Abstract
Regulatory T (Treg) cells play critical roles in maintaining immune tolerance and tissue homeostasis, but impede anti-tumor immunity. Recent work has established how Treg cells metabolically adapt within the tumor microenvironment (TME), and these adaptations frequently provide a functional advantage over effector T cells. Further, enhanced Treg cell function in the TME may contribute to the limited efficacy of current immunotherapies, especially immune checkpoint blockade (ICB). Here, we review recent progress in understanding mechanisms of Treg cell heterogeneity and function in tumors, with a particular focus on cellular metabolism as an underlying factor by which Treg cells are uniquely poised to thrive in the TME and contribute to tumorigenesis. We describe how cellular metabolism and nutrient or metabolic communication shape Treg cell lineage identity and function in the TME. We also discuss the interplay between ICB and Treg cell metabolism and function, and highlight current strategies targeting Treg cell metabolism specifically in the TME. Understanding metabolic control of intratumoral Treg cells provides excellent opportunities to uncover new or combination therapies for cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) or adoptive cell therapy (ACT) show great potential as effective treatments for cancer. However, the therapeutic efficacies of these treatments are often limited due to multiple factors, including poor infiltration or persistence of effector cell populations or their reprogramming into dysfunctional or immunosuppressive states in the tumor microenvironment (TME). The TME is a complex mixture of cell types, including tumor and immune cells, and this cellular milieu is associated with an altered metabolic state of malignant cells. Specifically, tumor cells acquire and consume high levels of nutrients and produce immunosuppressive metabolites to support their growth and proliferation. In turn, these changes create a condition of metabolic competition or stress wherein the anti-tumor functions of macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), NK cells, and conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are reduced as recently summarized elsewhere [1,2,3,4,5]. Therefore, metabolic alterations in tumor cells have emerged as a hallmark of cancer [6].
CD4+ regulatory T (Treg) cells play a major role in limiting anti-tumor immunity, and Treg cell accumulation in tumors is often negatively associated with clinical outcomes and immunotherapeutic efficacy [7, 8]. While strategies that promote Treg cell depletion or dysfunction may overcome the obstacles with immunotherapeutic efficacy, these strategies can be associated with the development of autoimmune disorders owing to the requirement of Treg cells for mediating immunosuppression under homeostasis. Thus, it is critical to determine specific approaches to limit Treg cell immunoregulatory activity in the TME while minimizing the systemic impacts on disrupting immune tolerance or tissue homeostasis. In contrast to those immune cell types that restrict tumor growth, emerging studies establish that Treg cells often undergo metabolic adaptation to maintain immunosuppressive function in the TME. In this review, we discuss mechanisms underlying Treg cell immunosuppressive function within the TME, with a focus on cellular metabolism as a primary factor underlying the ability of Treg cells to thrive in the TME. First, we discuss mechanisms of Treg cell immunosuppressive function in the TME. Then, we describe how cellular metabolism and nutrient or metabolic communication shapes Treg cell stability and function in the TME and the consequences on anti-tumor immunity. Given their high expression of immune checkpoint molecules, we discuss how altering Treg cell metabolism impacts ICB efficacy, and conversely, how ICB affects Treg cell metabolic function. Finally, we summarize our current understanding of the specific molecular and metabolic processes underlying intratumoral Treg cell function.
Malicious compliance: Treg cell guardianship of “self” at the cost of tumorigenesis
Treg cells are a functionally and metabolically unique arm of the adaptive immune system that is responsible for maintaining immune homeostasis and tissue tolerance. Whereas pro-inflammatory functions of conventional T cells help eliminate invading pathogens or tumor cells, Treg cells suppress pro-inflammatory immune cell activation via multiple mechanisms [9]. Treg cells differentiate either directly from thymic precursors (called tTreg cells) or from naïve CD4+ T cells in peripheral tissues (called pTreg cells) including tumors; further, they are defined by expression of the master transcription factor FOXP3 [10] that controls the expression of many factors critical for Treg cell immunosuppressive function such as CTLA4 and ICOS [11]. Indeed, mice lacking functional FOXP3 from birth [12, 13] or adult mice undergoing Treg cell ablation [14] develop a fatal lymphoproliferative disease due to aberrant activation of T cells. This disease effect is reversed by genetically reinstating FOXP3 expression in CD4+ T cells [15], demonstrating that Treg cells are both necessary and sufficient to maintain immune homeostasis. Finally, Treg cells are highly heterogeneous and display differential gene expression and epigenetic profiles, corresponding to their specific activation state or tissue ___location [16,17,18].
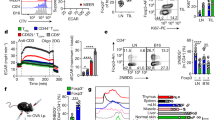
Though Treg cells are indispensable for immune tolerance and the prevention of autoimmunity, their suppressive function is detrimental to anti-tumor immunity. Since tumor cells originate from “self” tissues, tumors may exploit the self-antigen-sensing function of Treg cells. For example, self-antigen-specific (albeit tumor-non-reactive) Treg cells are enriched in prostate tumors [19]. In addition, TCR repertoire analyses have revealed considerable heterogeneity among intratumoral Treg cells, including those that are specific for tumor-associated antigens or neoantigens [20] or those that have differentiated from previously activated conventional CD4+ T cells [21, 22]. Treg cell accumulation and/or increased ratio of Treg cells:CD8+ T cells in tumors is often negatively associated with patient prognosis and survival [23, 24], including in ovarian [25, 26], breast [27, 28], lung [29, 30], and liver [31, 32] cancers. Further, Treg cells are abundant within the TME of “hot” tumors [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32] and limit the pro-inflammatory functions of innate and adaptive immune cells via multiple mechanisms as described below (Fig. 1).
Treg cells mediate immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment (TME) through various cell contact-dependent and contact-independent mechanisms. Treg cells migrate in proximity to dendritic cells (DCs) in the TME via the CXCL9–CXCR3 chemokine chemokine receptor axis. Molecules expressed on the Treg cell surface, such as CTLA4, LAG3, and TIGIT, bind to CD80/CD86, MHC-II, and CD155, respectively, on antigen presenting cells (APCs) such as DCs, thereby limiting the availability of these stimulatory signals for conventional T cells (e.g., CD8+ T cells). Treg cells sequester IL-2 via expression of the high-affinity IL-2 receptor CD25. Treg cell-derived immunosuppressive cytokines limit the development of effector T cells (by IL-10), memory T cells (by IL-35), and also the migratory and cytotoxic capacity of CD8+ T cells (by TGF-β). Treg cells produce granzymes and perforin for cytotoxic and cytolytic effects on CD8+ T cells. Extracellular ATP (eATP) is enzymatically converted to adenosine by the CD39 and CD73 ectoenzymes expressed on Treg cells, resulting in suppression of anti-tumor immunity. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) produce IL-23 in the TME, which maintains highly suppressive effector Treg (eTreg) cells in the TME. In turn, Treg cells indirectly support TAM phenotypes via suppression of CD8+ T cells.
Conventional T cells are major mediators of anti-tumor immunity and require antigen (via TCR recognition; signal 1), co-stimulatory (signal 2), cytokine (signal 3), and nutrient (e.g., glucose, amino acids, lipids; signal 4) signals for their activation and effector differentiation [33, 34]. Treg cells can disrupt co-stimulatory signals between antigen-presenting cells (APCs). For example, Treg cells impede DC–T cell interactions via expression of CTLA4, which competes with CD28 co-stimulatory receptor (expressed on T cells) for binding to CD80 or CD86 (expressed on adjacent DCs), culminating in decreased T cell activation. CTLA4+ Treg cells also directly extract CD80 and CD86 co-stimulatory molecules from APCs via trogocytosis [35], and intratumoral DCs show increased expression of these molecules upon depletion of intratumoral Treg cells [36]. Intratumoral Treg cells also highly express the checkpoint molecule LAG3 [37, 38], which competes for MHC-II binding with TCR and reduces expression of co-stimulatory molecules on APCs [38]. Additionally, TIGIT+ Treg cells enforce the tolerogenic function of DCs, owing to the competitive binding of TIGIT to the co-stimulatory molecule CD155, thereby limiting its engagement of CD226 expressed by T cells [39].
Intratumoral Treg cells also disrupt APC co-stimulation by exploiting CXCL9–CXCR3 chemokine signaling, resulting in DCs preferentially interacting with Treg cells over CD8+ T cells [40]. Another critical immunosuppressive mechanism of Treg cells is IL-2 sequestration. Specifically, Treg cells highly express IL-2Rα (CD25) [41], which has a much higher affinity for IL-2 than IL-2Rβ (CD122) chain expressed by conventional T cells [42], thereby decreasing IL-2 availability for nearby conventional T cells. The combined restriction of signals 2 and 3 consequently impedes the survival, differentiation, and anti-tumor function of T cells. Interestingly, reinvigoration of CD8+ T cells by anti-PD-1 ICB increases IL-2 production, which in turn increases ICOS expression on Treg cells to increase their stability and accumulation in tumors. Such effects dampen the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy and can be blocked by pre-treatment with anti-ICOSL antibody [43]. Of note, the cytokine IL-23 is produced by tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and maintains a highly suppressive effector Treg (eTreg) cell phenotype in tumors [44], highlighting complex cell–cell communication between Treg cells and other immune cells in the TME.
Treg cells also utilize cell contact-independent mechanisms to suppress immune cell functions. The immunosuppressive cytokines IL-10 and IL-35 are expressed by distinct intratumoral Treg cell populations, and such heterogeneity enables the suppression of both effector (via IL-10) [45, 46] and memory (via IL-35) [45,46,47] T cell responses. TGF-β is another immunosuppressive cytokine produced by Treg cells, leading to defects in CD8+ T cell cytotoxic function and trafficking to tumors [48, 49]. Intratumoral Treg cells may also express the surface ectoenzymes CD39 and CD73 that convert extracellular ATP to adenosine, a metabolite with immunosuppressive effects as described in more detail later in this review [50, 51]. Finally, Treg cells can also produce granzymes and perforin to exert direct cytotoxic function against pro-inflammatory immune cells, which impacts anti-tumor immune cells [52]. Taken together, Treg cells deploy multiple strategies to suppress anti-tumor immunity, and the functional redundancies and/or adaptation between these mechanisms likely underlie why direct targeting of Treg cell suppressive functions is challenging.
