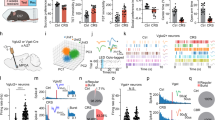
Abstract
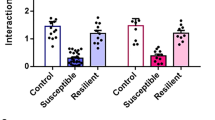
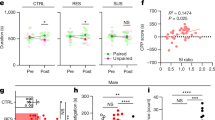
Stress-induced social deficits are related with the malfunction of dentate gyrus (DG). However, the exact molecular mechanism and/or neural circuit of DG participated in social impairments induced by chronic stress is not fully known. Here, we report that the sodium leak channel (NALCN) reduction in the dorsal DG (dDG) but not the ventral DG (vDG) induces social deficits of chronic stress through lowering the excitability and the firings of the glutamatergic neurons. Furthermore, the present study reveals that the medial septum (MS) is an important downstream projection region of dDG glutamatergic neurons involved in the social impairments of chronic stress; and activating the dDG-MS glutamatergic projection significantly relieves these social deficits. In summary, these findings indicate that NALCN in dDG glutamatergic neurons presents a promising molecular target for social deficits of chronic stress via influencing the activity of the dDG glutamatergic neurons (dDGGlu) and their projection to the MS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 22,42 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are presented in the form of graphs and available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Stein MB, Stein DJ. Social anxiety disorder. Lancet. 2008;371:1115–25.
Iozzino L, Harvey PD, Canessa N, Gosek P, Heitzman J, Macis A, et al. Neurocognition and social cognition in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders with and without a history of violence: results of a multinational European study. Transl Psychiatry. 2021;11:620.
Elmer T, Stadtfeld C. Depressive symptoms are associated with social isolation in face-to-face interaction networks. Sci Rep. 2020;10:1444.
DiSabato DJND, Liu X, Witcher KG, O’Neil SM, Oliver B, Bray CE, et al. Interleukin-1 receptor on hippocampal neurons drives social withdrawal and cognitive deficits after chronic social stress. Mol Psychiatry. 2021;26:4770–82.
Liu YDS, Li LX, Zhou ZX, Lv Q, Wang ZY, Wang F, et al. A circuit from dorsal hippocampal CA3 to parvafox nucleus mediates chronic social defeat stress-induced deficits in preference for social novelty. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabe8828.
Sandi C, Haller J. Stress and the social brain: behavioural effects and neurobiological mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2015;16:290–304.
Friedman AKWJ, Juarez B, Ku SM, Chaudhury D, Wang J, Li X, et al. Enhancing depression mechanisms in midbrain dopamine neurons achieves homeostatic resilience. Science. 2014;344:313–9.
Kim J, Lei Y, Lu X-Y, Kim CS. Glucocorticoid-glucocorticoid receptor-HCN1 channels reduce neuronal excitability in dorsal hippocampal CA1 neurons. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27:4035–49.
Donegan ML, Stefanini F, Meira T, Gordon JA, Fusi S, Siegelbaum SA. Coding of social novelty in the hippocampal CA2 region and its disruption and rescue in a 22q11.2 microdeletion mouse model. Nat Neurosci. 2020;23:1365–75.
Wegiel J, Kuchna I, Nowicki K, Imaki H, Wegiel J, Marchi E, et al. The neuropathology of autism: defects of neurogenesis and neuronal migration, and dysplastic changes. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;119:755–70.
Li J, Sun X, You Y, Li Q, Wei C, Zhao L, et al. Auts2 deletion involves in DG hypoplasia and social recognition deficit: the developmental and neural circuit mechanisms. Sci Adv. 2022;8:eabk1238.
van Dijk MTTA, Kashyap P, Desai K, Kelsall NC, Gameroff MJ, Aw N, et al. Dentate gyrus microstructure is associated with resilience after exposure to maternal stress across two human cohorts. Biol Psychiatry. 2024;95:27–36.
Anacker C, Luna VM, Stevens GS, Millette A, Shores R, Jimenez JC, et al. Hippocampal neurogenesis confers stress resilience by inhibiting the ventral dentate gyrus. Nature. 2018;559:98–102.
Snyder JSSA, Brewer M, Pickel J, Cameron HA. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis buffers stress responses and depressive behaviour. Nature. 2011;476:458–61.
