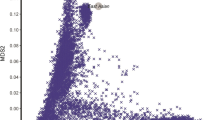
Abstract
This study investigated the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms underlying the comorbidity of five substance dependence diagnoses (SDs; alcohol, AD; cannabis, CaD; cocaine, CoD; opioid, OD; tobacco, TD). A latent class analysis (LCA) was performed on 22,668 individuals from six cohorts to identify comorbid DSM-IV SD patterns. In subsets of this sample, we tested SD-latent classes with respect to polygenic overlap of psychiatric and psychosocial traits in 7659 individuals of European descent and epigenome-wide changes in 886 individuals of African, European, and Admixed-American descents. The LCA identified four latent classes related to SD comorbidities: AD + TD, CoD + TD, AD + CoD + OD + TD (i.e., polysubstance addiction, PSU), and TD. In the epigenome-wide association analysis, SPATA4 cg02833127 was associated with CoD + TD, AD + TD, and PSU latent classes. AD + TD latent class was also associated with CpG sites located on ARID1B, NOTCH1, SERTAD4, and SIN3B, while additional epigenome-wide significant associations with CoD + TD latent class were observed in ANO6 and MOV10 genes. PSU-latent class was also associated with a differentially methylated region in LDB1. We also observed shared polygenic score (PGS) associations for PSU, AD + TD, and CoD + TD latent classes (i.e., attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, anxiety, educational attainment, and schizophrenia PGS). In contrast, TD-latent class was exclusively associated with posttraumatic stress disorder-PGS. Other specific associations were observed for PSU-latent class (subjective wellbeing-PGS and neuroticism-PGS) and AD + TD-latent class (bipolar disorder-PGS). In conclusion, we identified shared and unique genetic and epigenetic mechanisms underlying SD comorbidity patterns. These findings highlight the importance of modeling the co-occurrence of SD diagnoses when investigating the molecular basis of addiction-related traits.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 22,42 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Substance Use & Substance Use Disorders. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/yellowbook/2024/additional-considerations/substance-use. 2024.
Abuse NIoD. Common comorbidities with substance use disorders research report. Bethesda (MD): NCBI; 2020.
Owens PL, Heslin KC, Fingar KR, Weiss AJ. Co-occurrence of physical health conditions and mental health and substance use conditions among adult inpatient stays, 2010 versus 2014. Rockville (MD): Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project (HCUP) Statistical Briefs; 2006.
Stephenson M, Bollepalli S, Cazaly E, Salvatore JE, Barr P, Rose RJ, et al. Associations of alcohol consumption with epigenome-wide DNA methylation and epigenetic age acceleration: individual-level and co-twin comparison analyses. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021;45:318–28.
Montalvo-Ortiz JL, Cheng Z, Kranzler HR, Zhang H, Gelernter J. Genomewide study of epigenetic biomarkers of opioid dependence in European- American women. Sci Rep. 2019;9:4660.
Poisel E, Zillich L, Streit F, Frank J, Friske MM, Foo JC, et al. DNA methylation in cocaine use disorder-An epigenome-wide approach in the human prefrontal cortex. Front Psychiatry. 2023;14:1075250.
Lohoff FW, Roy A, Jung J, Longley M, Rosoff DB, Luo A, et al. Epigenome-wide association study and multi-tissue replication of individuals with alcohol use disorder: evidence for abnormal glucocorticoid signaling pathway gene regulation. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:2224–37.
Kember RL, Hartwell EE, Xu H, Rotenberg J, Almasy L, Zhou H, et al. Phenome-wide association analysis of substance use disorders in a deeply phenotyped sample. Biol Psychiatry. 2023;93:536–45.
Deak JD, Johnson EC. Genetics of substance use disorders: a review. Psychol Med. 2021;51:2189–200.
Gelernter J, Polimanti R. Genetics of substance use disorders in the era of big data. Nat Rev Genet. 2021;22:712–29.
Hatoum AS, Colbert SMC, Johnson EC, Huggett SB, Deak JD, Pathak G, et al. Multivariate genome-wide association meta-analysis of over 1 million subjects identifies loci underlying multiple substance use disorders. Nat Ment Health. 2023;1:210–23.