Tumors as a favorable metabolic niche for Treg cells
Cellular metabolism has emerged as a function-defining feature of immune cells and putative therapeutic target. Treg cells are metabolically distinguished from conventional T cells. As compared with effector CD4+ T cells, Treg cells are less dependent on glycolysis and instead rely upon mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) to produce energy [53,54,55], and these metabolic characteristics are regulated by FOXP3 [56]. Accordingly, mitochondrial metabolism plays a critical role in orchestrating Treg cell survival and suppressive function in vivo [57,58,59,60]. Mechanistically, mTOR- and MYC-dependent signaling drive metabolic reprogramming in Treg cells to support mitochondrial biogenesis and fitness, as well as lipid biosynthesis and downstream post-translational modifications; these metabolic pathways and signaling processes dictate Treg cell activation and suppressive function [57, 58, 61,62,63]. Recent studies also identified nutrient transport, sensing, and signaling mechanisms as crucial upstream signals mediating mTORC1 activation in Treg cells [64, 65]. Nonetheless, mTOR-associated signaling pathways must be carefully balanced to provide enough energy for proliferation and suppressive function without losing FOXP3 stability and Treg cell identity. For example, mice with Treg cell-specific deletion of mTOR [57] or the obligate mTORC1 complex molecule Raptor (but not the obligate mTORC2 complex molecule Rictor) [62] develop a severe, fatal autoimmune disease. However, mice with uncontrolled mTORC1/2 signaling in Treg cells, such as due to Treg cell-specific deletion of ATG7 [66] (mediated by mTORC1 activation) or PTEN [67, 68] (caused by increased mTORC2 function), or mice with Treg cell-specific overexpression of glucose transporter GLUT1 [56] also develop autoimmune symptoms due to decreased FOXP3 stability and Treg cell function; all of these phenotypes are associated with aberrant glycolysis [56, 66,67,68]. Thus, there is a “Goldilocks” effect of mTOR signaling and metabolic programs for tuning Treg cell function [69]. It is becoming more appreciated that Treg cells are metabolically heterogeneous [70,71,72,73,74,75,76]. Emerging studies highlight that the nutrient and metabolic requirements of different Treg cell states are shaped by immune and tissue contexts [77,78,79], including in tumors, and that the capacity to metabolically adapt to tissue niches underlies a functional advantage of Treg cells to thrive within tumors (Fig. 2). In this section, we discuss how specific features of the TME promote immunosuppression, and the metabolic mechanisms involved in enhancing Treg cell accumulation and function to limit anti-tumor immunity.
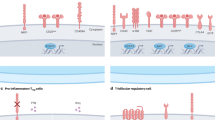
A Treg cells uptake available lactate in the TME via the lactate transporter MCT1. Lactate is converted to pyruvate via lactate dehydrogenase and then shuttled into the TCA cycle to support cellular ATP production and overall metabolic fitness. Increased intracellular lactate also promotes Treg cell differentiation and immunosuppressive function by enhancing TGF-β signaling and CTLA4 expression. Likewise, glucose uptake via its transporter GLUT1 is another mechanism for cellular energy production. Intratumoral Treg cells rely on fatty acid metabolism for energy production and FOXP3 stability, including de novo fatty acid synthesis and uptake of exogenous fatty acids via CD36. Increased expression of antioxidant mechanisms such as GPX4 and serine-derived glutathione production helps to shield Treg cells from ROS-induced damage that is associated with increased fatty acid oxidation. Hypoxic conditions in the TME activate HIF-1α, which boosts glycolytic metabolism in Treg cells and promotes Treg cell migration into tumors (see text for more details). B Extracellular adenosine levels are increased in the TME, owing to its conversion from eATP via CD39 and CD73 expressed on Treg cells. Adenosine has immunosuppressive effects on CD8+ T cells and certain antigen-presenting cell populations (not depicted). Tumor and myeloid cells (e.g., myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs)) in the TME express indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), which metabolizes tryptophan to kynurenine. Kynurenine promotes Treg cell differentiation and function, which inhibits CD8+ T cell function.
In the TME, immune cells must adapt to nutrient scarcity, hypoxia, and low pH conditions [2]. One hallmark of malignant cell transformation is the switch to glycolytic catabolism to support aberrant cellular proliferation [2]. This process is associated with enhanced cellular uptake of nutrients such as glucose and amino acids. Consequently, the finite availability of these in-demand nutrients, combined with an abundance of lactate produced by tumor cells, leads to suboptimal microenvironmental conditions to support anti-tumor immune cell function and survival. As opposed to conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, Treg cells more readily metabolically adapt to the TME, and this metabolic plasticity selectively sustains their accumulation and immunosuppressive effects as discussed below (Fig. 2A). For example, intratumoral Treg cells utilize extracellular lactate by increasing expression of its transporter monocarboxylate transporter-1 (MCT1) and the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, which shuttles lactate into the TCA cycle (via conversion to pyruvate) to support OXPHOS [80, 81]. Further, this mechanism effectively replenishes NAD+ stores in Treg cells but not in conventional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that oxidize excessive lactate, thereby limiting NAD+-dependent support of activation-associated glycolytic metabolism [82]. Elevated intracellular lactate also enhances OXPHOS in Treg cells by promoting expression of acetylglucosaminyltransferase, which is important for post-translational modification of mitochondrial proteins [83]. In addition to metabolic reprogramming effects, lactate promotes Treg cell stability by enhancing TGF-β signaling through SMAD3 [84]. Additionally, lactate uptake by Treg cells regulates RNA splicing machinery in intratumoral Treg cells; in turn, CTLA4 expression is induced, thereby promoting the efficacy of anti-CTLA4 therapy [85]. Further, anti-CTLA4 promotes metabolic rewiring in Treg cells to further destabilize their pro-tumorigenic function in glucose-deprived TME [86]. Interestingly, lactate causes a similar anti-inflammatory effect in TAMs, promoting an M2-like phenotype associated with decreased tumor control [87], which may also affect Treg cell–TAM interactions (i.e., via TAM-derived IL-23) in the TME [44]. Together, these studies demonstrate the multi-potent effects of lactate in negatively regulating pro-inflammatory gene programs in favor of immunosuppressive gene programs in the TME.
From a therapeutic perspective, limiting lactate production by tumor cells can decrease intratumoral Treg cell accumulation and function, as demonstrated in one study via treatment with the curcumin analog GO-Y030 [88]. These effects may be mediated by direct metabolic or signaling effects of lactate, as discussed above, or alterations of acidity in the TME. Indeed, tumor-derived lactate, together with elevated local CO2 due to hypoperfusion, can lower the pH of the TME, and there is emerging evidence that acidity promotes Treg cell differentiation and immunosuppressive function independently of lactate. Specifically, the enhanced differentiation of Treg cells upon treatment with lactate (pH 6.8) is abrogated with pH-neutral sodium lactate but recapitulated under HCl-acidified media conditions [89]. Additionally, Treg cell pretreatment with acidified media appears to increase their suppressive function in an adoptive transfer model, associated with increased tumor growth and impaired intratumoral CD8+ T cell infiltration [90]. Thus, more work is warranted to better understand the overlapping and distinct effects of lactate versus general acidity on intratumoral Treg cells.
Tumor cells must increase lipid synthesis to meet biosynthetic demands of proliferation, and also use lipids as an energy source for OXPHOS via fatty acid oxidation. As such, lipids are often plentiful in tumors, and alterations in lipid metabolism are linked to tumor progression and resistance to immunotherapies [91]. Similar to their adaptive utilization of lactate, Treg cells upregulate lipid metabolism pathways to support their survival and immunosuppressive functions in tumors [92,93,94]. Indeed, blockade of free fatty acid release by tumor cells or free fatty acid uptake by Treg cells (via anti-CD36 antibody treatment or Treg cell-specific deletion of CD36) decreases intratumoral Treg cell accumulation and reverses tumor resistance to anti-PD-1 treatment [93, 95]. Importantly, the adaptive capability to increase lipid storage is critical to maintain intratumoral Treg cell identity [96]. In addition to uptake of exogenous free fatty acids, intratumoral Treg cells increase de novo synthesis of fatty acids via activation of SREBPs and downstream fatty acid synthase (FASN), which supports Treg cell suppressive function by protecting against TCR signaling-mediated Treg cell fragility [92, 94]. Deficiency of SCAP (an obligatory regulator of SREBPs) or FASN in Treg cells inhibits tumor growth without systemic autoimmunity toxicity [92]. Of note, inhibition of FABP5 (a fatty acid binding protein) in Treg cells disrupts intracellular lipid trafficking and mitochondrial metabolic fitness, which increases the suppressive function of Treg cells [97]. Thus, deeper mechanistic dissection of distinct components involved in Treg cell lipid uptake, intracellular transport, and de novo synthesis is warranted to unravel the mechanisms underlying the complexities of lipid metabolism in intratumoral Treg cells.
In line with this notion, the sphingolipid intermediate sphinganine interacts with the transcription factor c-FOS and enhances its recruitment to target genes such as Pdcd1 (encodes PD-1) [98]. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) transcription factors, which are activated by certain lipids, also contribute to Treg cell biology. For example, PPAR-γ plays critical roles in Treg cell programming and accumulation in multiple non-lymphoid tissues [16, 99]. Additionally, PPAR-β functions downstream of CD36 to support lipid-associated metabolic adaptation of intratumoral Treg cells [93], thereby linking lipid metabolism to transcriptional regulation of Treg cells in tumors. Finally, steroid hormones such as glucocorticoids have well-known immunosuppressive effects, and it was recently shown that some tumors can enzymatically regenerate glucocorticoids from inactive metabolites, thereby dampening local immune responses [100]. Intratumoral Treg cells exposed to tumor-derived glucocorticoids showed enriched Treg cell activation gene signatures [100]. The pleotropic effects of glucocorticoids on Treg cells and non-Treg immune cells suggest a two-pronged mechanism for tumor cells to evade anti-tumor immunity.
Increased lipid catabolism is associated with the production of cellular ROS. Although intratumoral CD8+ T cells may also increase lipid uptake via upregulation of CD36, increased lipid peroxidation and ROS production in those cells induce ferroptotic cell death and ultimately dampen anti-tumor cytokine production [101, 102]. Further, Treg cells can be made susceptible to lipid peroxidation-induced ferroptosis via deletion of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) without affecting Treg cell homeostasis in other tissues [103], suggesting that redox balance dictates intratumoral Treg cell function. Accordingly, Treg cells also synthesize the critical antioxidant molecule glutathione (GSH), and disruption of serine-dependent GSH generation in Treg cells results in boosting of anti-tumor immunity, albeit at the expense of developing autoimmunity [104]. However, these autoimmune effects are rectified by feeding mice bearing GSH-deficient Treg cells a serine- and glycine-deficient diet [104], which is interesting considering that a serine-free diet also limits intratumoral Treg cell function and inhibits tumor growth [98]. Thus, intratumoral Treg cells prioritize the control of ROS, which represents a putative target to dampen Treg cell function in tumors.
Owing to limited vascularity, solid tumors often contain hypoxic regions that are conducive for the hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) activation, thereby reprogramming glucose metabolism towards the generation of lactate over pyruvate [60]. HIF-1α negatively regulates the differentiation of Treg cells in vitro by directly inhibiting FOXP3 [54, 105, 106]. However, HIF-1α enhances Treg cell differentiation and suppressive function under hypoxic conditions in vivo, such as in colon cancer [107] and inflammation [108]. Further, hypoxia promotes recruitment of Treg cells to tumors and helps trigger vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production for the expansion of intratumoral Treg cells [109, 110]. Similarly, hypoxia and HIF-1α support Treg cell migration into glioblastoma tumors, although Treg cell suppressive function is decreased under such conditions due to aberrantly increased glycolysis [60]. Accordingly, HIF-1α-deficiency boosts Treg cell suppressive function in hypoxic glioblastoma tumors [60], possibly due to their preferences for lactate or lipid metabolism as discussed above [81, 92,93,94].
