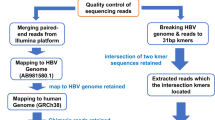
Abstract
Background
Studies have shown that hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) constitutes a unique subgroup with distinct clinical features. It still leaves open the question of whether the integration of HBV DNA into the B-cell genome is a causal mechanism in the development of lymphoma.
Methods
Using the hybridisation capture-based next generation sequencing and RNA sequencing, we characterised the HBV integration pattern in 45 HBV-associated B-cell NHL tumour tissues.
Results
A total of 354 HBV integration sites were identified in 13 (28.9%) samples, indicating the relatively low integration frequency in B-cell NHLs. High plasma HBV DNA loads were not associated with the existence of HBV integration. The insertion sites distributed randomly across all the lymphoma genome without any preferential hotspot neither at the chromosomal level nor at the genetic level. Intriguingly, most HBV integrations were nonclonal in B-cell NHLs, implying that they did not confer a survival advantage. Analysis of the paired diagnosis-relapse samples showed the unstable status of HBV integrations during disease progression. Furthermore, transcriptomic analysis revealed the limited biological impact of HBV integration.
Conclusion
Our study provides an unbiased HBV integration map in B-cell NHLs, revealing the insignificant role of HBV DNA integration in B-cell lymphomagenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 11,21 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary file.
References
Mesri EA, Feitelson MA, Munger K. Human viral oncogenesis: a cancer hallmarks analysis. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15:266–82.
Zapatka M, Borozan I, Brewer DS, Iskar M, Grundhoff A, Alawi M, et al. The landscape of viral associations in human cancers. Nat Genet. 2020;52:320–30.
Engels EA, Cho ER, Jee SH. Hepatitis B virus infection and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in South Korea: a cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:827–34.
Marcucci F, Mele A, Spada E, Candido A, Bianco E, Pulsoni A, et al. High prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Haematologica. 2006;91:554–7.
Su TH, Liu CJ, Tseng TC, Chou SW, Liu CH, Yang HC, et al. Chronic hepatitis B is associated with an increased risk of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Aliment Pharm Ther. 2019;49:589–98.
Li M, Gan Y, Fan C, Yuan H, Zhang X, Shen Y, et al. Hepatitis B virus and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: an updated meta-analysis of 58 studies. J Viral Hepat. 2018;25:894–903.
Cheng CL, Huang SC, Chen JH, Wei CH, Fang WQ, Su TH, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen positivity is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the rituximab era. Oncologist. 2020;25:793–802.
Deng L, Song Y, Young KH, Hu S, Ding N, Song W, et al. Hepatitis B virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: unique clinical features, poor outcome, and hepatitis B surface antigen-driven origin. Oncotarget. 2015;6:25061–73.
Ren W, Ye X, Su H, Li W, Liu D, Pirmoradian M, et al. Genetic landscape of hepatitis B virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2018;131:2670–81.
Yan X, Zhou M, Lou Z, Mu Q, Sheng L, Zhang P, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with concurrent hepatitis B virus infection in the MabThera era: unique clinical features and worse outcomes. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14:S248–S53.
Cheng CL, Fang WQ, Lin YJ, Yuan CT, Ko BS, Tang JL, et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen positivity is associated with progression of disease within 24 months in follicular lymphoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022;148:1211–22.
Ren W, Wang X, Yang M, Wan H, Li X, Ye X, et al. Distinct clinical and genetic features of hepatitis B virus-associated follicular lymphoma in Chinese patients. Blood Adv. 2022;6:2731–44.
Marcucci F, Spada E, Mele A, Caserta CA, Pulsoni A. The association of hepatitis B virus infection with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma—a review. Am J Blood Res. 2012;2:18–28.
Wang Y, Wang H, Pan S, Hu T, Shen J, Zheng H, et al. Capable infection of hepatitis B virus in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Cancer. 2018;9:1575–81.
Yoffe B, Burns DK, Bhatt HS, Combes B. Extrahepatic hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in patients with acute hepatitis B infection. Hepatology. 1990;12:187–92.
Bouffard P, Lamelin JP, Zoulim F, Lepot D, Trepo C. Phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A activate hepatitis B virus in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Med Virol. 1992;37:255–62.
Pontisso P, Vidalino L, Quarta S, Gatta A. Biological and clinical implications of HBV infection in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Autoimmun Rev. 2008;8:13–7.
Lamontagne RJ, Bagga S, Bouchard MJ. Hepatitis B virus molecular biology and pathogenesis. Hepatoma Res. 2016;2:163–86.
Valaydon ZS, Locarnini SA. The virological aspects of hepatitis B. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017;31:257–64.
Tu T, Budzinska MA, Shackel NA, Urban S. HBV DNA integration: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Viruses. 2017;9:75.
Sung WK, Zheng H, Li S, Chen R, Liu X, Li Y, et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2012;44:765–9.
Zhao LH, Liu X, Yan HX, Li WY, Zeng X, Yang Y, et al. Genomic and oncogenic preference of HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12992.