Schoeler T, Baldwin J, Allegrini A, Barkhuizen W, McQuillin A, Pirastu N, et al. Novel biological insights into the common heritable liability to substance involvement: a multivariate genome-wide association study. Biol Psychiatry. 2023;93:524–35.
Sinha P, Calfee CS, Delucchi KL. Practitioner’s guide to latent class analysis: methodological considerations and common pitfalls. Crit Care Med. 2021;49:e63–e79.
Stiltner B, Pietrzak RH, Tylee DS, Nunez YZ, Adhikari K, Kranzler HR, et al. Polysubstance addiction patterns among 7989 individuals with cocaine use disorder. iScience. 2023;26:107336.
Bonfiglio NS, Portoghese I, Renati R, Mascia ML, Penna MP. Polysubstance use patterns among outpatients undergoing substance use disorder treatment: a latent class analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19:16759.
Park JN, Schneider KE, Fowler D, Sherman SG, Mojtabai R, Nestadt PS. Polysubstance overdose deaths in the fentanyl Era: a latent class analysis. J Addict Med. 2022;16:49–55.
Tryka KA, Hao L, Sturcke A, Jin Y, Wang ZY, Ziyabari L, et al. NCBI’s database of genotypes and phenotypes: dbGaP. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D975–79.
Nagin DS. Group-based modeling of development. Cambridge and London: Harvard University Press; 2005. p. 2012005.
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, Almasy L, Koesterer R, Smith AH, et al. Genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence:significant findings in African- and European-Americans including novel risk loci. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:41–9.
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, Koesterer R, Almasy L, Zhao H, et al. Genome-wide association study of opioid dependence: multiple associations mapped to calcium and potassium pathways. Biol Psychiatry. 2014;76:66–74.
Gelernter J, Kranzler HR, Sherva R, Almasy L, Herman AI, Koesterer R, et al. Genome-wide association study of nicotine dependence in American populations: identification of novel risk loci in both African-Americans and European-Americans. Biol Psychiatry. 2015;77:493–503.
Gelernter J, Sherva R, Koesterer R, Almasy L, Zhao H, Kranzler HR, et al. Genome-wide association study of cocaine dependence and related traits: FAM53B identified as a risk gene. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:717–23.
Sherva R, Wang Q, Kranzler H, Zhao H, Koesterer R, Herman A, et al. Genome-wide association study of cannabis dependence severity, novel risk variants, and shared genetic risks. JAMA Psychiatry. 2016;73:472–80.
Rice JP, Hartz SM, Agrawal A, Almasy L, Bennett S, Breslau N, et al. CHRNB3 is more strongly associated with Fagerstrom test for cigarette dependence-based nicotine dependence than cigarettes per day: phenotype definition changes genome-wide association studies results. Addiction. 2012;107:2019–28.
Nelson EC, Lynskey MT, Heath AC, Wray N, Agrawal A, Shand FL, et al. ANKK1, TTC12, and NCAM1 polymorphisms and heroin dependence: importance of considering drug exposure. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70:325–33.
Bierut LJ, Madden PA, Breslau N, Johnson EO, Hatsukami D, Pomerleau OF, et al. Novel genes identified in a high-density genome wide association study for nicotine dependence. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:24–35.
Pergadia ML, Agrawal A, Heath AC, Martin NG, Bucholz KK, Madden PA. Nicotine withdrawal symptoms in adolescent and adult twins. Twin Res Hum Genet. 2010;13:359–69.
Manichaikul A, Mychaleckyj JC, Rich SS, Daly K, Sale M, Chen WM. Robust relationship inference in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:2867–73.
Linzer DA, Lewis JB. poLCA: an R package for polytomous variable latent class analysis. J Stat Softw. 2011;42:1–29.
Finch WH, Bronk KC. Conducting confirmatory latent class analysis using mplus. Struct Equ Modeling. 2011;18:132–51.
Wendt FR, Pathak GA, Vahey J, Qin X, Koller D, Cabrera-Mendoza B, et al. Modeling the longitudinal changes of ancestry diversity in the million veteran program. Hum Genomics. 2023;17:46.
