Abstract
Interstitial deletions of 2q32 are typically identified after investigation for developmental delay. Two genes associated with Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS); COL3A1 and COL5A2 associated with vascular EDS and classical EDS respectively, may be incorporated in the region. Although many reports of 2q32 microdeletion patients exist, there is little mention of these genes with only a few reports highlighting features potentially linked with EDS. This paper reviews the literature and presents eleven new patients with 2q32 deletions that encompass COL3A1 and COL5A2. We describe their clinical manifestations with a particular focus on the EDS phenotype. Most patients showed some minor features of vascular EDS and one patient had vessel rupture at a young age. Analysis of skin biopsy findings from two patients showed features consistent with vascular EDS but no features of classical EDS. The findings from this cohort provide additional evidence that haploinsufficiency is an important disease mechanism in COL3A1 but not COL5A2. We highlight the importance of pre-test counselling for incidental findings from broad genetic testing and appropriate post-test counselling to ensure follow up is provided to manage the implications of a vascular EDS diagnosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 22,42 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data generated during this study can be found in the published article and supplementary files. It is not available in a repository.
References
Glass I, Swindlehurst C, Aitken D, McCrea W, Boyd E. Interstitial deletion of the long arm of chromosome 2 with normal levels of isocitrate dehydrogenase. J Med Genet. 1989;26:127–30.
Balasubramanian M, Smith K, Basel-Vanagaite L, Feingold M, Brock P, Gowans G, et al. Case series: 2q33. 1 microdeletion syndrome—further delineation of the phenotype. J Med Genet. 2011;48:290–8.
Zarate YA, Fish JL. SATB2‐associated syndrome: Mechanisms, phenotype, and practical recommendations. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2017;173:327–37.
Malfait F, Francomano C, Byers P, Belmont J, Berglund B, Black J, et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers–Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet Part C: Semin Med Genet. 2017;175:8–26.
Sobey G. Ehlers–Danlos syndrome: how to diagnose and when to perform genetic tests. Arch Dis Child. 2015;100:57–61.
Leistritz D, Pepin M, Schwarze U, Byers PH. COL3A1haploinsufficiency results in a variety of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV with delayed onset of complications and longer life expectancy. Genet Med. 2011;13:717–22.
Pepin MG, Schwarze U, Rice KM, Liu M, Leistritz D, Byers PH. Survival is affected by mutation type and molecular mechanism in vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS type IV). Genet Med. 2014;16:881–8.
Ritelli M, Dordoni C, Venturini M, Chiarelli N, Quinzani S, Traversa M, et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of 40 patients with classic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: identification of 18 COL5A1 and 2 COL5A2 novel mutations. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;12:1–19.
Ritelli M, Venturini M, Cinquina V, Chiarelli N, Colombi M. Multisystemic manifestations in a cohort of 75 classical Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patients: natural history and nosological perspectives. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020;15:1–18.
Martin AR, Williams E, Foulger RE, Leigh S, Daugherty LC, Niblock O, et al. PanelApp crowdsources expert knowledge to establish consensus diagnostic gene panels. Nat Genet. 2019;51:1560–1565. https://nhsgms-panelapp.genomicsengland.co.uk/panels/53/v3.0
Angwin C, Ghali N, Baker D, Brady A, Pope F, Vandersteen A, et al. Electron microscopy in the diagnosis of Ehlers–Danlos syndromes: correlation with clinical and genetic investigations. Br J Dermatol. 2020;182:698–707.
Crowther MA, Lach B, Dunmore PJ, Roach MR. Vascular collagen fibril morphology in type IV Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Connect Tissue Res. 1991;25:209–17.
Bowen JM, Sobey GJ, Burrows NP, Colombi M, Lavallee ME, Malfait F, et al. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, classical type. Am J Med Genet. 2017;175:27–39.
Van Buggenhout G, Van Ravenswaaij-Arts C, Mc Maas N, Thoelen R, Vogels A, Smeets D, et al. The del(2)(q32.2q33) deletion syndrome defined by clinical and molecular characterization of four patients. Eur J Med Genet. 2005;48:276–89.
Mencarelli MA, Caselli R, Pescucci C, Hayek G, Zappella M, Renieri A, et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of a patient with a 2q31.2-32.3 deletion identified by array-CGH. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2007;143A:858–65.
Prontera P, Bernardini L, Stangoni G, Capalbo A, Rogaia D, Ardisia, et al. 2q31.2q32.3 deletion syndrome: report of an adult patient. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2009;149A:706–12.
Rifai L, Port‐Lis M, Tabet A, Bailleul‐Forestier I, Benzacken B, Drunat, et al. Ectodermal dysplasia-like syndrome with mental retardation due to contiguous gene deletion: further clinical and molecular delineation of del(2q32) syndrome. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2010;152A:111–7.
Meienberg J, Rohrbach M, Neuenschwander S, Spanaus K, Giunta C, Alonso S, et al. Hemizygous deletion of COL3A1, COL5A2, and MSTN causes a complex phenotype with aortic dissection: a lesson for and from true haploinsufficiency. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010;18:1315–21.