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive and integrative genomic characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. 2017;169:1327–41.e23.
Li M, Shen Y, Chen Y, Gao H, Zhou J, Wang Q, et al. Characterization of hepatitis B virus infection and viral DNA integration in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 2020;147:2199–209.
Li CL, Li CY, Lin YY, Ho MC, Chen DS, Chen PJ, et al. Androgen receptor enhances hepatic telomerase reverse transcriptase gene transcription after hepatitis B virus integration or point mutation in promoter region. Hepatology. 2019;69:498–512.
Lin YY, Hsieh CH, Chen JH, Lu X, Kao JH, Chen PJ, et al. De novo assembly of highly polymorphic metagenomic data using in situ generated reference sequences and a novel BLAST-based assembly pipeline. BMC Bioinforma. 2017;18:223.
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:15–21.
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:e47.
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16:284–7.
Cibulskis K, Lawrence MS, Carter SL, Sivachenko A, Jaffe D, Sougnez C, et al. Sensitive detection of somatic point mutations in impure and heterogeneous cancer samples. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31:213–9.
Mansi L, Tangaro MA, Lo Giudice C, Flati T, Kopel E, Schaffer AA, et al. REDIportal: millions of novel A-to-I RNA editing events from thousands of RNAseq experiments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:D1012–D9.
Li C-L, Hsu C-L, Lin Y-Y, Ho M-C, Hu, Chen C-L, et al. HBV DNA integration into telomerase or MLL4 genes and TERT promoter point mutation as three independent signatures in subgrouping HBV-related HCC with distinct features. Liver Cancer. 2023;13:1–15.
Danaher P, Warren S, Dennis L, D’Amico L, White A, Disis ML, et al. Gene expression markers of Tumor Infiltrating Leukocytes. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5:18.
Levrero M, Zucman-Rossi J. Mechanisms of HBV-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2016;64:S84–S101.
Chaturvedi VK, Singh A, Dubey SK, Hetta HF, John J, Singh MP. Molecular mechanistic insight of hepatitis B virus-mediated hepatocellular carcinoma. Micro Pathog. 2019;128:184–94.
Li CL, Ho MC, Lin YY, Tzeng ST, Chen YJ, Pai HY, et al. Cell-free virus-host chimera DNA from hepatitis B virus integration sites as a circulating biomarker of hepatocellular cancer. Hepatology. 2020;72:2063–76.
Peneau C, Imbeaud S, La Bella T, Hirsch TZ, Caruso S, Calderaro J, et al. Hepatitis B virus integrations promote local and distant oncogenic driver alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2022;71:616–26.
Lu P, Chen J, Yan L, Yang L, Zhang L, Dai J, et al. RasGRF2 promotes migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by modulating expression of MMP9 through Src/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20:435–43.
Du Y, Wang Z, Wan W. High expression of ERK-related RASGRF2 predicts poor prognosis in patients with stomach adenocarcinoma and correlates with M2 macrophage. J Cancer. 2021;12:7177–89.
Chapuy B, McKeown MR, Lin CY, Monti S, Roemer MG, Qi J, et al. Discovery and characterization of super-enhancer-associated dependencies in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2013;24:777–90.
Duncavage EJ, Magrini V, Becker N, Armstrong JR, Demeter RT, Wylie T, et al. Hybrid capture and next-generation sequencing identify viral integration sites from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. J Mol Diagn. 2011;13:325–33.
Wang Y, Liu Y, Deng W, Fu F, Yan S, Yang H, et al. Viral integration in BK polyomavirus-associated urothelial carcinoma in renal transplant recipients: multistage carcinogenesis revealed by next-generation virome capture sequencing. Oncogene. 2020;39:5734–42.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the High-throughput Genomics & Dig Data Analysis Core, Department of Medical Research, National Taiwan University Hospital for technical support and the National Center for High-performance Computing (NCHC) for providing computational and storage resources. We also thank the relevant medical staff and patients who contributed to this study.
Funding
This work was sponsored by the general research project grants from the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan (NSTC 109-2314-B-002-276, NSTC 111-2314-B-002-126, and NSTC 112-2314-B-002-188).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CC designed the study, interpreted data, did statistical analysis, and wrote the manuscript. YL interpreted next-generation sequencing data and performed bioinformatics analysis. CH performed transcriptome analysis. CL participated in the assembly of data and wrote the manuscript. CY performed an independent review of all pathology data. YL was responsible for DNA extraction and quantitative polymerase chain reaction. WF did a statistical analysis. PC designed the study, interpreted data, obtained funding, and wrote the manuscript. SY designed the study, interpreted data, obtained funding, and supervised the study. HT obtained funding, coordinated the study over the entire period, and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the National Taiwan University Hospital and was performed in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki (IRB No. 201911040RINB). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, CL., Lin, YY., Hsu, CL. et al. Unraveling the role of hepatitis B virus DNA integration in B-cell lymphomagenesis. Br J Cancer 131, 996–1004 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-024-02763-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-024-02763-y