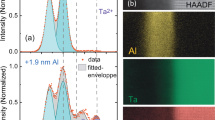
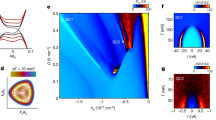
Abstract
Two-dimensional electron systems in gallium arsenide and graphene have enabled ground-breaking discoveries in condensed-matter physics, in part because they are easily modulated by voltages on nanopatterned gate electrodes. Electron systems at oxide interfaces hold a similarly large potential for fundamental studies of correlated electrons and novel device technologies1,2,3, but typically have carrier densities too large to control by conventional gating techniques. Here we present a quantum transport study of a superconducting strontium titanate (STO) interface, enabled by a combination of electrolyte4,5,6,7 and metal-oxide gating. Our structure consists of two superconducting STO banks flanking a nanoscale STO weak link, which is tunable at low temperatures from insulating to superconducting behaviour by a local metallic gate. At low gate voltages, our device behaves as a quantum point contact that exhibits a minimum conductance plateau of e2/h in zero applied magnetic field, half the expected value for spin-degenerate electrons, but consistent with predictions8,9,10,11,12 and experimental signatures13,14,15,16,17,18 of a magnetically ordered ground state. The quantum point contact mediates tunnelling between normal and superconducting regions, enabling lateral tunnelling spectroscopy of the local superconducting state. Our work provides a generic scheme for quantum transport studies of STO and other surface electron liquids.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
269,00 € per year
only 22,42 € per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mannhart, J. & Schlom, D. G. Oxide interfaces—An opportunity for electronics. Science 327, 1607–1611 (2010).
Zubko, P., Gariglio, S., Gabay, M., Ghosez, P. & Triscone, J-M. Interface physics in complex oxide heterostructures. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 2, 141–165 (2011).
Hwang, H. Y. et al. Emergent phenomena at oxide interfaces. Nature Mater. 11, 103–113 (2012).
Ueno, K. et al. Electric-field-induced superconductivity in an insulator. Nature Mater. 7, 855–858 (2008).
Lee, Y. et al. Phase diagram of electrostatically doped SrTiO3 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 136809 (2011).
Lee, M., Williams, J. R., Zhang, S., Frisbie, C. D. & Goldhaber-Gordon, D. Electrolyte gate-controlled Kondo effect in SrTiO3 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 256601 (2011).
Li, M., Graf, T., Schladt, T. D., Jiang, X. & Parkin, S. S. P. Role of percolation in the conductance of electrolyte-gated SrTiO3 . Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, 196803 (2012).
Pentcheva, R. & Pickett, W. Charge localization or itineracy at LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interfaces: Hole polarons, oxygen vacancies, and mobile electrons. Phys. Rev. B 74, 035112 (2006).
Pavlenko, N., Kopp, T., Tsymbal, E. Y., Sawatzky, G. A. & Mannhart, J. Magnetic and superconducting phases at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface: The role of interfacial Ti 3d electrons. Phys. Rev. B 85, 020407 (2012).
Michaeli, K., Potter, A. C. & Lee, P. A. Superconducting and ferromagnetic phases in SrTiO3/LaAlO3 oxide interface structures: Possibility of finite momentum pairing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 117003 (2012).
Fidkowski, L., Jiang, H-C., Lutchyn, R. M. & Nayak, C. Magnetic and superconducting ordering in one-dimensional nanostructures at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface. Phys. Rev. B 87, 014436 (2013).
Banerjee, S., Erten, O. & Randeria, M. Ferromagnetic exchange, spin–orbit coupling and spiral magnetism at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface. Nature Phys. 9, 626–630 (2013).
Brinkman, A. et al. Magnetic effects at the interface between non-magnetic oxides. Nature Mater. 6, 493–496 (2007).
Dikin, D. A. et al. Coexistence of superconductivity and ferromagnetism in two dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 056802 (2011).
Ariando, et al. Electronic phase separation at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface. Nature Commun. 2, 188 (2011).
Li, L., Richter, C., Mannhart, J. & Ashoori, R. C. Coexistence of magnetic order and two-dimensional superconductivity at LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interfaces. Nature Phys. 7, 762–766 (2011).
Bert, J. A. et al. Direct imaging of the coexistence of ferromagnetism and superconductivity at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface. Nature Phys. 7, 767–771 (2011).
Lee, J. S. et al. Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface. Nature Mater. 12, 703–706 (2013).
