Abstract
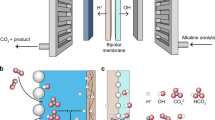
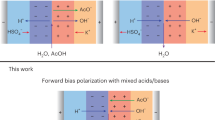
CO2 electrolysis allows the sustainable production of carbon-based fuels and chemicals. However, state-of-the-art CO2 electrolysers employing anion exchange membranes (AEMs) suffer from (bi)carbonate crossover, causing low CO2 utilization and limiting anode choices to those based on precious metals. Here we argue that bipolar membranes (BPMs) could become the primary option for intrinsically stable and efficient CO2 electrolysis without the use of scarce metals. Although both reverse- and forward-bias BPMs can inhibit CO2 crossover, forward-bias BPMs fail to solve the rare-earth metals requirement at the anode. Unfortunately, reverse-bias BPM systems presently exhibit comparatively lower Faradaic efficiencies and higher cell voltages than AEM-based systems. We argue that these performance challenges can be overcome by focusing research on optimizing the catalyst, reaction microenvironment and alkali cation availability. Furthermore, BPMs can be improved by using thinner layers and a suitable water dissociation catalyst, thus alleviating core remaining challenges in CO2 electrolysis to bring this technology to the industrial scale.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
27,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
118,99 € per year
only 9,92 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Salvatore, D. A. et al. Designing anion exchange membranes for CO2 electrolysers. Nat. Energy 6, 339–348 (2021).
Vass, Á. et al. Local chemical environment governs anode processes in CO2 electrolyzers. ACS Energy Lett. 6, 3801–3808 (2021).
Minke, C., Suermann, M., Bensmann, B. & Hanke-Rauschenbach, R. Is iridium demand a potential bottleneck in the realization of large-scale PEM water electrolysis? Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 46, 23581–23590 (2021).
Rabinowitz, J. A. & Kanan, M. W. The future of low-temperature carbon dioxide electrolysis depends on solving one basic problem. Nat. Commun. 11, 5231 (2020).
Sharifian, R., Wagterveld, R. M., Digdaya, I. A., Xiang, C. & Vermaas, D. A. Electrochemical carbon dioxide capture to close the carbon cycle. Energy Environ. Sci. 14, 781–814 (2021).
McQueen, N. et al. A review of direct air capture (DAC): scaling up commercial technologies and innovating for the future. Prog. Energy 3, 032001 (2021).
Xie, X. et al. Oxygen evolution reaction in alkaline environment: material challenges and solutions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2110036 (2022).
Kim, B., Ma, S., Molly Jhong, H.-R. & Kenis, P. J. A. Influence of dilute feed and pH on electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO on Ag in a continuous flow electrolyzer. Electrochim. Acta 166, 271–276 (2015).
Monteiro, M. C. O., Philips, M. F., Schouten, K. J. P. & Koper, M. T. M. Efficiency and selectivity of CO2 reduction to CO on gold gas diffusion electrodes in acidic media. Nat. Commun. 12, 4943 (2021).
Erick, H. J. et al. CO2 electrolysis to multicarbon products in strong acid. Science 372, 1074–1078 (2021).
Bondue, C. J., Graf, M., Goyal, A. & Koper, M. T. M. Suppression of hydrogen evolution in acidic electrolytes by electrochemical CO2 reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 279–285 (2021).
O’Brien, C. P. et al. Single pass CO2 conversion exceeding 85% in the electrosynthesis of multicarbon products via local CO2 regeneration. ACS Energy Lett. 6, 2952–2959 (2021).
Xie, K. et al. Bipolar membrane electrolyzers enable high single-pass CO2 electroreduction to multicarbon products. Nat. Commun. 13, 3609 (2022).
Eriksson, B. et al. Mitigation of carbon crossover in CO2 electrolysis by use of bipolar membranes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 169, 034508 (2022).
Aydogan Gokturk, P. et al. The Donnan potential revealed. Nat. Commun. 13, 5880 (2022).
Pärnamäe, R. et al. Bipolar membranes: a review on principles, latest developments, and applications. J. Memb. Sci. 617, 118538 (2021).
Blommaert, M. A., Verdonk, J. A. H., Blommaert, H. C. B., Smith, W. A. & Vermaas, D. A. Reduced ion crossover in bipolar membrane electrolysis via increased current density, molecular size, and valence. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 3, 5804–5812 (2020).
Li, Y. C. et al. Bipolar membranes inhibit product crossover in CO2 electrolysis cells. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2, 1700187 (2018).