Additionally, increased glycolysis may enhance the immunosuppressive function of activated Treg cells in humans [111], and thus, the specific roles of HIF-1α in different clinical contexts remain to be elucidated. Interestingly, excessive availability of the tumor-derived oncometabolite D-2-hydroxyglutarate destabilizes HIF-1α and boosts OXPHOS in Treg cells, thereby promoting their accumulation in tumors [112]. Besides glycolysis, HIF-1α can induce autophagy under hypoxic conditions [113]. Further, autophagy is required for Treg cell stability and survival [66, 114], as well as their function to suppress anti-tumor immunity and autoimmunity [66]. Beyond Treg cells, hypoxia-associated HIF-1α activation also promotes immunosuppressive phenotypes in tumor-resident γδ T cells [115] and TAMs [116], highlighting a broad effect of hypoxia in limiting anti-tumor immunity.
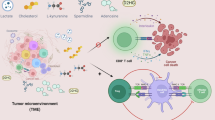
Treg cell differentiation and function are regulated by nutrient and metabolite communication with neighboring cells in the TME (Fig. 2B). Tumor cells, tolerogenic DCs, TAMs, and/or myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) can express indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). This enzyme reduces tryptophan availability and generates the immunoregulatory metabolite kynurenine, which can promote Treg cell differentiation and support the stability of activated Treg cells in the TME [117, 118]. Mechanistically, kynurenine directly promotes the nuclear localization and activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR), a transcription factor that is critical for Treg cell differentiation in the gut [119]. Inhibiting kynurenine–AHR interactions is sufficient to disrupt the IDO-associated immunosuppressive axis between intratumoral Treg cells and TAMs [120, 121]. Further, Treg cells may directly induce IDO expression in DCs via CTLA4–CD80 interactions [122], thereby fostering a positive feedback loop for immunosuppression in the TME. In addition, arginine is a critical amino acid to license mTOR signaling during Treg cell activation [65]. Interestingly, intratumoral Treg cells show increased expression of arginase-2 that dampens mTOR signaling, thereby maintaining Treg cell stability and functionality in tumors [123].
Treg cells also influence the function of neighboring immune cells by altering the type and availability of various nutrient or energy signals. For example, intratumoral Treg cells indirectly support SREBP function and lipid metabolism of immunosuppressive TAMs via suppression of CD8+ T cells [124], thereby driving an immunosuppressive feedforward loop in the TME. Another important example is Treg cell-dependent modulation of extracellular ATP, which signals through purinergic receptors to inhibit Treg cell function [125]. To circumvent this inhibitory effect, Treg cells have elevated expression of CD39 and CD73, which hydrolyze extracellular ATP to AMP and AMP to adenosine, respectively [50, 126]. Of note, adenosine activates A2A receptor signaling in effector T cells and APCs, which dampens the anti-tumor function of those cells [51, 126]. Further, mice lacking either CD39 or CD73 show enhanced anti-tumor immunity [127, 128]. Interestingly, CD39 and CD73 remain enzymatically active on Treg cells after undergoing cellular apoptosis, thereby providing a mechanism for continued immunosuppression in tumors upon Treg cell death [51]. As exhausted CD8+ T cells may upregulate CD39 expression and promote immunosuppression in tumors [129], this pathway is likely an important therapeutic target as discussed in more detail below. Collectively, these studies demonstrate that Treg cells are poised for metabolic adaptation within the TME.
Immune checkpoint blockade and Treg cell metabolism
Biologic therapies aimed at reinvigorating anti-tumor immune responses (e.g., anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 antibodies) may also positively affect Treg cells, and this phenomenon impairs the overall treatment efficacy. In this section, we discuss how ICB reshapes Treg cell metabolism and function, based primarily on studies in mouse models of cancer (Fig. 3).
Immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-1, LAG3, and CTLA4 help to stabilize Foxp3 expression by dampening PI3K–AKT signaling and glycolysis. TIM-3 expression is associated with enhanced glycolysis in Treg cells. Deletion of PD-1 or blockade of CTLA4 signaling is associated with increased PI3K–AKT signaling and glycolysis pathways in Treg cells, thereby reducing FOXP3 stability; this effect is associated with increased autocrine IFN-γ signaling, which further destabilizes Treg cell identity.
Inhibitory molecules such as PD-1, LAG3, and CTLA4 on Treg cells serve important roles in suppressing the activation of nearby immune cells and represent perturbation targets to unleash anti-tumor immunity. Accordingly, though anti-PD-1 ICB targeted at CD8+ T cells has shown clinical efficacy, there remains a high rate of non-responder patients, and such effects may be partly attributed to increased function and accumulation of PD-1+ Treg cells upon anti-PD-1 treatment [130, 131]. Further, the uptake of lactate by Treg cells within highly glycolytic tumors directly promotes PD-1 expression, thereby facilitating an anti-PD-1 treatment-induced reinvigoration effect on Treg cells associated with treatment failure [80]. In turn, PD-1 signaling inhibits PI3K–AKT signaling and preserves the metabolic fitness of Treg cells [130, 132, 133]. Of note, PD-1 is a complex regulator of Treg cell biology. PD-1 restrains Treg cell activation, with PD-1 targeting in Treg cells improving their immunosuppressive function in mouse models of autoimmunity owing to the accumulation of highly activated eTreg cells [131, 133]. Additionally, deficiency of LKB1, a crucial regulator of metabolic homeostasis, results in pronounced loss of Treg cell function associated with aberrant upregulation of PD-1 and other immunoregulatory molecules [134], suggesting that PD-1 inhibits Treg cell function under homeostasis. In contrast, PD-1 deletion specifically in Treg cells reduces their stability or promotes fragility to impede tumor growth [92, 132]. Nonetheless, anti-PD-1 blockade often promotes the accumulation of highly suppressive eTreg cells in the TME, thereby limiting ICB efficacy and promoting tumor growth [43, 130, 131]. Although intrinsic PD-1 signaling in Treg cells may be involved as described above, these effects are also attributed to effects of anti-PD-1 blockade at increasing intratumoral IL-2 production by CD8+ T cells, which cooperates with ICOS signals to promote eTreg cell expansion in tumors as noted above [43]. Thus, combination therapy approaches to co-target PD-1 with other Treg cell-targeted approaches will likely be beneficial to counteract the effects on improving Treg cell function under conditions of PD-1 blockade.
More recently, LAG3 was shown to inhibit PI3K–AKT and MYC signaling in Treg cells [37], suggesting that the shortcomings of different ICB targets may be mechanistically linked to metabolic invigoration of Treg cells in tumors, though this has not yet been clinically established. Of note, while PTEN deletion in Treg cells leads to the development of autoimmunity [67, 68], PTEN targeting also reduces Treg cell suppressive function in the TME [118]. Interestingly, Treg cells rely upon the PI3K isoform p110δ, whereas p110δ, p110α, and p110β isoforms are functionally redundant in conventional T cells, indicating that pharmacological or genetic perturbation of p110δ may largely affect Treg cells over conventional T cells. Indeed, mice with Treg cell-specific inactivation of p110δ or those treated with a p110δ-specific inhibitor show increased anti-tumor immunity [135, 136], further illustrating the metabolic “Goldilocks” effect for Treg cell function [69]. Further, intermittent dosing with the p110δ inhibitor AMG319 circumvents systemic immune-related adverse events while preserving anti-tumor immune phenotypes in humans and mice [137]. Direct pharmacological activation of AKT also boosts anti-tumor immunity by converting Treg cells into TH1-like, IFN-γ-producing cells, thereby destabilizing FOXP3 expression [138]. Though TH1-like Treg cells have important immunosuppressive functions, especially in the contexts of infection or autoimmunity [139], the conversion of intratumoral Treg cells into TH1-like Treg cells (and autocrine IFN-γ signaling) is mechanistically critical for anti-PD-1 ICB efficacy [140]. Additionally, scRNA-seq analysis in human patients has found that TH1-like Treg cells are enriched in tumors that are responsive to anti-PD-1 ICB [141], and PD-1 deletion specifically in Treg cells causes intratumoral Treg cells to produce IFN-γ [92]. Together, these findings suggest that therapeutic manipulation of PI3K–AKT signaling in intratumoral Treg cells can improve anti-PD-1 ICB efficacy via its direct causal link to IFN-γ-induced Treg cell fragility.
As discussed above, Treg cells take advantage of the lactate-rich TME by utilizing this by-product for metabolic and functional support [80,81,82]. However, glycolytic activity is markedly variable, especially between tumors originating in different tissues [142] (e.g., lung versus liver), and these differences in lactate availability may affect Treg cell phenotypes that are relevant to ICB. Specifically, lactate promotes PD-1 expression on intratumoral Treg cells via increased transcription factor NFAT1 activity; thus, Treg cells from more glycolytic tumors show increased PD-1 expression and are resistant to anti-PD-1 ICB [80]. In addition to blocking co-stimulatory molecules, CTLA4-mediated interactions between Treg cells and adjacent immune cells can dampen immune cell glycolysis. Thus, in tumors with low glycolytic activity (i.e., higher glucose availability for infiltrating immune cells), anti-CTLA4 blockade improves anti-tumor immune responses by permitting increased glycolysis; this is beneficial for CD8+ T cell activation and effector function but is detrimental to Treg cell stability [86]. Of note, human Treg cells require glycolysis to support FOXP3 expression, proliferation, and suppressive function [76, 143], suggesting that anti-CTLA4 or other ICB therapies may impart discrete mechanistic effects in human and mouse Treg cells. Likewise, TIM-3 is another clinically relevant inhibitory molecule that is highly expressed on intratumoral Treg cells [144, 145], but its expression is instead associated with enhanced glycolysis and dampened OXPHOS metabolic phenotypes [146]. Further, TIM-3+ Treg cells have enhanced suppressive function and increased expression of IL-10, and mice with enforced expression of TIM-3 on Treg cells show impaired anti-tumor immunity and increased tumor growth [146]. This positive association of suppressive function and glycolytic metabolism suggests a complex signaling network downstream of inhibitory molecules that direct Treg cell function in tumors; thus, more work is needed to clarify the discrete metabolic effects of inhibitory molecules, especially for those effects that may be species-dependent (i.e., human versus mouse). Taken together, these studies indicate that lowering metabolic competition may prime the TME for efficacious ICB effects by shifting the conditions favoring Treg cell function to those favoring CD8+ T cells.
As previously stated, increased lipid metabolism is another important metabolic adaptation of intratumoral Treg cells [92,93,94], and lipid synthesis pathways are critical for PD-1 expression (but not other Treg cell-activation-associated molecules) specifically in intratumoral Treg cells [92]. Accordingly, inhibition of lipid synthesis in Treg cells leads to decreased PD-1 expression concomitant with enhanced PI3K–AKT signaling and IFN-γ production, and these effects sensitize B16F10 melanoma to anti-PD-1 treatment [92]. In radiotherapy-treated glioblastoma, anti-PD-1 treatment after receiving radiotherapy leads to a selective increase of highly suppressive CD103+ Treg cells with a selective enrichment of lipid metabolism signatures [147]. Further, Treg cell depletion following radiotherapy reverses the effects of anti-PD-1 treatment, which induces anti-tumor immune responses against ICB-resistant glioblastoma [147]. Together, these studies suggest that targeting lipid metabolism in intratumoral Treg cells may be critical for improving ICB efficacy.
