Abstract
Background
To analyze the optical coherence tomography (OCT) characteristics and visual outcome of vitrectomy in myopic foveoschisis (MF) patients and identify prognostic factors.
Methods
This study is a retrospective clinical cohort study in tertiary care hospital. Thirty-two eyes of 32 patients who underwent MF-related vitrectomy in were investigated retrospectively. Best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) measured at 1 year post surgery and changes in central foveal thickness (CFT) and co-existing macular pathologies, such as foveal detachment (FD), lamellar holes, and macular holes were the main outcome measures. Prognostic factors were identified using multivariate linear regression analysis.
Results
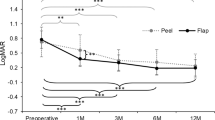
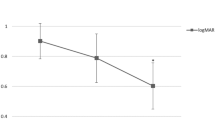
Average BCVA (in logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution) and mean CFT had improved from 0.46 ± 0.06 to 0.37 ± 0.07 (P = 0.089) and from 485.72 ± 164.69 to 341.71 ± 109.70 (P < 0.001), respectively. Univariate analysis identified baseline BCVA, epiretinal membrane, no coexisting OCT features other than MF, FD on OCT, and gas injection as significantly associated with visual outcome (P < 0.001, 0.014, 0.022, < 0.001, and 0.030). Better baseline BCVA and absence of FD on OCT remained significant (P < 0.001 and < 0.001, respectively) after multivariate analysis.
Conclusion
Good preoperative visual acuity and absence of FD pre-surgery are important predictors of good visual prognosis. Thus, timely surgical intervention, before development of macular complications, may improve visual outcome after surgical treatment of patients with MF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Login or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Shimada N, Ohno-Matsui K, Baba T, Futagami S, Tokoro T, Mochizuki M. Natural course of macular retinoschisis in highly myopic eyes without macular hole or retinal detachment. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;142:497–500.
Benhamou N, Massin P, Haouchine B, Erginay A, Gaudric A. Macular retinoschisis in highly myopic eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002;133:794–800.
Sayanagi K, Morimoto Y, Ikuno Y, Tano Y. Spectral-___domain optical coherence tomographic findings in myopic foveoschisis. Retina. 2010;30:623–8.
Gohil R, Sivaprasad S, Han LT, Mathew R, Kiousis G, Yang Y. Myopic foveoschisis: a clinical review. Eye (Lond). 2015;29:593–601.
Rim TH, Kim SH, Lim KH, Choi M, Kim HY, Baek SH. Refractive errors in Koreans: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2012. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2016;30:214–24.
Lin LL, Shih YF, Hsiao CK, Chen CJ. Prevalence of myopia in Taiwanese schoolchildren: 1983 to 2000. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2004;33:27–33.
Guo K, Yang DY, Wang Y, Yang XR, Jing XX, Guo YY, et al. Prevalence of myopia in schoolchildren in Ejina: the Gobi Desert Children Eye Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56:1769–74.
Baba T, Ohno-Matsui K, Futagami S, Yoshida T, Yasuzumi K, Kojima A, et al. Prevalence and characteristics of foveal retinal detachment without macular hole in high myopia. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135:338–42.
Panozzo G, Mercanti A. Optical coherence tomography findings in myopic traction maculopathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:1455–60.
Lee DH, Kang HG, Lee SC, Kim M. Features of optical coherence tomography predictive of choroidal neovascularisation treatment response in pathological myopia in association with fluorescein angiography. Br J Ophthalmol. 2018;102:238–42.
Lehmann M, Devin F, Rothschild PR, Gaucher D, Morin B, Philippakis E, et al. Preoperative factors influencing visual recovery after vitrectomy for myopic foveoschisis. Retina. 2017;39:594-600.
Lim LS, Ng WY, Wong D, Wong E, Yeo I, Ang CL, et al. Prognostic factor analysis of vitrectomy for myopic foveoschisis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015;99:1639–43.
Yun LN, Xing YQ. Long-term outcome of highly myopic foveoschisis treated by vitrectomy with or without gas tamponade. Int J Ophthalmol. 2017;10:1392–5.
Meng B, Zhao L, Yin Y, Li H, Wang X, Yang X, et al. Internal limiting membrane peeling and gas tamponade for myopic foveoschisis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Ophthalmol. 2017;17:166.
Uchida A, Shinoda H, Koto T, Mochimaru H, Nagai N, Tsubota K, et al. Vitrectomy for myopic foveoschisis with internal limiting membrane peeling and no gas tamponade. Retina. 2014;34:455–60.
Zhu X, Shen P, Li C, Li H, Huang H, Shi K, et al. Intravitreal gas injection with laser photocoagulation for highly myopic foveoschisis: Technique and outcome. Retina. 2018; https://doi.org/10.1097/iae.0000000000002145.
Alkabes M, Mateo C. Macular buckle technique in myopic traction maculopathy: a 16-year review of the literature and a comparison with vitreous surgery. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2018;256:863–77.
Li XJ, Yang XP, Li QM, Wang YY, Wang J, Lyu XB, et al. Posterior scleral reinforcement combined with vitrectomy for myopic foveoschisis. Int J Ophthalmol. 2016;9:258–61.
Lim SJ, Kwon YH, Kim SH, You YS, Kwon OW. Vitrectomy and internal limiting membrane peeling without gas tamponade for myopic foveoschisis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012;250:1573–7.
Kim KS, Lee SB, Lee WK. Vitrectomy and internal limiting membrane peeling with and without gas tamponade for myopic foveoschisis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;153:320–6.
Qi Y, Duan AL, Meng X, Wang N. Vitrectomy without inner limiting membrane peeling for macular retinoschisis in highly myopic eyes. Retina. 2016;36:953–6.
Shimada N, Sugamoto Y, Ogawa M, Takase H, Ohno-Matsui K. Fovea-sparing internal limiting membrane peeling for myopic traction maculopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;154:693–701.
Fujimoto S, Ikuno Y, Nishida K. Postoperative optical coherence tomographic appearance and relation to visual acuity after vitrectomy for myopic foveoschisis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013;156:968–73.
Seppey C, Wolfensberger TJ. Vitrectomy with fovea-sparing internal limiting membrane peeling for myopic foveoschisis. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2017;234:497–500.
Huang Y, Huang W, Ng DSC, Duan A. Risk factors for development of macular hole retinal detachment after pars plana vitrectomy for pathologic myopic foveoschisis. Retina. 2017;37:1049–54.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Yonsei University Faculty Research Grant (6-2017-0149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D., Moon, I., Kang, H. et al. Surgical outcome and prognostic factors influencing visual acuity in myopic foveoschisis patients. Eye 33, 1642–1648 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-019-0462-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-019-0462-7
This article is cited by
-
Surgical Outcomes of Myopic Foveoschisis According to the ATN Classification System
Ophthalmology and Therapy (2023)
-
Vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane peeling and gas tamponade for myopic foveoschisis
BMC Ophthalmology (2022)