Du Preez AOD, Eiben I, Musaelyan K, Egeland M, Zunszain PA, Fernandes C, et al. Chronic stress followed by social isolation promotes depressive-like behaviour, alters microglial and astrocyte biology and reduces hippocampal neurogenesis in male mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2021;91:24–47.
Wang ZNT, Mueller SG, Lenoci M, Truran D, Marmar CR, Weiner MW, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of hippocampal subfields in posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:296–303.
Aoki Y, Nishimura Y, Hondrich T, Nakayama R, Igata H, Sasaki T, et al. Selective attenuation of electrophysiological activity of the dentate gyrus in a social defeat mouse model. J Physiological Sci. 2016;67:507–13.
Deng S-L, Hu Z-L, Mao L, Gao B, Yang Q, Wang F, et al. The effects of Kctd12, an auxiliary subunit of GABAB receptor in dentate gyrus on behavioral response to chronic social defeat stress in mice. Pharmacol Res. 2021;163:105355.
Borzello M, Ramirez S, Treves A, Lee I, Scharfman H, Stark C, et al. Assessments of dentate gyrus function: discoveries and debates. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2023;24:502–17.
Wang C, Liu H, Li K, Wu Z-Z, Wu C, Yu J-Y, et al. Tactile modulation of memory and anxiety requires dentate granule cells along the dorsoventral axis. Nat Commun. 2020;11:6045.
Yeates DCM, Ussling A, Lee ACH, Ito R. Double dissociation of learned approach-avoidance conflict processing and spatial pattern separation along the dorsoventral axis of the dentate gyrus. Hippocampus. 2020;30:596–609.
Zhang T-Y, Keown CL, Wen X, Li J, Vousden DA, Anacker C, et al. Environmental enrichment increases transcriptional and epigenetic differentiation between mouse dorsal and ventral dentate gyrus. Nat Commun. 2018;9:298.
Maaswinkel HBA, Gispen WH, Spruijt BM. Roles of the basolateral amygdala and hippocampus in social recognition in rats. Physiol Behav. 1996;60:55–63.
Doucette E, Merfeld E, Leblanc H, Monasterio A, Cincotta C, Grella SL, et al. Social behavior in mice following chronic optogenetic stimulation of hippocampal engrams. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2020;176:107321.
Raam T, McAvoy KM, Besnard A, Veenema AH, Sahay A. Hippocampal oxytocin receptors are necessary for discrimination of social stimuli. Nat Commun. 2017;8:2001.
Yun S, Reynolds RP, Petrof I, White A, Rivera PD, Segev A, et al. Stimulation of entorhinal cortex–dentate gyrus circuitry is antidepressive. Nat Med. 2018;24:658–66.
Cochet-Bissuel M, Lory P, Monteil A. The sodium leak channel, NALCN, in health and disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:132.
Lu B, Su Y, Das S, Liu J, Xia J, Ren D. The neuronal channel NALCN contributes resting sodium permeability and is required for normal respiratory rhythm. Cell. 2007;129:371–83.
Kschonsak M, Chua HC, Noland CL, Weidling C, Clairfeuille T, Bahlke OØ, et al. Structure of the human sodium leak channel NALCN. Nature. 2020;587:313–8.
Al-Sayed Moeenaldeen D, Al-Zaidan H, Albakheet A, Hakami H, Kenana R, Al-Yafee Y, et al. Mutations in NALCN cause an autosomal-recessive syndrome with severe hypotonia, speech impairment, and cognitive delay. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;93:721–6.
Terracciano A, Tanaka T, Sutin AR, Sanna S, Deiana B, Lai S, et al. Genome-wide association scan of trait depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;68:811–7.
Al-Mazidi S, Al-Ayadhi L, Alqahtany F, Abualnaja A, Alzarroug A, Alharbi T, et al. The possible role of sodium leakage channel localization factor-1 in the pathophysiology and severity of autism spectrum disorders. Sci Rep. 2023;13:9747.
Ghezzi A, Liebeskind BJ, Thompson A, Atkinson NS, Zakon HH. Ancient association between cation leak channels and Mid1 proteins is conserved in fungi and animals. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014;7:15.