Aside from TME-derived molecules, host factors may also influence anti-tumor immunity by acting upon Treg cells. Obesity is a systemic metabolic disorder associated with excessive adipose tissue and increased incidence and progression of cancers [148], and it is increasingly understood that obesity is accompanied by dysregulated immunity [149, 150]. PPAR-γ+ Treg cells maintain immune and metabolic homeostasis within visceral adipose tissue (VAT) [151]; however, VAT-resident Treg cells are decreased in frequency in obesity, and this effect is coincident with increased pro-inflammatory responses [152, 153]. Despite an increase in baseline inflammation, obesity has a suppressive impact on anti-tumor immunity [154] that is possibly due to suboptimal anti-tumor immune surveillance [155]. Intriguingly, several studies highlight a positive correlation between obesity and responsiveness to ICB [155,156,157], termed the ‘obesity paradox’. One proposed mechanism for this phenomenon is increased tumor immunogenicity due to impaired CD8+ T cell function (prior to ICB), which imparts a functional advantage to those CD8+ T cells reinvigorated by ICB [155]. Nonetheless, the effects of obesity on Treg cell metabolism and immunosuppressive function in the TME remain incompletely understood.
The microbiome is another factor with a proven influence on cancer development [158, 159] and immunotherapeutic efficacy [160,161,162]. In the intestines, Treg cell differentiation and function are regulated by microbiota-derived metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids [163, 164] and secondary bile acids [165,166,167], which support Treg cell mitochondrial fitness. The possible impact of microbiota-derived metabolites on Treg cells in cancer is also emerging. Indeed, patients with elevated microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids have increased proportions of Treg cells and are more resistant to anti-CTLA4 treatment [168], suggesting that microbiome composition-associated effects on Treg cells are clinically relevant and may be used as a prognostic marker or manipulated for ICB efficacy. Taken together, metabolism-associated host factors such as obesity and microbiome composition have clear consequences in cancer, and thus, future work should mechanistically dissect how Treg cells are affected by these important aspects.
The search for specificity in targeting intratumoral Treg cells
Treg cells are a major factor limiting the potential of immunotherapies. However, it is now understood that Treg cell functions extend to homeostatic tissue maintenance (e.g., in the skin [169]) and wound repair (e.g., in damaged muscle tissue [170]), and adoptive Treg cell therapies have been proposed for treatment of non-immune diseases [171]. Moreover, depletion of bulk Treg cells may consequently induce conventional CD4+ T cells to express the immunosuppressive cytokine IL-10 [172], causing a paradoxical immunosuppressive barrier to anti-tumor immunity. Awareness of these and other possible adverse events associated with the indiscriminate inhibition of Treg cells has resulted in much effort to identify molecular mechanisms utilized specifically by Treg cells in tumors, as reviewed elsewhere [7, 8, 24, 171, 173]. In this section, we describe the potential therapeutic targets relevant to this notion, with a particular focus on metabolism-associated molecules that have shown promise as therapeutic targets (Fig. 4).
Various molecules and/or pathways may be exploited to specifically target Treg cells in the TME. Those targets expressed on the cell surface include the extracellular adenosine-producing enzymes CD39 and CD73, the Treg cell activation marker 4-1BB, the receptor for VEGF (VEGF-R), the invariant chain of MHC-II (CD74), and the neutrophil-associated marker CD177. Additionally, some therapeutic targets are associated with cell signaling pathways, including the ATPase p97 in complex with its co-factor NPL4 (p97–NPL4 complex), the CARMA1–BCL10–MALT1 (CBM) complex, and LCK–ZAP–70 signaling downstream of TCR activation. The histone demethylase JMJD1C serves as an epigenetic modifier target to disrupt intratumoral Treg cells. Transcription factors whose disruption is associated with impaired intratumoral Treg cell function include FOXP3E2, FOXO1, c-REL (subunit of the canonical NF-κB complex), BATF, and TRPS1. Finally, direct metabolic targets include SREBP and FASN, associated with de novo fatty acid synthesis, and the fatty acid transporter CD36.
Given that intratumoral Treg cells express CD39 and CD73 to mediate immunoregulatory effects [51, 125], this enzymatic pathway is of therapeutic interest. Indeed, antibody-mediated neutralization of CD39 and/or CD73 increases effector T cell activation and reduces tumor growth [127, 128, 174, 175]. Further, CD73 blockade synergizes with anti-PD-1 therapy in murine models of pancreatic cancer [175]. The expression of the Treg cell-activation-associated molecule 4-1BB is also linked to various types of cancers [176], highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. Mice with autophagy-defective Treg cells also show enhanced anti-tumor immunity and control of tumor growth [66, 177, 178], suggesting that this may be a viable therapeutic target. Accordingly, tumor cell-intrinsic upregulation of autophagy is a common mechanism for immune evasion via decreased MHC-I expression on the cell surface [179], further indicating that targeting of this process may improve disease outcomes. Indeed, genetic or pharmacological inhibition of autophagy enhances anti-tumor immunity and sensitizes previously non-responding tumors to ICB [179]. Moreover, inhibition of tumor cell-intrinsic autophagy reduces tumor growth, with such effects partly related to reduced intratumoral Treg cell accumulation [180]. Thus, tumor cell–Treg cell metabolic interplay via autophagy may shape cancer therapeutic outcomes.
Other studies have identified the expression of unique genes in intratumoral Treg cells from various cancer types. Developing tumors produce angiogenic signals such as VEGF, and Treg cells expressing VEGF receptor (VEGF-R) infiltrate tumors and proliferate in response to tumor-derived VEGF [109, 110, 181]. Antibody-mediated blockade of VEGF–VEGFR signaling limits intratumoral Treg cell accumulation and sensitizes ICB-resistant tumors to anti-PD-1 treatment [181, 182]. Additionally, intratumoral Treg cells in humans overexpress CD74 (the invariant chain of MHC-II), and CD74-deficient Treg cells show decreased activation and accumulation in tumors [183]. The neutrophil-associated marker CD177 is also enriched on Treg cells in renal clear cell carcinoma patients with poor prognoses [184]; antibody-mediated blockade or Treg cell-specific deletion of CD177 decreases Treg cell accumulation in tumors and improves tumor control [184]. Finally, a previously known anti-tumor drug target was recently shown to have an unexpected role in intratumoral Treg cells; specifically, the ATPase p97 in complex with co-factor NPL4 functions to dampen STAT3 signaling and preserve Treg cell identity and function in tumors [185]. Future studies can explore whether and how these molecules interplay with metabolism to shape Treg cell stability and function.
TCR-related signaling is another area of interest to target intratumoral Treg cells. For example, disruption of the CARMA1–BCL10–MALT1 (CBM) complex via deletion of one Carma1 allele induces an IFN-γ+ fragile Treg cell phenotype, which improves overall tumor control and sensitizes tumors to ICB [186], thereby demonstrating a mechanism to modify TCR–PKC signaling and “rewire” Treg cell function. Interestingly, a small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor (imatinib) used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia has off-target inhibitory effects on LCK and ZAP-70, which are downstream of TCR activation. Imatinib treatment promotes a selective loss of activated Treg cells, but not tumor antigen-specific CD8+ T cells, due to the relatively lower levels of tonic LCK signaling in activated Treg cells, thus rendering them more susceptible to TCR deprivation-induced apoptosis [187].
FOXP3 proteins include several splicing variants associated with differential impacts on cellular metabolism and suppressive function [143], suggesting that these variants could be involved in regulating intratumoral Treg cells. Indeed, the exon 2 splicing variant of FOXP3 (FOXP3E2) is promoted by CXCL12–CXCR4 signaling in the TME and is associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer [188]. Further, FOXP3E2+ Treg cells show relative impairments in glycolysis compared to Treg cells expressing full-length FOXP3 [143, 188], further supporting the notion of enhanced metabolic adaptation of Treg cells within the TME. Besides FOXP3, additional transcription factors regulate and coordinate Treg cellular functions with context- and/or tissue-dependent specificity, including the support of Treg cell identity [189]. Because their perturbance can result in many downstream effects being altered, including metabolic effects [54, 58, 92, 190, 191], the search for putative transcription factor targets in intratumoral Treg cells has been a primary area of focus. One of the first candidates to be described is the AKT signaling target FOXO1, which plays critical roles in Treg cell activation, metabolism, and survival [77, 192]. Activated Treg cells dampen FOXO1 signaling, which allows for expression of trafficking molecules and accumulation in tissues such as tumors [193]. Importantly, bi-allelic expression of a constitutively active FOXO1 mutant results in systemic functional defects in Treg cells and autoimmune disease; however, mono-allelic expression of this constitutively active mutant reduces Treg cell accumulation specifically in tumors, thus enhancing anti-tumor immunity without systemic autoimmune effects [193]. Additionally, c-REL, a subunit of the canonical complex of the transcription factor NF-κB, is critical for the differentiation of activated Treg cells commonly found in tumors [194, 195]. Accordingly, c-REL inhibition in Treg cells reduces their function in tumors and potentiates the effects of anti-PD-1 ICB [196]. BATF is also a major coordinator of Treg cell activation and function in tumors [197, 198], although the function of BATF also extends to Treg cell functions in multiple non-lymphoid tissues [199, 200]. A more recent study used pooled CRISPR–Cas9 screening combined with the chimeric immune editing (CHIME) model to investigate putative intratumoral Treg cell master transcriptional regulators nominated from analysis of primary human patient samples [201]; this study described TRPS1 as a “master” transcriptional regulator of intratumoral Treg cells versus peripheral Treg cells. As such, genetic or pharmacological inhibition of TRPS1 specifically depletes intratumoral Treg cells, inhibits tumor growth, and increases the efficacy of anti-PD-1 ICB [201]. Similar to context-specific transcription factors, Treg cells in different tissues are epigenetically heterogeneous [16, 202], suggesting that epigenetic modulators may also be targetable in intratumoral Treg cells. Indeed, the histone demethylase JMJD1C limits AKT signaling-induced IFN-γ production in intratumoral Treg cells, and inhibiting JMJD1C function in Treg cells selectively impairs intratumoral, and not peripheral, Treg cell function [203].