Ohtomo, A. & Hwang, H. Y. A high-mobility electron gas at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 heterointerface. Nature 427, 423–426 (2004).
Reyren, N. et al. Superconducting interfaces between insulating oxides. Science 317, 1196–1199 (2007).
Caviglia, A. D. et al. Tunable Rashba spin–orbit interaction at oxide interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 126803 (2010).
Stornaiuolo, D. et al. In-plane electronic confinement in superconducting LaAlO3/SrTiO3 nanostructures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 222601 (2012).
Cheng, G. et al. Anomalous transport in sketched nanostructures at the LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface. Phys. Rev. X 3, 011021 (2013).
Richter, C. et al. Interface superconductor with gap behaviour like a high-temperature superconductor. Nature 502, 528–531 (2013).
Winkelmann, C. B., Roch, N., Wernsdorfer, W., Bouchiat, V. & Balestro, F. Superconductivity in a single-C60 transistor. Nature Phys. 5, 876–879 (2009).
Likharev, K. Superconducting weak links. Rev. Mod. Phys. 51, 101–159 (1979).
Tinkham, M. Introduction to Superconductivity 2nd edn (Dover, 2004).
Patel, N. et al. Evolution of half plateaus as a function of electric field in a ballistic quasi-one-dimensional constriction. Phys. Rev. B 44, 13549–13555 (1991).
Debray, P. et al. All-electric quantum point contact spin-polarizer. Nature Nanotech. 4, 759–764 (2009).
Pleceník, A., Grajcar, M., Beňačka, Š., Seidel, P. & Pfuch, A. Finite-quasiparticle-lifetime effects in the differential conductance of Bi2Sr2CaCu2Oy/Au junctions. Phys. Rev. B 49, 10016–10019 (1994).
Takagaki, Y. & Ploog, K. Quantum point contact spectroscopy of d-wave superconductors. Phys. Rev. B 60, 9750–9754 (1999).
Duckheim, M. & Brouwer, P. W. Andreev reflection from noncentrosymmetric superconductors and Majorana bound-state generation in half-metallic ferromagnets. Phys. Rev. B 83, 054513 (2011).
Béri, B. Dephasing-enabled triplet Andreev conductance. Phys. Rev. B 79, 245315 (2009).
Eschrig, M. & Löfwander, T. Triplet supercurrents in clean and disordered half-metallic ferromagnets. Nature Phys. 4, 138–143 (2008).
Wilken, F. B. & Brouwer, P. W. Impurity-assisted Andreev reflection at a spin-active half-metal–superconductor interface. Phys. Rev. B 85, 134531 (2012).
Naidyuk, Y., Häussler, R. & Löhneysen, H. Magnetic field dependence of the Andreev reflection structure in the conductivity of SN point contacts. Physica B 218, 122–125 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank J-M. Triscone and J. Mannhart for helpful discussions concerning this work, and S. Ilani for broader discussions concerning the properties of STO. Sample fabrication was supported by the Air Force Office of Science Research, Award No. FA9550-12-1-02520. Sample measurement was supported by the MURI Program of the Army Research Office, Grant No. W911-NF-09-1-0398. Development of the ionic liquid gating technique was supported by the Center on Nanostructuring for Efficient Energy Conversion (CNEEC) at Stanford University, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the US Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences under Award No. DE-SC0001060. P.G. acknowledges support from the DOE Office of Science Graduate Fellowship Program. M.L. acknowledges support from Samsung and Stanford University. J.R.W. and D.G-G. acknowledge support from the W. M. Keck Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.G. designed the experiment, fabricated the sample, and performed the measurements. All authors contributed to data analysis. P.G. prepared the manuscript with input from all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 3135 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallagher, P., Lee, M., Williams, J. et al. Gate-tunable superconducting weak link and quantum point contact spectroscopy on a strontium titanate surface. Nature Phys 10, 748–752 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3049
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphys3049
This article is cited by
-
Selective control of conductance modes in multi-terminal Josephson junctions
Nature Communications (2022)
-
A Model of Competing Orders and Its Application to a Novel Junction
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism (2019)
-
Transport regimes of a split gate superconducting quantum point contact in the two-dimensional LaAlO3/SrTiO3 superfluid
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Highly gate-tuneable Rashba spin-orbit interaction in a gate-all-around InAs nanowire metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Highly crystalline 2D superconductors
Nature Reviews Materials (2016)