Burg ED, Langan ST, Nash HA. Drosophila social clustering is disrupted by anesthetics and in narrow abdomen ion channel mutants. Genes Brain Behav. 2013;12:338–47.
Wang J, Yang Y, Liu J, Qiu J, Zhang D, Ou M, et al. Loss of sodium leak channel (NALCN) in the ventral dentate gyrus impairs neuronal activity of the glutamatergic neurons for inflammation-induced depression in male mice. Brain Behavior Immun. 2023;110:13–29.
Toth I, Neumann ID. Animal models of social avoidance and social fear. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;354:107–18.
Li M, Sun X, Wang Z, Li Y. Caspase-1 affects chronic restraint stress-induced depression-like behaviors by modifying GABAergic dysfunction in the hippocampus. Transl Psychiatry. 2023;13:229.
Brooks SP, Dunnett SB. Tests to assess motor phenotype in mice: a user’s guide. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:519–29.
Rein B, Ma K, Yan Z. A standardized social preference protocol for measuring social deficits in mouse models of autism. Nat Protoc. 2020;15:3464–77.
Cui Y, Yang Y, Ni Z, Dong Y, Cai G, Foncelle A, et al. Astroglial Kir4.1 in the lateral habenula drives neuronal bursts in depression. Nature. 2018;554:323–7.
Zhang D, Zhao W, Liu J, Ou M, Liang P, Li J, et al. Sodium leak channel contributes to neuronal sensitization in neuropathic pain. Prog Neurobiol. 2021;202:102041.
Hagihara H, Toyama K, Yamasaki N, Miyakawa T. Dissection of hippocampal dentate gyrus from adult mouse. J Vis Exp. 2009:1543. https://doi.org/10.3791/1543.
Feng Y, Chang P, Kang Y, Liao P, Li C-y, Liu J, et al. Etomidate-induced myoclonus in sprague-dawley rats involves neocortical glutamate accumulation and N-Methyl-d-Aspartate receptor activity. Anesthesia & Analgesia. 2023;137:221–33.
Wang R, Hu X, Liu S, Wang J, Xiong F, Zhang X, et al. Kaempferol‐3‐O‐sophoroside (PCS‐1) contributes to modulation of depressive‐like behaviour in C57BL/6J mice by activating AMPK. Br J Pharmacol. 2023;181:1182–202.
Ou M, Zhao W, Liu J, Liang P, Huang H, Yu H, et al. The general anesthetic isoflurane bilaterally modulates neuronal excitability. iScience. 2020;23:100760.
Yang Y, Ou M, Liu J, Zhao W, Zhuoma L, Liang Y, et al. Volatile anesthetics activate a leak sodium conductance in retrotrapezoid nucleus neurons to maintain breathing during anesthesia in mice. Anesthesiology. 2020;133:824–38.
Zhu X, Tang H-D, Dong W-Y, Kang F, Liu A, Mao Y, et al. Distinct thalamocortical circuits underlie allodynia induced by tissue injury and by depression-like states. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24:542–53.
Tripathi A, Bartosh A, Whitehead C, Pillai A. Activation of cell-free mtDNA-TLR9 signaling mediates chronic stress-induced social behavior deficits. Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28:3806–15.
Manski CF. Economic Analysis of Social Interactions. J Economic Perspect. 2000;14:115–36.
Monninger M, Aggensteiner P-M, Pollok TM, Reinhard I, Hall ASM, Zillich L, et al. Real-time individual benefit from social interactions before and during the lockdown: the crucial role of personality, neurobiology and genes. Transl Psychiatry. 2022;12:28.
Wersebe H, Lieb R, Meyer AH, Miche M, Mikoteit T, Imboden C, et al. Well-being in major depression and social phobia with and without comorbidity. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2018;18:201–8.
Wittchen HUBE. The impact of social phobia on quality of life. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 1996;11:15–23.
Kheirbek Mazen A, Drew Liam J, Burghardt Nesha S, Costantini Daniel O, Tannenholz L, Ahmari Susanne E, et al. Differential control of learning and anxiety along the dorsoventral axis of the dentate gyrus. Neuron. 2013;77:955–68.