Advances in biomedical engineering and synthetic biology have allowed for exciting new strategies in anti-tumor immunotherapy. For example, because of the requirement for IL-2 signaling for successful rejuvenation of intratumoral CD8+ T cells, one study engineered anti-PD-1 paired with a low-affinity IL-2 molecule, which showed reduced effects on Treg cells but stronger and more specific effects on CD8+ T cells [204]. Another biomedically engineered antibody with bi-specific targeting of CD25 and TIGIT promotes Treg cell depletion specifically in tumors [205]. Moreover, rather than directly inhibiting the molecular and metabolic pathways that confer functional advantages to Treg cells in tumors, it may be feasible to imbue those features into CD8+ T cells used in ACT. As proof-of-principle, CD8+ T cells with enforced expression of FOXP3 gain Treg cell-associated metabolic adaptations in tumors, including enhanced lipid metabolism in nutrient-limited conditions [206]. When used for ACT, these FOXP3+CD8+ T cells showed improved recruitment and cytotoxicity in tumors [206]. Similar immunometabolic effects are observed in intratumoral CD8+ T cells upon treatment with a bioengineered IL-10–Fc fusion protein [207] and in CAR T cells with enforced expression of IL-10 [208]. In summary, targeting Treg cell accumulation or immunosuppressive functions holds tremendous promise for cancer immunotherapy, and we are only beginning to understand how targeting Treg cell metabolism contributes to these therapeutic benefits.
Conclusions
Treg cells are a critical component of the immune system in distinguishing self from non-self and in minimizing the deleterious effects of inflammation. However, such functions of Treg cells underlie why many tumors are non-responsive to immunotherapies, and thus, a greater understanding is needed for how Treg cells mechanistically thrive within the TME. Understanding these context-dependent mechanisms is especially important, due to adverse effects of systemic Treg cell depletion or functional blockade [171, 209]. There is increasing evidence that Treg cells metabolically adapt to the harsh TME, and these unique survival mechanisms may be the key to specifically targeting those cells and also informing the future design of CD8+ ACT [206]. In this review, we have discussed how metabolic factors shape Treg cell function against tumors and metabolism-related targets that affect intratumoral Treg cell biology of various cancers. These important findings have translational potential, either as new therapies or for use to bolster existing therapies in combination.
Cancer is a highly heterogeneous condition with starkly different inter-tissue and intra-tissue phenotypes that are likely to impact Treg cell metabolism, heterogeneity, and function. Our knowledge of the metabolic adaptations of Treg cells in tumors has advanced in recent years. However, there is still much to be learned about how Treg cells seemingly thrive in this harsh environment, and also how these findings in pre-clinical models translate into the clinic. Recent advances in single-cell and/or spatial metabolomics [1, 210] combined with assays to uncover transporters, sensors, or signaling transducers of nutrients or metabolites [64] will advance our understanding of how metabolic adaptation or signaling regulates intratumoral Treg cell function. In this regard, flow cytometry-based approaches such as SCENITH [211] could be used to explore metabolic profiles at the single-cell level. Additionally, in vivo tracing of stable isotopes and imaging analysis by positron emission tomography may illuminate the spatial regulation of Treg cell metabolism in the TME as previously demonstrated in other cell types [212, 213], thereby enhancing our knowledge of nutrient utilization, metabolic reprogramming, and metabolic signaling that shapes intratumoral Treg cell function.
The inhibition of intratumoral Treg cells can enhance tumor sensitization to ICB, supporting the notion that combination therapy to neutralize Treg cell functions in tumors may unleash the full potential of ICB. However, we have limited understanding of the specific pathways that shape intratumoral Treg cell fitness versus their counterparts in healthy lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues. To this end, powerful screening technologies such as CRISPR–Cas9 have revolutionized our ability to discover and test previously unknown regulators of T cell function [214]. Though genome-wide CRISPR screening can identify targets to improve CD8+ T cell-mediated ACT [215, 216], the use of CRISPR-based screening in Treg cells has been less commonly applied. Modified CRISPR-based strategies such as CHIME [201, 217, 218] may permit screening for functional regulators of Treg cells, including novel targets that convey functional advantages to Treg cells in tumors. Further, the application of single-cell CRISPR screening technology [219] to Treg cells will potentially illuminate unknown gene regulatory networks and Treg cell heterogeneity to exploit for therapeutic benefit.
References
Chapman NM, Chi H. Metabolic rewiring and communication in cancer immunity. Cell Chem Biol. 2024;31:862–83.
Arner EN, Rathmell JC. Metabolic programming and immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2023;41:421–33.
Kao KC, Vilbois S, Tsai CH, Ho PC. Metabolic communication in the tumour-immune microenvironment. Nat Cell Biol. 2022;24:1574–83.
Zhang X, Ji L, Li MO. Control of tumor-associated macrophage responses by nutrient acquisition and metabolism. Immunity. 2023;56:14–31.
Bantug GR, Hess C. The immunometabolic ecosystem in cancer. Nat Immunol. 2023;24:2008–20.
Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:31–46.
Tay C, Tanaka A, Sakaguchi S. Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells as targets of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Cell. 2023;41:450–65.
Togashi Y, Shitara K, Nishikawa H. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunosuppression - implications for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019;16:356–71.
Dikiy S, Rudensky AY. Principles of regulatory T cell function. Immunity. 2023;56:240–55.
Savage PA, Klawon DEJ, Miller CH. Regulatory T cell development. Annu Rev Immunol. 2020;38:421–53.
Zheng Y, Josefowicz SZ, Kas A, Chu TT, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Genome-wide analysis of Foxp3 target genes in developing and mature regulatory T cells. Nature. 2007;445:936–40.
Brunkow ME, Jeffery EW, Hjerrild KA, Paeper B, Clark LB, Yasayko SA, et al. Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat Genet. 2001;27:68–73.
Wildin RS, Ramsdell F, Peake J, Faravelli F, Casanova JL, Buist N, et al. X-linked neonatal diabetes mellitus, enteropathy and endocrinopathy syndrome is the human equivalent of mouse scurfy. Nat Genet. 2001;27:18–20.
Kim JM, Rasmussen JP, Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cells prevent catastrophic autoimmunity throughout the lifespan of mice. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:191–7.
Hu W, Wang ZM, Feng Y, Schizas M, Hoyos BE, van der Veeken J, et al. Regulatory T cells function in established systemic inflammation and reverse fatal autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2021;22:1163–74.
DiSpirito JR, Zemmour D, Ramanan D, Cho J, Zilionis R, Klein AM, et al. Molecular diversification of regulatory T cells in nonlymphoid tissues. Sci Immunol. 2018;3:eaat5861.
Miragaia RJ, Gomes T, Chomka A, Jardine L, Riedel A, Hegazy AN, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics of regulatory T cells reveals trajectories of tissue adaptation. Immunity. 2019;50:493–504 e497.
Munoz-Rojas AR, Mathis D. Tissue regulatory T cells: regulatory chameleons. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:597–611.
Malchow S, Leventhal DS, Nishi S, Fischer BI, Shen L, Paner GP, et al. Aire-dependent thymic development of tumor-associated regulatory T cells. Science. 2013;339:1219–24.
Ahmadzadeh M, Pasetto A, Jia L, Deniger DC, Stevanovic S, Robbins PF, et al. Tumor-infiltrating human CD4(+) regulatory T cells display a distinct TCR repertoire and exhibit tumor and neoantigen reactivity. Sci Immunol. 2019;4:eaao4310.
Xydia M, Rahbari R, Ruggiero E, Macaulay I, Tarabichi M, Lohmayer R, et al. Common clonal origin of conventional T cells and induced regulatory T cells in breast cancer patients. Nat Commun. 2021;12:1119.
Zhang L, Yu X, Zheng L, Zhang Y, Li Y, Fang Q, et al. Lineage tracking reveals dynamic relationships of T cells in colorectal cancer. Nature. 2018;564:268–72.
Shang B, Liu Y, Jiang SJ, Liu Y. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15179.
Saleh R, Elkord E. FoxP3(+) T regulatory cells in cancer: prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cancer Lett. 2020;490:174–85.
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med. 2004;10:942–9.
Sato E, Olson SH, Ahn J, Bundy B, Nishikawa H, Qian F, et al. Intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high CD8+/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:18538–43.
Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C, Leek RD, Garcia JF, Harris AL, et al. Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5373–80.
Liu S, Foulkes WD, Leung S, Gao D, Lau S, Kos Z, et al. Prognostic significance of FOXP3+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer depends on estrogen receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 expression status and concurrent cytotoxic T-cell infiltration. Breast Cancer Res. 2014;16:432.
Soo RA, Chen Z, Yan Teng RS, Tan HL, Iacopetta B, Tai BC, et al. Prognostic significance of immune cells in non-small cell lung cancer: meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2018;9:24801–20.
Suzuki K, Kachala SS, Kadota K, Shen R, Mo Q, Beer DG, et al. Prognostic immune markers in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:5247–56.
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang XY, Xiao YS, et al. Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:2586–93.
Ormandy LA, Hillemann T, Wedemeyer H, Manns MP, Greten TF, Korangy F. Increased populations of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2457–64.
Chi H, Pepper M, Thomas PG. Principles and therapeutic applications of adaptive immunity. Cell. 2024;187:2052–78.
Raynor JL, Chi H. Nutrients: signal 4 in T cell immunity. J Exp Med. 2024;221:e20221839.
Tekguc M, Wing JB, Osaki M, Long J, Sakaguchi S. Treg-expressed CTLA-4 depletes CD80/CD86 by trogocytosis, releasing free PD-L1 on antigen-presenting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118:e2023739118.
Kidani Y, Nogami W, Yasumizu Y, Kawashima A, Tanaka A, Sonoda Y, et al. CCR8-targeted specific depletion of clonally expanded Treg cells in tumor tissues evokes potent tumor immunity with long-lasting memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022;119:e2114282119.
Kim D, Kim G, Yu R, Lee J, Kim S, Gleason MR, et al. Inhibitory co-receptor Lag3 supports Foxp3(+) regulatory T cell function by restraining Myc-dependent metabolic programming. Immunity. 2024;57:2634–2650 e2635.
Liang B, Workman C, Lee J, Chew C, Dale BM, Colonna L, et al. Regulatory T cells inhibit dendritic cells by lymphocyte activation gene-3 engagement of MHC class II. J Immunol. 2008;180:5916–26.
Yu X, Harden K, Gonzalez LC, Francesco M, Chiang E, Irving B, et al. The surface protein TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:48–57.
Moreno Ayala MA, Campbell TF, Zhang C, Dahan N, Bockman A, Prakash V, et al. CXCR3 expression in regulatory T cells drives interactions with type I dendritic cells in tumors to restrict CD8(+) T cell antitumor immunity. Immunity. 2023;56:1613–1630 e1615.
Burchill MA, Yang J, Vogtenhuber C, Blazar BR, Farrar MA. IL-2 receptor beta-dependent STAT5 activation is required for the development of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2007;178:280–90.
Spangler JB, Tomala J, Luca VC, Jude KM, Dong S, Ring AM, et al. Antibodies to interleukin-2 elicit selective t cell subset potentiation through distinct conformational mechanisms. Immunity. 2015;42:815–25.
Geels SN, Moshensky A, Sousa RS, Murat C, Bustos MA, Walker BL, et al. Interruption of the intratumor CD8(+) T cell: treg crosstalk improves the efficacy of PD-1 immunotherapy. Cancer Cell. 2024;42:1051–1066 e1057.