Das S, Forer L, Schonherr S, Sidore C, Locke AE, Kwong A, et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat Genet. 2016;48:1284–7.
Teschendorff AE, Marabita F, Lechner M, Bartlett T, Tegner J, Gomez-Cabrero D, et al. A beta-mixture quantile normalization method for correcting probe design bias in Illumina Infinium 450 k DNA methylation data. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:189–96.
Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Jaffe AE, Storey JD. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:882–3.
Houseman EA, Accomando WP, Koestler DC, Christensen BC, Marsit CJ, Nelson HH, et al. DNA methylation arrays as surrogate measures of cell mixture distribution. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012;13:86.
Bollepalli S, Korhonen T, Kaprio J, Anders S, Ollikainen M. EpiSmokEr: a robust classifier to determine smoking status from DNA methylation data. Epigenomics. 2019;11:1469–86.
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:e47.
Turner SD. qqman: an R package for visualizing GWAS results using Q-Q and manhattan plots. J Open Source Softw. 2018;3:731.
Mägi R, Morris AP. GWAMA: software for genome-wide association meta-analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010;11:288.
Suderman M, Staley JR, French R, Arathimos R, Simpkin A, Tilling K dmrff: identifying differentially methylated regions efficiently with power and control. bioRxiv. 2018:508556.
Battram T, Yousefi P, Crawford G, Prince C, Sheikhali Babaei M, Sharp G, et al. The EWAS catalog: a database of epigenome-wide association studies. Wellcome Open Res. 2022;7:41.
Edgar RD, Jones MJ, Meaney MJ, Turecki G, Kobor MS. BECon: a tool for interpreting DNA methylation findings from blood in the context of brain. Transl Psychiatry. 2017;7:e1187.
Demontis D, Walters GB, Athanasiadis G, Walters R, Therrien K, Nielsen TT, et al. Genome-wide analyses of ADHD identify 27 risk loci, refine the genetic architecture and implicate several cognitive domains. Nat Genet. 2023;55:198–208.
Friligkou E, Lokhammer S, Cabrera-Mendoza B, Shen J, He J, Deiana G, et al. Gene discovery and biological insights into anxiety disorders from a large-scale multi-ancestry genome-wide association study. Nat Genet. 2024;56:2036–45.
Grove J, Ripke S, Als TD, Mattheisen M, Walters RK, Won H, et al. Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nat Genet. 2019;51:431–44.
Mullins N, Forstner AJ, O’Connell KS, Coombes B, Coleman JRI, Qiao Z, et al. Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology. Nat Genet. 2021;53:817–29.
Als TD, Kurki MI, Grove J, Voloudakis G, Therrien K, Tasanko E, et al. Depression pathophysiology, risk prediction of recurrence and comorbid psychiatric disorders using genome-wide analyses. Nat Med. 2023;29:1832–44.
Okbay A, Wu Y, Wang N, Jayashankar H, Bennett M, Nehzati SM, et al. Polygenic prediction of educational attainment within and between families from genome-wide association analyses in 3 million individuals. Nat Genet. 2022;54:437–49.
Kim Y, Saunders GRB, Giannelis A, Willoughby EA, DeYoung CG, Lee JJ. Genetic and neural bases of the neuroticism general factor. Biol Psychol. 2023;184:108692.
Nievergelt CM, Maihofer AX, Atkinson EG, Chen CY, Choi KW, Coleman JRI, et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 95 risk loci and provide insights into the neurobiology of post-traumatic stress disorder. Nat Genet. 2024;56:792–808.
Trubetskoy V, Pardinas AF, Qi T, Panagiotaropoulou G, Awasthi S, Bigdeli TB, et al. Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in schizophrenia. Nature. 2022;604:502–8.
Okbay A, Baselmans BM, De Neve JE, Turley P, Nivard MG, Fontana MA, et al. Genetic variants associated with subjective well-being, depressive symptoms, and neuroticism identified through genome-wide analyses. Nat Genet. 2016;48:624–33.
Ge T, Chen C-Y, Ni Y, Feng Y-CA, Smoller JW. Polygenic prediction via bayesian regression and continuous shrinkage priors. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1776.