Fanselow MS, Dong HW. Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron. 2010;65:7–19.
Iossifov I, Ronemus M, Levy D, Wang Z, Hakker I, Rosenbaum J, et al. De novo gene disruptions in children on the autistic spectrum. Neuron. 2012;74:285–99.
Bickle JGLY, Millette A, Dixon R, Wu S, Arias EC, Luna VM, et al. 5-HT1A receptors on dentate gyrus granule cells confer stress resilience. Psychiatry Res. 2024;95:800–9.
Levone BR, Codagnone MG, Moloney GM, Nolan YM, Cryan JF, O’ Leary OF. Adult-born neurons from the dorsal, intermediate, and ventral regions of the longitudinal axis of the hippocampus exhibit differential sensitivity to glucocorticoids. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;26:3240–52.
Seo D-o, Zhang ET, Piantadosi SC, Marcus DJ, Motard LE, Kan BK, et al. A locus coeruleus to dentate gyrus noradrenergic circuit modulates aversive contextual processing. Neuron. 2021;109:2116–2130.e2116.
Ngodup T, Irie T, Elkins SP, Trussell LO. The Na+ leak channel NALCN controls spontaneous activity and mediates synaptic modulation by α2-adrenergic receptors in auditory neurons. Elife. 2024;12:RP89520.
Kesner RP. An analysis of dentate gyrus function (an update). Behavioural Brain Res. 2018;354:84–91.
Zou D, Chen L, Deng D, Jiang D, Dong F, McSweeney C, et al. DREADD in Parvalbumin Interneurons of the Dentate Gyrus modulates anxiety social interaction and memory extinction. Curr Mol Med. 2016;16:91–102.
Király B, Domonkos A, Jelitai M, Lopes-dos-Santos V, Martínez-Bellver S, Kocsis B, et al. The medial septum controls hippocampal supra-theta oscillations. Nat Commun. 2023;14:6159.
Banker SM, Gu X, Schiller D, Foss-Feig JH. Hippocampal contributions to social and cognitive deficits in autism spectrum disorder. Trends Neurosci. 2021;44:793–807.
Griguoli M, Pimpinella D. Medial septum: relevance for social memory. Front Neural Circuits. 2022;16:965172.
Wu X, Morishita W, Beier KT, Heifets BD, Malenka RC. 5-HT modulation of a medial septal circuit tunes social memory stability. Nature. 2021;599:96–101.
Pimpinella DMV, Giorgi C, Coemans S, Lecca S, Lalive AL, Ostermann H, et al. Septal cholinergic input to CA2 hippocampal region controls social novelty discrimination via nicotinic receptor- mediated disinhibition. eLife. 2021;10:e65580.
Freund TF, Antal M. GABA-containing neurons in the septum control inhibitory interneurons in the hippocampus. Nature. 1988;336:170–3.
Li HH, Liu Y, Chen HS, Wang J, Li YK, Zhao Y, et al. PDGF‐BB‐dependent neurogenesis buffers depressive‐like behaviors by inhibition of GABAergic projection from medial septum to dentate gyrus. Adv Sci. 2023;10:e2301110.
Kohara K, Pignatelli M, Rivest AJ, Jung H-Y, Kitamura T, Suh J, et al. Cell type–specific genetic and optogenetic tools reveal hippocampal CA2 circuits. Nat Neurosci. 2013;17:269–79.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant No. 82301360, to JPW] and [Grant No. 82271290, to CZ] and [Grant No. 82371281, to TZ]; Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan Province [Grant No. 2023NSFSC1488, to JPW] and [Grant No. 2023ZYD0168, to CZ].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CZ, GC and JL designed the research. JW YZ and YY performed the research including virus injection, behavioral tests, and electrophysiological recordings. XW, and TZ analyzed the data. XJ and YH prepared figures and created illustrations. JW, and CZ wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, L., Liu, J. et al. Stress-induced reduction of sodium leak currents causes social deficits by impairing dorsal dentate gyrus-medial septum glutamatergic projection. Mol Psychiatry (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03101-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-025-03101-1