Wertheimer T, Zwicky P, Rindlisbacher L, Sparano C, Vermeer M, de Melo BMS, et al. IL-23 stabilizes an effector T(reg) cell program in the tumor microenvironment. Nat Immunol. 2024;25:512–24.
Sawant DV, Yano H, Chikina M, Zhang Q, Liao M, Liu C, et al. Adaptive plasticity of IL-10(+) and IL-35(+) T(reg) cells cooperatively promotes tumor T cell exhaustion. Nat Immunol. 2019;20:724–35.
Wei X, Zhang J, Gu Q, Huang M, Zhang W, Guo J, et al. Reciprocal expression of IL-35 and IL-10 defines two distinct effector treg subsets that are required for maintenance of immune tolerance. Cell Rep. 2017;21:1853–69.
Turnis ME, Sawant DV, Szymczak-Workman AL, Andrews LP, Delgoffe GM, Yano H, et al. Interleukin-35 Limits Anti-Tumor Immunity. Immunity. 2016;44:316–29.
Gunderson AJ, Yamazaki T, McCarty K, Fox N, Phillips M, Alice A, et al. TGFbeta suppresses CD8(+) T cell expression of CXCR3 and tumor trafficking. Nat Commun. 2020;11:1749.
Chen ML, Pittet MJ, Gorelik L, Flavell RA, Weissleder R, von Boehmer H, et al. Regulatory T cells suppress tumor-specific CD8 T cell cytotoxicity through TGF-beta signals in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:419–24.
Allard B, Longhi MS, Robson SC, Stagg J. The ectonucleotidases CD39 and CD73: novel checkpoint inhibitor targets. Immunol Rev. 2017;276:121–44.
Maj T, Wang W, Crespo J, Zhang H, Wang W, Wei S, et al. Oxidative stress controls regulatory T cell apoptosis and suppressor activity and PD-L1-blockade resistance in tumor. Nat Immunol. 2017;18:1332–41.
Cao X, Cai SF, Fehniger TA, Song J, Collins LI, Piwnica-Worms DR, et al. Granzyme B and perforin are important for regulatory T cell-mediated suppression of tumor clearance. Immunity. 2007;27:635–46.
Michalek RD, Gerriets VA, Jacobs SR, Macintyre AN, MacIver NJ, Mason EF, et al. Cutting edge: distinct glycolytic and lipid oxidative metabolic programs are essential for effector and regulatory CD4+ T cell subsets. J Immunol. 2011;186:3299–303.
Shi LZ, Wang R, Huang G, Vogel P, Neale G, Green DR, et al. HIF1alpha-dependent glycolytic pathway orchestrates a metabolic checkpoint for the differentiation of TH17 and Treg cells. J Exp Med. 2011;208:1367–76.
Gerriets VA, Kishton RJ, Nichols AG, Macintyre AN, Inoue M, Ilkayeva O, et al. Metabolic programming and PDHK1 control CD4+ T cell subsets and inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:194–207.
Gerriets VA, Kishton RJ, Johnson MO, Cohen S, Siska PJ, Nichols AG, et al. Foxp3 and Toll-like receptor signaling balance T(reg) cell anabolic metabolism for suppression. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:1459–66.
Chapman NM, Zeng H, Nguyen TM, Wang Y, Vogel P, Dhungana Y, et al. mTOR coordinates transcriptional programs and mitochondrial metabolism of activated T(reg) subsets to protect tissue homeostasis. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2095.
Saravia J, Zeng H, Dhungana Y, Bastardo Blanco D, Nguyen TM, Chapman NM, et al. Homeostasis and transitional activation of regulatory T cells require c-Myc. Sci Adv. 2020;6:eaaw6443.
Weinberg SE, Singer BD, Steinert EM, Martinez CA, Mehta MM, Martinez-Reyes I, et al. Mitochondrial complex III is essential for suppressive function of regulatory T cells. Nature. 2019;565:495–9.
Miska J, Lee-Chang C, Rashidi A, Muroski ME, Chang AL, Lopez-Rosas A, et al. HIF-1alpha Is a Metabolic switch between glycolytic-driven migration and oxidative phosphorylation-driven immunosuppression of tregs in glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 2019;27:226–237 e224.
Chapman NM, Boothby MR, Chi H. Metabolic coordination of T cell quiescence and activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:55–70.
Zeng H, Yang K, Cloer C, Neale G, Vogel P, Chi H. mTORC1 couples immune signals and metabolic programming to establish T(reg)-cell function. Nature. 2013;499:485–90.
Su W, Chapman NM, Wei J, Zeng H, Dhungana Y, Shi H, et al. Protein prenylation drives discrete signaling programs for the differentiation and maintenance of effector T(reg) cells. Cell Metab. 2020;32:996–1011 e1017.
Long L, Wei J, Lim SA, Raynor JL, Shi H, Connelly JP, et al. CRISPR screens unveil signal hubs for nutrient licensing of T cell immunity. Nature. 2021;600:308–13.
Shi H, Chapman NM, Wen J, Guy C, Long L, Dhungana Y, et al. Amino acids license kinase mTORC1 activity and treg cell function via small G proteins rag and Rheb. Immunity. 2019;51:1012–1027 e1017.
Wei J, Long L, Yang K, Guy C, Shrestha S, Chen Z, et al. Autophagy enforces functional integrity of regulatory T cells by coupling environmental cues and metabolic homeostasis. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:277–85.
Huynh A, DuPage M, Priyadharshini B, Sage PT, Quiros J, Borges CM, et al. Control of PI(3) kinase in Treg cells maintains homeostasis and lineage stability. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:188–96.
Shrestha S, Yang K, Guy C, Vogel P, Neale G, Chi H. Treg cells require the phosphatase PTEN to restrain TH1 and TFH cell responses. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:178–87.
Zeng H, Chi H. mTOR signaling in the differentiation and function of regulatory and effector T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 2017;46:103–11.
Delgoffe GM, Woo SR, Turnis ME, Gravano DM, Guy C, Overacre AE, et al. Stability and function of regulatory T cells is maintained by a neuropilin-1-semaphorin-4a axis. Nature. 2013;501:252–6.
Gualdoni GA, Mayer KA, Goschl L, Boucheron N, Ellmeier W, Zlabinger GJ. The AMP analog AICAR modulates the Treg/Th17 axis through enhancement of fatty acid oxidation. FASEB J. 2016;30:3800–9.
Kishore M, Cheung KCP, Fu H, Bonacina F, Wang G, Coe D, et al. Regulatory T cell migration is dependent on glucokinase-mediated glycolysis. Immunity. 2017;47:875–889 e810.
Magnuson AM, Kiner E, Ergun A, Park JS, Asinovski N, Ortiz-Lopez A, et al. Identification and validation of a tumor-infiltrating Treg transcriptional signature conserved across species and tumor types. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E10672–E10681.
Plitas G, Konopacki C, Wu K, Bos PD, Morrow M, Putintseva EV, et al. Regulatory T cells exhibit distinct features in human breast cancer. Immunity. 2016;45:1122–34.
Priyadharshini B, Loschi M, Newton RH, Zhang JW, Finn KK, Gerriets VA, et al. Cutting Edge: TGF-beta and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signals modulate distinct metabolism of regulatory T cell subsets. J Immunol. 2018;201:2215–9.
Procaccini C, Carbone F, Di Silvestre D, Brambilla F, De Rosa V, Galgani M, et al. The proteomic landscape of human Ex vivo regulatory and conventional T cells reveals specific metabolic requirements. Immunity. 2016;44:406–21.
Shi H, Chi H. Metabolic control of treg cell stability, plasticity, and tissue-specific heterogeneity. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2716.
Bacigalupa ZA, Landis MD, Rathmell JC. Nutrient inputs and social metabolic control of T cell fate. Cell Metab. 2024;36:10–20.
Campbell C, Rudensky A. Roles of regulatory T cells in tissue pathophysiology and metabolism. Cell Metab. 2020;31:18–25.
Kumagai S, Koyama S, Itahashi K, Tanegashima T, Lin YT, Togashi Y, et al. Lactic acid promotes PD-1 expression in regulatory T cells in highly glycolytic tumor microenvironments. Cancer Cell. 2022;40:201–218 e209.
Watson MJ, Vignali PDA, Mullett SJ, Overacre-Delgoffe AE, Peralta RM, Grebinoski S, et al. Metabolic support of tumour-infiltrating regulatory T cells by lactic acid. Nature. 2021;591:645–51.
Angelin A, Gil-de-Gomez L, Dahiya S, Jiao J, Guo L, Levine MH, et al. Foxp3 reprograms T cell metabolism to function in low-glucose, high-lactate environments. Cell Metab. 2017;25:1282–1293 e1287.
Zhou J, Gu J, Qian Q, Zhang Y, Huang T, Li X, et al. Lactate supports Treg function and immune balance via MGAT1 effects on N-glycosylation in the mitochondria. J Clin Invest. 2024;134:e175897.
Gu J, Zhou J, Chen Q, Xu X, Gao J, Li X, et al. Tumor metabolite lactate promotes tumorigenesis by modulating MOESIN lactylation and enhancing TGF-beta signaling in regulatory T cells. Cell Rep. 2022;39:110986.
Ding R, Yu X, Hu Z, Dong Y, Huang H, Zhang Y, et al. Lactate modulates RNA splicing to promote CTLA-4 expression in tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells. Immunity. 2024;57:528–540 e526.
Zappasodi R, Serganova I, Cohen IJ, Maeda M, Shindo M, Senbabaoglu Y, et al. CTLA-4 blockade drives loss of T(reg) stability in glycolysis-low tumours. Nature. 2021;591:652–8.
Colegio OR, Chu NQ, Szabo AL, Chu T, Rhebergen AM, Jairam V, et al. Functional polarization of tumour-associated macrophages by tumour-derived lactic acid. Nature. 2014;513:559–63.
MaruYama T, Kobayashi S, Shibata H, Chen W, Owada Y. Curcumin analog GO-Y030 boosts the efficacy of anti-PD-1 cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Sci. 2021;112:4844–52.
Rao D, Stunnenberg JA, Lacroix R, Dimitriadis P, Kaplon J, Verburg F, et al. Acidity-mediated induction of FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2023;53:e2250258.
Mani NL, Weinberg SE, Chaudhuri S, Montauti E, Tang A, Iyer R, et al. Acidity induces durable enhancement of T(reg) cell suppressive functions for tumor immune evasion. Mol Immunol. 2024;174:57–68.
Hoy AJ, Nagarajan SR, Butler LM. Tumour fatty acid metabolism in the context of therapy resistance and obesity. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:753–66.
Lim SA, Wei J, Nguyen TM, Shi H, Su W, Palacios G, et al. Lipid signalling enforces functional specialization of T(reg) cells in tumours. Nature. 2021;591:306–11.
Wang H, Franco F, Tsui YC, Xie X, Trefny MP, Zappasodi R, et al. CD36-mediated metabolic adaptation supports regulatory T cell survival and function in tumors. Nat Immunol. 2020;21:298–308.
Pacella I, Procaccini C, Focaccetti C, Miacci S, Timperi E, Faicchia D, et al. Fatty acid metabolism complements glycolysis in the selective regulatory T cell expansion during tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E6546–E6555.