Balduzzi S, Rucker G, Schwarzer G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: a practical tutorial. Evid Based Ment Health. 2019;22:153–60.
Kalman D, Morissette SB, George TP. Co-morbidity of smoking in patients with psychiatric and substance use disorders. Am J Addict. 2005;14:106–23.
Bailey AJ, McHugh RK. Why do we focus on the exception and not the rule? Examining the prevalence of mono- versus polysubstance use in the general population. Addiction. 2023;118:2026–9.
Hatoum AS, Johnson EC, Colbert SMC, Polimanti R, Zhou H, Walters RK, et al. The addiction risk factor: a unitary genetic vulnerability characterizes substance use disorders and their associations with common correlates. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022;47:1739–45.
Patrick ME, Berglund PA, Joshi S, Bray BC. A latent class analysis of heavy substance use in young adulthood and impacts on physical, cognitive, and mental health outcomes in middle age. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020;212:108018.
Schepis TS, McCabe SE. The latent class structure of substance use in US adults 50 years and older. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2021;36:1867–77.
Agrawal A, Lynskey MT, Madden PA, Bucholz KK, Heath AC. A latent class analysis of illicit drug abuse/dependence: results from the national epidemiological survey on alcohol and related conditions. Addiction. 2007;102:94–104.
Chan G, Connor J, Hall W, Leung J. The changing patterns and correlates of population-level polysubstance use in Australian youth: a multi-group latent class analysis of nationally representative samples spanning 12 years. Addiction. 2020;115:145–55.
Rodriguez AS, Robinson LD, Kelly PJ, Hudson S. Polysubstance use classes and health outcomes among women attending specialist substance use treatment services. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2022;41:488–500.
Mulder RH, Neumann A, Cecil CAM, Walton E, Houtepen LC, Simpkin AJ, et al. Epigenome-wide change and variation in DNA methylation in childhood: trajectories from birth to late adolescence. Hum Mol Genet. 2021;30:119–34.
Li Z, Xu K, Zhao S, Guo Y, Chen H, Ni J, et al. SPATA4 improves aging-induced metabolic dysfunction through promotion of preadipocyte differentiation and adipose tissue expansion. Aging Cell. 2021;20:e13282.
Islam SA, Goodman SJ, MacIsaac JL, Obradovic J, Barr RG, Boyce WT, et al. Integration of DNA methylation patterns and genetic variation in human pediatric tissues help inform EWAS design and interpretation. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2019;12:1.
Spiers H, Hannon E, Schalkwyk LC, Smith R, Wong CC, O’Donovan MC, et al. Methylomic trajectories across human fetal brain development. Genome Res. 2015;25:338–52.
Inkster AM, Yuan V, Konwar C, Matthews AM, Brown CJ, Robinson WP. A cross-cohort analysis of autosomal DNA methylation sex differences in the term placenta. Biol Sex Differ. 2021;12:38.
Zhang L, Silva TC, Young JI, Gomez L, Schmidt MA, Hamilton-Nelson KL, et al. Epigenome-wide meta-analysis of DNA methylation differences in prefrontal cortex implicates the immune processes in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6114.
Tsai PC, Glastonbury CA, Eliot MN, Bollepalli S, Yet I, Castillo-Fernandez JE, et al. Smoking induces coordinated DNA methylation and gene expression changes in adipose tissue with consequences for metabolic health. Clin Epigenetics. 2018;10:126.
Harper JD, Fan KH, Aslam MM, Snitz BE, DeKosky ST, Lopez OL, et al. Genome-wide association study of incident dementia in a community-based sample of older subjects. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;88:787–98.
He L, Loika Y, Park Y, Genotype Tissue Expression C, Bennett DA, Kellis M, et al. Exome-wide age-of-onset analysis reveals exonic variants in ERN1 and SPPL2C associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11:146.
Lampada A, Taylor V. Notch signaling as a master regulator of adult neurogenesis. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1179011.
Ni T, Zhu L, Wang S, Zhu W, Xue Y, Zhu Y, et al. Medial prefrontal cortex Notch1 signalling mediates methamphetamine-induced psychosis via Hes1-dependent suppression of GABA(B1) receptor expression. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27:4009–22.