Disch, J., Ingenhoven, S. & Vierrath, S. Bipolar membrane with porous anion exchange layer for efficient and long-term stable electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO. Adv. Energy Mater. 13, 2301614 (2023).
Subramanian, S., Middelkoop, J. & Burdyny, T. Spatial reactant distribution in CO2 electrolysis: balancing CO2 utilization and faradaic efficiency. Sustain. Energy Fuels 5, 6040–6048 (2021).
Liu, X., Monteiro, M. C. O. & Koper, M. T. M. Interfacial pH measurements during CO2 reduction on gold using a rotating ring-disk electrode. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25, 2897–2906 (2023).
Bui, J. C. et al. Analysis of bipolar membranes for electrochemical CO2 capture from air and oceanwater. Energy Environ. Sci. 16, 5076–5095 (2023).
Toh, W. L., Dinh, H. Q., Chu, A. T., Sauvé, E. R. & Surendranath, Y. The role of ionic blockades in controlling the efficiency of energy recovery in forward bias bipolar membranes. Nat. Energy 8, 1405–1416 (2023).
Dinh, H. Q., Toh, W. L., Chu, A. T. & Surendranath, Y. Neutralization short-circuiting with weak electrolytes erodes the efficiency of bipolar membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15, 4001–4010 (2023).
Petrov, K. V. et al. Anion-exchange membranes with internal microchannels for water control in CO2 electrolysis. Sustain. Energy Fuels 6, 5077–5088 (2022).
Xu, Y. et al. A microchanneled solid electrolyte for carbon-efficient CO2 electrolysis. Joule 6, 1333–1343 (2022).
Kim, J. Y. ‘T. ’ et al. Recovering carbon losses in CO2 electrolysis using a solid electrolyte reactor. Nat. Catal. 5, 288–299 (2022).
Monteiro, M. C. O. et al. Absence of CO2 electroreduction on copper, gold and silver electrodes without metal cations in solution. Nat. Catal. 4, 654–662 (2021).
Birdja, Y. Y. et al. Advances and challenges in understanding the electrocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to fuels. Nat. Energy 4, 732–745 (2019).
Xiao, T. et al. Proton antagonist membrane towards exclusive CO2 reduction. Nano Res. 16, 4589–4595 (2023).
Siritanaratkul, B. et al. Zero-gap bipolar membrane electrolyzer for carbon dioxide reduction using acid-tolerant molecular electrocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 7551–7556 (2022).
Guo, J. et al. Direct seawater electrolysis by adjusting the local reaction environment of a catalyst. Nat. Energy 8, 264–272 (2023).
Yan, Z., Hitt, J. L., Zeng, Z., Hickner, M. A. & Mallouk, T. E. Improving the efficiency of CO2 electrolysis by using a bipolar membrane with a weak-acid cation exchange layer. Nat. Chem. 13, 33–40 (2021).
Endrődi, B. et al. Operando cathode activation with alkali metal cations for high current density operation of water-fed zero-gap carbon dioxide electrolysers. Nat. Energy 6, 439–448 (2021).
Baumgartner, L. M., Koopman, C. I., Forner-Cuenca, A. & Vermaas, D. A. Narrow pressure stability window of gas diffusion electrodes limits the scale-up of CO2 electrolyzers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 10, 4683–4693 (2022).
Blommaert, M. A. et al. Insights and challenges for applying bipolar membranes in advanced electrochemical energy systems. ACS Energy Lett. 6, 2539–2548 (2021).
Khalid, H., Najibah, M., Park, H. S., Bae, C. & Henkensmeier, D. Properties of anion exchange membranes with a focus on water electrolysis. Membranes (Basel) 12, 989 (2022).
Liu, Z., Yang, H., Kutz, R. & Masel, R. I. CO2 electrolysis to CO and O2 at high selectivity, stability and efficiency using sustainion membranes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 165, J3371–J3377 (2018).
Yang, K. et al. Cation-driven increases of CO2 utilization in a bipolar membrane electrode assembly for CO2 electrolysis. ACS Energy Lett. 6, 4291–4298 (2021).
Kitto, D. & Kamcev, J. The need for ion-exchange membranes with high charge densities. J. Membr. Sci. 677, 121608 (2023).
Hyun, J. et al. Magnetic field-induced through-plane alignment of the proton highway in a proton exchange membrane. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 3, 4619–4628 (2020).
Powers, D. et al. Freestanding bipolar membranes with an electrospun junction for high current density water splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 36092–36104 (2022).
Xu, Z. et al. Continuous ammonia electrosynthesis using physically interlocked bipolar membrane at 1000 mA cm−2. Nat. Commun. 14, 1619 (2023).