Kumagai S, Togashi Y, Sakai C, Kawazoe A, Kawazu M, Ueno T, et al. An oncogenic alteration creates a microenvironment that promotes tumor progression by conferring a metabolic advantage to regulatory T cells. Immunity. 2020;53:187–203 e188.
Howie D, Ten Bokum A, Cobbold SP, Yu Z, Kessler BM, Waldmann H. A novel role for triglyceride metabolism in Foxp3 expression. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1860.
Field CS, Baixauli F, Kyle RL, Puleston DJ, Cameron AM, Sanin DE, et al. Mitochondrial integrity, regulated by lipid metabolism is a cell-intrinsic checkpoint for Treg suppressive function. Cell Metab. 2020;31:422–437 e425.
Ma S, Sandhoff R, Luo X, Shang F, Shi Q, Li Z, et al. Serine enrichment in tumors promotes regulatory T cell accumulation through sphinganine-mediated regulation of c-Fos. Sci Immunol. 2024;9:eadg8817.
Li C, Munoz-Rojas AR, Wang G, Mann AO, Benoist C, Mathis D. PPARgamma marks splenic precursors of multiple nonlymphoid-tissue Treg compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118:e2025197118.
Taves MD, Otsuka S, Taylor MA, Donahue KM, Meyer TJ, Cam MC, et al. Tumors produce glucocorticoids by metabolite recycling, not synthesis, and activate Tregs to promote growth. J Clin Investig. 2023;133:e164599.
Ma X, Xiao L, Liu L, Ye L, Su P, Bi E, et al. CD36-mediated ferroptosis dampens intratumoral CD8(+) T cell effector function and impairs their antitumor ability. Cell Metab. 2021;33:1001–1012 e1005.
Xu S, Chaudhary O, Rodriguez-Morales P, Sun X, Chen D, Zappasodi R, et al. Uptake of oxidized lipids by the scavenger receptor CD36 promotes lipid peroxidation and dysfunction in CD8(+) T cells in tumors. Immunity. 2021;54:1561–1577 e1567.
Xu C, Sun S, Johnson T, Qi R, Zhang S, Zhang J, et al. The glutathione peroxidase Gpx4 prevents lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis to sustain Treg cell activation and suppression of antitumor immunity. Cell Rep. 2021;35:109235.
Kurniawan H, Franchina DG, Guerra L, Bonetti L, Baguet LS, Grusdat M, et al. Glutathione restricts serine metabolism to preserve regulatory T cell function. Cell Metab. 2020;31:920–936 e927.
Dang EV, Barbi J, Yang HY, Jinasena D, Yu H, Zheng Y, et al. Control of T(H)17/T(reg) balance by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell. 2011;146:772–84.
Hsiao HW, Hsu TS, Liu WH, Hsieh WC, Chou TF, Wu YJ, et al. Deltex1 antagonizes HIF-1alpha and sustains the stability of regulatory T cells in vivo. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6353.
Westendorf AM, Skibbe K, Adamczyk A, Buer J, Geffers R, Hansen W, et al. Hypoxia enhances immunosuppression by inhibiting CD4+ effector T cell function and promoting treg activity. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41:1271–84.
Clambey ET, McNamee EN, Westrich JA, Glover LE, Campbell EL, Jedlicka P, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha-dependent induction of FoxP3 drives regulatory T-cell abundance and function during inflammatory hypoxia of the mucosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:E2784–2793.
Facciabene A, Peng X, Hagemann IS, Balint K, Barchetti A, Wang LP, et al. Tumour hypoxia promotes tolerance and angiogenesis via CCL28 and T(reg) cells. Nature. 2011;475:226–30.
Ren L, Yu Y, Wang L, Zhu Z, Lu R, Yao Z. Hypoxia-induced CCL28 promotes recruitment of regulatory T cells and tumor growth in liver cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:75763–73.
Li L, Liu X, Sanders KL, Edwards JL, Ye J, Si F, et al. TLR8-mediated metabolic control of human treg function: a mechanistic target for cancer immunotherapy. Cell Metab. 2019;29:103–123 e105.
Bottcher M, Renner K, Berger R, Mentz K, Thomas S, Cardenas-Conejo ZE, et al. D-2-hydroxyglutarate interferes with HIF-1alpha stability skewing T-cell metabolism towards oxidative phosphorylation and impairing Th17 polarization. Oncoimmunology. 2018;7:e1445454.
Jiang GM, Tan Y, Wang H, Peng L, Chen HT, Meng XJ, et al. The relationship between autophagy and the immune system and its applications for tumor immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:17.
Kabat AM, Harrison OJ, Riffelmacher T, Moghaddam AE, Pearson CF, Laing A, et al. The autophagy gene Atg16l1 differentially regulates Treg and TH2 cells to control intestinal inflammation. Elife. 2016;5:e12444.
Park JH, Kim HJ, Kim CW, Kim HC, Jung Y, Lee HS, et al. Tumor hypoxia represses gammadelta T cell-mediated antitumor immunity against brain tumors. Nat Immunol. 2021;22:336–46.
Sattiraju A, Kang S, Giotti B, Chen Z, Marallano VJ, Brusco C, et al. Hypoxic niches attract and sequester tumor-associated macrophages and cytotoxic T cells and reprogram them for immunosuppression. Immunity. 2023;56:1825–1843 e1826.
Munn DH, Mellor AL. IDO in the tumor microenvironment: inflammation, counter-regulation, and tolerance. Trends Immunol. 2016;37:193–207.
Sharma MD, Shinde R, McGaha TL, Huang L, Holmgaard RB, Wolchok JD, et al. The PTEN pathway in Tregs is a critical driver of the suppressive tumor microenvironment. Sci Adv. 2015;1:e1500845.
Ye J, Qiu J, Bostick JW, Ueda A, Schjerven H, Li S, et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor preferentially marks and promotes gut regulatory T cells. Cell Rep. 2017;21:2277–90.
Campesato LF, Budhu S, Tchaicha J, Weng CH, Gigoux M, Cohen IJ, et al. Blockade of the AHR restricts a Treg-macrophage suppressive axis induced by L-Kynurenine. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4011.
Zhang X, Liu X, Zhou W, Du Q, Yang M, Ding Y, et al. Blockade of IDO-kynurenine-AhR axis ameliorated colitis-associated colon cancer via inhibiting immune tolerance. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;12:1179–99.
Holmgaard RB, Zamarin D, Munn DH, Wolchok JD, Allison JP. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is a critical resistance mechanism in antitumor T cell immunotherapy targeting CTLA-4. J Exp Med. 2013;210:1389–402.
Lowe MM, Boothby I, Clancy S, Ahn RS, Liao W, Nguyen DN, et al. Regulatory T cells use arginase 2 to enhance their metabolic fitness in tissues. JCI Insight. 2019;4:e129756.
Liu C, Chikina M, Deshpande R, Menk AV, Wang T, Tabib T, et al. Treg cells promote the SREBP1-dependent metabolic fitness of tumor-promoting macrophages via repression of CD8(+) T Cell-derived interferon-gamma. Immunity. 2019;51:381–397 e386.
Schenk U, Frascoli M, Proietti M, Geffers R, Traggiai E, Buer J, et al. ATP inhibits the generation and function of regulatory T cells through the activation of purinergic P2X receptors. Sci Signal. 2011;4:ra12.
Deaglio S, Dwyer KM, Gao W, Friedman D, Usheva A, Erat A, et al. Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression. J Exp Med. 2007;204:1257–65.
Sun X, Wu Y, Gao W, Enjyoji K, Csizmadia E, Muller CE, et al. CD39/ENTPD1 expression by CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells promotes hepatic metastatic tumor growth in mice. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1030–40.
Stagg J, Divisekera U, Duret H, Sparwasser T, Teng MW, Darcy PK, et al. CD73-deficient mice have increased antitumor immunity and are resistant to experimental metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2892–2900.
Vignali PDA, DePeaux K, Watson MJ, Ye C, Ford BR, Lontos K, et al. Hypoxia drives CD39-dependent suppressor function in exhausted T cells to limit antitumor immunity. Nat Immunol. 2023;24:267–79.
Kumagai S, Togashi Y, Kamada T, Sugiyama E, Nishinakamura H, Takeuchi Y, et al. The PD-1 expression balance between effector and regulatory T cells predicts the clinical efficacy of PD-1 blockade therapies. Nat Immunol. 2020;21:1346–58.
Kamada T, Togashi Y, Tay C, Ha D, Sasaki A, Nakamura Y, et al. PD-1(+) regulatory T cells amplified by PD-1 blockade promote hyperprogression of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:9999–10008.
Kim MJ, Kim K, Park HJ, Kim GR, Hong KH, Oh JH, et al. Deletion of PD-1 destabilizes the lineage identity and metabolic fitness of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2023;24:148–61.
Tan CL, Kuchroo JR, Sage PT, Liang D, Francisco LM, Buck J, et al. PD-1 restraint of regulatory T cell suppressive activity is critical for immune tolerance. J Exp Med. 2021;218:e20182232.
Yang K, Blanco DB, Neale G, Vogel P, Avila J, Clish CB, et al. Homeostatic control of metabolic and functional fitness of T(reg) cells by LKB1 signalling. Nature. 2017;548:602–6.
Ali K, Soond DR, Pineiro R, Hagemann T, Pearce W, Lim EL, et al. Inactivation of PI(3)K p110delta breaks regulatory T-cell-mediated immune tolerance to cancer. Nature. 2014;510:407–11.
Ahmad S, Abu-Eid R, Shrimali R, Webb M, Verma V, Doroodchi A, et al. Differential PI3Kdelta signaling in CD4(+) T-cell subsets enables selective targeting of T regulatory cells to enhance cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2017;77:1892–904.
Eschweiler S, Ramirez-Suastegui C, Li Y, King E, Chudley L, Thomas J, et al. Intermittent PI3Kdelta inhibition sustains anti-tumour immunity and curbs irAEs. Nature. 2022;605:741–6.
Santinon F, Ezzahra BF, Bachais M, Sarabia Pacis A, Rudd CE. Direct AKT activation in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes markedly increases interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) for the regression of tumors resistant to PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Sci Rep. 2022;12:18509.
Levine AG, Mendoza A, Hemmers S, Moltedo B, Niec RE, Schizas M, et al. Stability and function of regulatory T cells expressing the transcription factor T-bet. Nature. 2017;546:421–5.
Overacre-Delgoffe AE, Chikina M, Dadey RE, Yano H, Brunazzi EA, Shayan G, et al. Interferon-gamma drives T(reg) fragility to promote anti-tumor immunity. Cell. 2017;169:1130–1141 e1111.
Dykema AG, Zhang J, Cheung LS, Connor S, Zhang B, Zeng Z, et al. Lung tumor-infiltrating T(reg) have divergent transcriptional profiles and function linked to checkpoint blockade response. Sci Immunol. 2023;8:eadg1487.
Kim J, DeBerardinis RJ. Mechanisms and implications of metabolic heterogeneity in cancer. Cell Metab. 2019;30:434–46.