Ferreira SI, Matoso E, Venâncio M, Saraiva J, Melo JB, et al. Critical region in 2q31.2q32.3 deletion syndrome: report of two phenotypically distinct patients, one with an additional deletion in alagille syndrome region. Mol Cytogenet. 2012;5:25–25.
Mc Cormack A, Taylor J, Gregersen N, George AM, & Love DR. Delineation of 2q32q35 deletion phenotypes: two apparent “Proximal” and “Distal” syndromes. Case Rep Genet 2013;823451.
Kempers MJ, Wessels M, Van Berendoncks A, van de Laar IM, de Leeuw N, Loeys B. Phenotype of COL3A1/COL5A2 deletion patients. Eur J Med Genet. 2022;65:104593.
Shalhub S, Black JH, Cecchi AC, Xu Z, Griswold BF, Safi HJ, et al. Molecular diagnosis in Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome predicts pattern of arterial involvement and outcomes. J Vasc Surg. 2014;60:160–9. (2014)
Frank M, Albuisson J, Ranque B, Golmard L, Mazzella J-M, Bal-Theoleyre L, et al. The type of variants at the COL3A1 gene associates with the phenotype and severity of vascular Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015;23:1657–64.
Demirdas S, van den Bersselaar LM, Lechner R, Bos J, Alsters SIM, Baars MJH, et al. Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: a comprehensive natural history study in a Dutch national cohort of 142 patients. Circulation: Genom Precis Med. 2024, https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCGEN.122.003978.
Adham S M, Zinzindohoué F, Jeunemaitre X, Frank M. Natural history and surgical management of colonic perforations in Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: a retrospective review. Dis Colon Rectum. 2019;62:859–66. 859-866
Bowen JM, Hernandez M, Johnson DS, Green C, Kammin T, Baker D, et al. Diagnosis and management of vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: experience of the UK National Diagnostic Service, Sheffield. Eur J Hum Genet. 2023;31:749–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-023-01343-7
Byers PH, Belmont J, Black J, De Backer J, Frank M, Jeunemaitre X, et al. J Med Genet Part C: Semin Med Genet, 2017;175:40–47.
Drera B, Zoppi N, Ritelli M, Barlati S, Colombi M, Tadini G, et al. Diagnosis of vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in Italy: clinical findings and novel COL3A1 mutations. J Dermatol Sci. 2011;64:237–40.
Shimaoka Y, Kosho T, Wataya‐Kaneda M, Funakoshi M, Suzuki T, Hayashi S, et al. Clinical and genetic features of 20 Japanese patients with vascular-type Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 2010;163:704–10.
Oderich GS, Panneton JM, Bower TC, Lindor NM, Cherry KJ, Noel AA, et al. The spectrum, management and clinical outcome of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV: a 30-year experience. J Vasc Surg. 2005;42:98–106.
Kuming B, Joffe L. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome associated with keratoconus-a case report. South Afr Med J. 1977;52:403–5.
Henneton P, Albuisson J, Denarié N, Mazzella J-M, Mousseaux E. Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: long-term observational study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73:1948–57.
Zarate YA, Bosanko KA, Thomas MA, Miller DT, Cusmano‐Ozog K, Martinez‐Monseny A, et al. Growth, development, and phenotypic spectrum of individuals with deletions of 2q33. 1 involving SATB2. Clin Genet. 2021;99:547–57.
Park AC, Phillips CL, Pfeiffer FM, Roenneburg DA, Kernien JF, Adams SM, et al. Homozygosity and heterozygosity for null Col5a2 alleles produce embryonic lethality and a novel classic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome-related phenotype. Am J Pathol. 2015;185:2000–11.
Acknowledgements
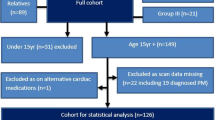
We thank the clinicians and scientists who referred these patients for allowing us to publish our findings. Thank you to Bart Wagner and David Ferguson for providing electron microscopy images. Thank you to Sam Nalty, Clinical Scientist for compiling Fig. 1. We would also like to thank the families for consenting to this publication.
Funding
No financial assistance was received in support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CG conceived and designed the work, acquired, and reviewed medical records and drafted the manuscript. DD and AM were involved in the conception and design of the work and contributed to the drafting of the first manuscripts. SA produced Fig. 1, DB, and SM provided genotype results for their patients and ensured correct nomenclature. GS, DD, AM, NG, FVD, MC, MR, EH, JR, EK, AD, and FS provided patient data. FVD, AM, and TK proofread and edited the manuscript, and GS, DSJ, JB, MC and MR provided considerable and detailed feedback throughout the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
No formal research ethics approval or research and development approval was required as stipulated by the UK Policy Framework for Health and Social Care Research and the Health Research Authority decision tool. Written consent for publication, including photographs, was obtained from all individuals.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Green, C.E., Albaba, S., Sobey, G.J. et al. Vascular Ehlers Danlos Syndrome and Chromosome 2q32 Microdeletion Syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-025-01849-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-025-01849-2