Latypova X, Vincent M, Molle A, Adebambo OA, Fourgeux C, Khan TN, et al. Haploinsufficiency of the Sin3/HDAC corepressor complex member SIN3B causes a syndromic intellectual disability/autism spectrum disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 2021;108:929–41.
Moffat JJ, Jung EM, Ka M, Jeon BT, Lee H, Kim WY. Differential roles of ARID1B in excitatory and inhibitory neural progenitors in the developing cortex. Sci Rep. 2021;11:3856.
Zhu G, Liu J, Li Y, Huang H, Chen C, Wu D, et al. ARID1B deficiency leads to impaired DNA damage response and activated cGAS-STING pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer. 2024;15:2601–12.
Carnes MU, Quach BC, Zhou L, Han S, Tao R, Mandal M et al. Smoking-informed methylation and expression QTLs in human brain and colocalization with smoking-associated genetic loci. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024;49:1749–57.
Cardenas A, Ecker S, Fadadu RP, Huen K, Orozco A, McEwen LM, et al. Epigenome-wide association study and epigenetic age acceleration associated with cigarette smoking among Costa Rican adults. Sci Rep. 2022;12:4277.
Mishra PP, Mishra BH, Raitoharju E, Mononen N, Viikari J, Juonala M, et al. Gene set based integrated methylome and transcriptome analysis reveals potential molecular mechanisms linking cigarette smoking and related diseases. OMICS. 2023;27:193–204.
Ponomarev I. Epigenetic control of gene expression in the alcoholic brain. Alcohol Res. 2013;35:69–76.
Dugue PA, Wilson R, Lehne B, Jayasekara H, Wang X, Jung CH, et al. Alcohol consumption is associated with widespread changes in blood DNA methylation: analysis of cross-sectional and longitudinal data. Addict Biol. 2021;26:e12855.
Liu C, Marioni RE, Hedman AK, Pfeiffer L, Tsai PC, Reynolds LM, et al. A DNA methylation biomarker of alcohol consumption. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:422–33.
Skariah G, Seimetz J, Norsworthy M, Lannom MC, Kenny PJ, Elrakhawy M, et al. Mov10 suppresses retroelements and regulates neuronal development and function in the developing brain. BMC Biol. 2017;15:54.
Hofer E, Roshchupkin GV, Adams HHH, Knol MJ, Lin H, Li S, et al. Genetic correlations and genome-wide associations of cortical structure in general population samples of 22,824 adults. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4796.
Grasby KL, Jahanshad N, Painter JN, Colodro-Conde L, Bralten J, Hibar DP, et al. The genetic architecture of the human cerebral cortex. Science. 2020;367:eaay6690.
Towers EB, Shapiro DA, Abel JM, Bakhti-Suroosh A, Kupkova K, Auble DT, et al. Transcriptional profile of exercise-induced protection against relapse to cocaine seeking in a rat model. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2023;3:734–45.
Schreiber R, Ousingsawat J, Wanitchakool P, Sirianant L, Benedetto R, Reiss K, et al. Regulation of TMEM16A/ANO1 and TMEM16F/ANO6 ion currents and phospholipid scrambling by Ca(2+) and plasma membrane lipid. J Physiol. 2018;596:217–29.
Sikdar S, Joehanes R, Joubert BR, Xu CJ, Vives-Usano M, Rezwan FI, et al. Comparison of smoking-related DNA methylation between newborns from prenatal exposure and adults from personal smoking. Epigenomics. 2019;11:1487–1500.
Joehanes R, Just AC, Marioni RE, Pilling LC, Reynolds LM, Mandaviya PR, et al. Epigenetic signatures of cigarette smoking. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2016;9:436–47.
Kinare V, Pal S, Tole S. LDB1 is required for the early development of the dorsal telencephalon and the thalamus. eNeuro. 2019;6:ENEURO.0356-18.2019.
Monahan K, Horta A, Lomvardas S. LHX2- and LDB1-mediated trans interactions regulate olfactory receptor choice. Nature. 2019;565:448–53.