Chen, Y. et al. High-performance bipolar membrane development for improved water dissociation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2, 4559–4569 (2020).
Mitchell, J. B., Chen, L., Langworthy, K., Fabrizio, K. & Boettcher, S. W. Catalytic proton–hydroxide recombination for forward-bias bipolar membranes. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 3967–3973 (2022).
Chen, L., Xu, Q. & Boettcher, S. W. Kinetics and mechanism of heterogeneous voltage-driven water-dissociation catalysis. Joule 7, 1867–1886 (2023).
Lucas, É. et al. Asymmetric bipolar membrane for high current density electrodialysis operation with exceptional stability. Preprint at ChemRxiv https://doi.org/10.26434/chemrxiv-2023-n4c6x (2023).
Mayerhöfer, B. et al. Bipolar membrane electrode assemblies for water electrolysis. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 3, 9635–9644 (2020).
Mardle, P., Cassegrain, S., Habibzadeh, F., Shi, Z. & Holdcroft, S. Carbonate ion crossover in zero-gap, KOH anolyte CO2 electrolysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 125, 25446–25454 (2021).
Blommaert, M. A., Subramanian, S., Yang, K., Smith, W. A. & Vermaas, D. A. High indirect energy consumption in AEM-based CO2 electrolyzers demonstrates the potential of bipolar membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 557–563 (2022).
Larrazábal, G. O. et al. Analysis of mass flows and membrane cross-over in CO2 reduction at high current densities in an MEA-type electrolyzer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 41281–41288 (2019).
Endrődi, B. et al. High carbonate ion conductance of a robust PiperION membrane allows industrial current density and conversion in a zero-gap carbon dioxide electrolyzer cell. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 4098–4105 (2020).
Jeng, E. & Jiao, F. Investigation of CO2 single-pass conversion in a flow electrolyzer. React. Chem. Eng. 5, 1768–1775 (2020).
Ma, M. et al. Insights into the carbon balance for CO2 electroreduction on Cu using gas diffusion electrode reactor designs. Energy Environ. Sci. 13, 977–985 (2020).
Ma, M., Kim, S., Chorkendorff, I. & Seger, B. Role of ion-selective membranes in the carbon balance for CO2 electroreduction via gas diffusion electrode reactor designs. Chem. Sci. 11, 8854–8861 (2020).
Hansen, K. U., Cherniack, L. H. & Jiao, F. Voltage loss diagnosis in CO2 electrolyzers using five-electrode technique. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 4504–4511 (2022).
Khan, M. A. et al. Zero-crossover electrochemical CO2 reduction to ethylene with co-production of valuable chemicals. Chem. Catal. 2, 2077–2095 (2022).
Jeanty, P. et al. Upscaling and continuous operation of electrochemical CO2 to CO conversion in aqueous solutions on silver gas diffusion electrodes. J. CO2 Util. 24, 454–462 (2018).
Del Castillo, A. et al. Sn nanoparticles on gas diffusion electrodes: synthesis, characterization and use for continuous CO2 electroreduction to formate. J. CO2 Util. 18, 222–228 (2017).
Vennekoetter, J.-B., Sengpiel, R. & Wessling, M. Beyond the catalyst: how electrode and reactor design determine the product spectrum during electrochemical CO2 reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 364, 89–101 (2019).
Acknowledgements
This work is part of the research programme Towards Large-Scale Electroconversion Systems financed by Shell and the top sectors Chemistry, High Tech Systems and Materials and Energy. This project has received funding from the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement 852115). This work reflects the authors’ views and the European Research Council Executive Agency is not responsible for any use resulting from the information it contains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Energy thanks Amitava Sarkar and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
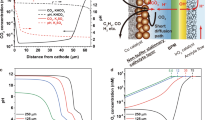
Source data
Source Data Fig. 2
Table with data from 22 references and the calculations for Faradaic efficiency and CO2 crossover.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Petrov, K.V., Koopman, C.I., Subramanian, S. et al. Bipolar membranes for intrinsically stable and scalable CO2 electrolysis. Nat Energy 9, 932–938 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-024-01574-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-024-01574-y
This article is cited by
-
Atomically dispersed cerium on copper tailors interfacial water structure for efficient CO-to-acetate electroreduction
Nature Communications (2025)
-
Techno-economics of polymer-membrane-based CO2 electrolysers
Nature Reviews Clean Technology (2025)
-
Scaling and heating will drive low-temperature CO2 electrolysers to operate at higher temperatures
Nature Energy (2025)