Philibert R, Dogan M, Beach SRH, Mills JA, Long JD. AHRR methylation predicts smoking status and smoking intensity in both saliva and blood DNA. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2020;183:51–60.
Milivojevic V, Sinha R. Central and Peripheral Biomarkers of Stress Response for Addiction Risk and Relapse Vulnerability. Trends Mol Med. 2018;24:173–86.
Levis SC, Baram TZ, Mahler SV. Neurodevelopmental origins of substance use disorders: evidence from animal models of early-life adversity and addiction. Eur J Neurosci. 2022;55:2170–95.
Bart CP, Titone MK, Ng TH, Nusslock R, Alloy LB. Neural reward circuit dysfunction as a risk factor for bipolar spectrum disorders and substance use disorders: a review and integration. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021;87:102035.
Bourgault Z, Rubin-Kahana DS, Hassan AN, Sanches M, Le Foll B. Multiple substance use disorders and self-reported cognitive function in U.S. Adults: associations and sex-differences in a nationally representative sample. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:797578.
Martin AR, Kanai M, Kamatani Y, Okada Y, Neale BM, Daly MJ. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat Genet. 2019;51:584–91.
Alameda L, Trotta G, Quigley H, Rodriguez V, Gadelrab R, Dwir D, et al. Can epigenetics shine a light on the biological pathways underlying major mental disorders? Psychol Med. 2022;52:1645–65.
Shen X, Barbu M, Caramaschi D, Arathimos R, Czamara D, David FS et al. A methylome-wide association study of major depression with out-of-sample case-control classification and trans-ancestry comparison. medRxiv. 2023;2023.10.27.23297630.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, R33 DA047527. GAP acknowledges support from the Yale Biological Sciences Training Program (T32 MH014276), Alzheimer’s Association (AARF-22-967171), NIH National Institute of Aging (K99 AG078503), Yale Franke Fellowship in Science & Humanities, and Yale Women’s Faculty Forum Award. RP acknowledges grants from the National Institute of Mental Health (RF1 MH132337) and One Mind Rising Star Award. JDD acknowledges support from the National Institute on Drug Abuse K01 DA058807. DFL is funded by a Career Development Award from the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development (1IK2BX005058). HK acknowledges support from the Department of Veterans Affairs (VISN 4 MIRECC and I01 BX004820). JLMO acknowledges support from U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs via 1IK2CX002095 and NIDA R21 DA050160. JG reports support from the Department of Veterans Affairs (5IO1CX001849-04 and the VISN 1 New England MIRECC) and NIH/NIDA (R01 DA037974, R01 DA058862).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GAP and RP designed the study. GAP analyzed the data. RHP, CO, FRW, JDD, EF, and GAP supported the data analysis. AL and YZN contributed to generating the Yale-Penn phenotypic and molecular data. JLM, DFL, HRK, JG, and RP supported the collection, assessment, or molecular assays of Yale-Penn cohort. GAP and RP wrote the manuscript. All the other authors provided critical feedback, context interpretation, draft revision, and editing. RP supervised the study and received the primary funding that supported the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
RP received a research grant from Alkermes outside the scope of the present study. RP and JG are paid for their editorial work on the journal Complex Psychiatry. JG and HRK are holders of U.S. patent 10,900,082 titled: “Genotype-guided dosing of opioid agonists,” issued 26 January 2021. HRK is a member of advisory boards for Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, Sophrosyne Pharmaceuticals, Enthion Pharmaceuticals, and Clearmind Medicine; a consultant to Sobrera Pharmaceuticals and Altimmune; the recipient of research funding and medication supplies for an investigator-initiated study from Alkermes; a member of the American Society of Clinical Psychopharmacology’s Alcohol Clinical Trials Initiative, which was supported in the last three years by Alkermes, Dicerna, Ethypharm, Lundbeck, Mitsubishi, Otsuka, and Pear Therapeutics. FRW is an employee of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals with no conflict of interest related to any intellectual property of the company. The other authors have no competing interests to report.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pathak, G.A., Pietrzak, R.H., Lacobelle, A. et al. Epigenetic and genetic profiling of comorbidity patterns among substance dependence diagnoses. Mol Psychiatry (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03031-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03031-y