De Rosa V, Galgani M, Porcellini A, Colamatteo A, Santopaolo M, Zuchegna C, et al. Glycolysis controls the induction of human regulatory T cells by modulating the expression of FOXP3 exon 2 splicing variants. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:1174–84.
Gao X, Zhu Y, Li G, Huang H, Zhang G, Wang F, et al. TIM-3 expression characterizes regulatory T cells in tumor tissues and is associated with lung cancer progression. PLoS One. 2012;7:e30676.
Liu Z, McMichael EL, Shayan G, Li J, Chen K, Srivastava R, et al. Novel effector phenotype of tim-3(+) regulatory T Cells leads to enhanced suppressive function in head and neck cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:4529–38.
Banerjee H, Nieves-Rosado H, Kulkarni A, Murter B, McGrath KV, Chandran UR, et al. Expression of Tim-3 drives phenotypic and functional changes in Treg cells in secondary lymphoid organs and the tumor microenvironment. Cell Rep. 2021;36:109699.
van Hooren L, Handgraaf SM, Kloosterman DJ, Karimi E, van Mil L, Gassama AA, et al. CD103(+) regulatory T cells underlie resistance to radio-immunotherapy and impair CD8(+) T cell activation in glioblastoma. Nat Cancer. 2023;4:665–81.
Sung H, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Pearson-Stuttard J, Islami F, Fedewa SA, et al. Global patterns in excess body weight and the associated cancer burden. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:88–112.
Shaikh SR, Beck MA, Alwarawrah Y, MacIver NJ. Emerging mechanisms of obesity-associated immune dysfunction. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2024;20:136–48.
Valentine Y, Nikolajczyk BS. T cells in obesity-associated inflammation: the devil is in the details. Immunol Rev. 2024;324:25–41.
Cipolletta D, Feuerer M, Li A, Kamei N, Lee J, Shoelson SE, et al. PPAR-gamma is a major driver of the accumulation and phenotype of adipose tissue Treg cells. Nature. 2012;486:549–53.
Li C, Wang G, Sivasami P, Ramirez RN, Zhang Y, Benoist C, et al. Interferon-alpha-producing plasmacytoid dendritic cells drive the loss of adipose tissue regulatory T cells during obesity. Cell Metab. 2021;33:1610–1623 e1615.
Deiuliis J, Shah Z, Shah N, Needleman B, Mikami D, Narula V, et al. Visceral adipose inflammation in obesity is associated with critical alterations in tregulatory cell numbers. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16376.
Ringel AE, Drijvers JM, Baker GJ, Catozzi A, Garcia-Canaveras JC, Gassaway BM, et al. Obesity shapes metabolism in the tumor microenvironment to suppress anti-tumor immunity. Cell. 2020;183:1848–1866 e1826.
Piening A, Ebert E, Gottlieb C, Khojandi N, Kuehm LM, Hoft SG, et al. Obesity-related T cell dysfunction impairs immunosurveillance and increases cancer risk. Nat Commun. 2024;15:2835.
McQuade JL, Daniel CR, Hess KR, Mak C, Wang DY, Rai RR, et al. Association of body-mass index and outcomes in patients with metastatic melanoma treated with targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or chemotherapy: a retrospective, multicohort analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:310–22.
Wang Z, Aguilar EG, Luna JI, Dunai C, Khuat LT, Le CT, et al. Paradoxical effects of obesity on T cell function during tumor progression and PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Nat Med. 2019;25:141–51.
Helmink BA, Khan MAW, Hermann A, Gopalakrishnan V, Wargo JA. The microbiome, cancer, and cancer therapy. Nat Med. 2019;25:377–88.
Sepich-Poore GD, Zitvogel L, Straussman R, Hasty J, Wargo JA, Knight R. The microbiome and human cancer. Science 2021; 371:eabc4552.
Gopalakrishnan V, Spencer CN, Nezi L, Reuben A, Andrews MC, Karpinets TV, et al. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science. 2018;359:97–103.
Matson V, Fessler J, Bao R, Chongsuwat T, Zha Y, Alegre ML, et al. The commensal microbiome is associated with anti-PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma patients. Science. 2018;359:104–8.
Sivan A, Corrales L, Hubert N, Williams JB, Aquino-Michaels K, Earley ZM, et al. Commensal bifidobacterium promotes antitumor immunity and facilitates anti-PD-L1 efficacy. Science. 2015;350:1084–9.
Smith PM, Howitt MR, Panikov N, Michaud M, Gallini CA, Bohlooly YM, et al. The microbial metabolites, short-chain fatty acids, regulate colonic Treg cell homeostasis. Science. 2013;341:569–73.
Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, Dikiy S, van der Veeken J, deRoos P, et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature. 2013;504:451–5.
Hang S, Paik D, Yao L, Kim E, Trinath J, Lu J, et al. Bile acid metabolites control T(H)17 and T(reg) cell differentiation. Nature. 2019;576:143–8.
Campbell C, McKenney PT, Konstantinovsky D, Isaeva OI, Schizas M, Verter J, et al. Bacterial metabolism of bile acids promotes generation of peripheral regulatory T cells. Nature. 2020;581:475–9.
Song X, Sun X, Oh SF, Wu M, Zhang Y, Zheng W, et al. Microbial bile acid metabolites modulate gut RORgamma(+) regulatory T cell homeostasis. Nature. 2020;577:410–5.
Coutzac C, Jouniaux JM, Paci A, Schmidt J, Mallardo D, Seck A, et al. Systemic short chain fatty acids limit antitumor effect of CTLA-4 blockade in hosts with cancer. Nat Commun. 2020;11:2168.
Ali N, Zirak B, Rodriguez RS, Pauli ML, Truong HA, Lai K, et al. Regulatory T cells in skin facilitate epithelial stem cell differentiation. Cell. 2017;169:1119–1129 e1111.
Burzyn D, Kuswanto W, Kolodin D, Shadrach JL, Cerletti M, Jang Y, et al. A special population of regulatory T cells potentiates muscle repair. Cell. 2013;155:1282–95.
Raffin C, Vo LT, Bluestone JA. T(reg) cell-based therapies: challenges and perspectives. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:158–72.
Whiteside SK, Grant FM, Alvisi G, Clarke J, Tang L, Imianowski CJ, et al. Acquisition of suppressive function by conventional T cells limits antitumor immunity upon T(reg) depletion. Sci Immunol. 2023;8:eabo5558.
Lucca LE, Dominguez-Villar M. Modulation of regulatory T cell function and stability by co-inhibitory receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:680–93.
Perrot I, Michaud HA, Giraudon-Paoli M, Augier S, Docquier A, Gros L, et al. Blocking Antibodies targeting the CD39/CD73 immunosuppressive pathway unleash immune responses in combination cancer therapies. Cell Rep. 2019;27:2411–2425 e2419.
Tang T, Huang X, Lu M, Zhang G, Han X, Liang T. Transcriptional control of pancreatic cancer immunosuppression by metabolic enzyme CD73 in a tumor-autonomous and -autocrine manner. Nat Commun. 2023;14:3364.
Freeman ZT, Nirschl TR, Hovelson DH, Johnston RJ, Engelhardt JJ, Selby MJ, et al. A conserved intratumoral regulatory T cell signature identifies 4-1BB as a pan-cancer target. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:1405–16.
Feng P, Yang Q, Luo L, Guan Z, Fu J, Zhao M, et al. Vps34 sustains Treg cell survival and function via regulating intracellular redox homeostasis. Cell Death Differ. 2024;31:1519–33.
Norton EG, Chapman NM, Shi H, Meng X, Huang H, KC A, et al. Vps34-orchestrated lipid signaling processes regulate the transitional heterogeneity and functional adaptation of effector regulatory T cells. PLoS Biol. 2025;23:e3003074.
Yamamoto K, Venida A, Yano J, Biancur DE, Kakiuchi M, Gupta S, et al. Autophagy promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer by degrading MHC-I. Nature. 2020;581:100–5.
Poillet-Perez L, Sharp DW, Yang Y, Laddha SV, Ibrahim M, Bommareddy PK, et al. Autophagy promotes growth of tumors with high mutational burden by inhibiting a T-cell immune response. Nat Cancer. 2020;1:923–34.
Terme M, Pernot S, Marcheteau E, Sandoval F, Benhamouda N, Colussi O, et al. VEGFA-VEGFR pathway blockade inhibits tumor-induced regulatory T-cell proliferation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2013;73:539–49.
Glasner A, Rose SA, Sharma R, Gudjonson H, Chu T, Green JA, et al. Conserved transcriptional connectivity of regulatory T cells in the tumor microenvironment informs new combination cancer therapy strategies. Nat Immunol. 2023;24:1020–35.
Bonnin E, Rodrigo Riestra M, Marziali F, Mena Osuna R, Denizeau J, Maurin M, et al. CD74 supports accumulation and function of regulatory T cells in tumors. Nat Commun. 2024;15:3749.
Kim MC, Borcherding N, Ahmed KK, Voigt AP, Vishwakarma A, Kolb R, et al. CD177 modulates the function and homeostasis of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells. Nat Commun. 2021;12:5764.
Nie P, Cao Z, Yu R, Dong C, Zhang W, Meng Y, et al. Targeting p97-Npl4 interaction inhibits tumor T(reg) cell development to enhance tumor immunity. Nat Immunol. 2024;25:1623–36.
Di Pilato M, Kim EY, Cadilha BL, Prussmann JN, Nasrallah MN, Seruggia D, et al. Targeting the CBM complex causes T(reg) cells to prime tumours for immune checkpoint therapy. Nature. 2019;570:112–6.
Tanaka A, Nishikawa H, Noguchi S, Sugiyama D, Morikawa H, Takeuchi Y, et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib augments tumor immunity by depleting effector regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 2020;217:e20191009.
Fusco C, Di Rella F, Liotti A, Colamatteo A, Ferrara AL, Gigantino V, et al. CD4(+)FOXP3Exon2(+) regulatory T cell frequency predicts breast cancer prognosis and survival. Sci Adv. 2025;11:eadr7934.
Trujillo-Ochoa JL, Kazemian M, Afzali B. The role of transcription factors in shaping regulatory T cell identity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023;23:842–56.
Baixauli F, Acin-Perez R, Villarroya-Beltri C, Mazzeo C, Nunez-Andrade N, Gabande-Rodriguez E, et al. Mitochondrial respiration controls lysosomal function during inflammatory T cell responses. Cell Metab. 2015;22:485–98.
Fu Z, Ye J, Dean JW, Bostick JW, Weinberg SE, Xiong L, et al. Requirement of mitochondrial transcription factor A in tissue-resident regulatory T cell maintenance and function. Cell Rep. 2019;28:159–171 e154.
Saravia J, Raynor JL, Chapman NM, Lim SA, Chi H. Signaling networks in immunometabolism. Cell Res. 2020;30:328–42.
Luo CT, Liao W, Dadi S, Toure A, Li MO. Graded Foxo1 activity in Treg cells differentiates tumour immunity from spontaneous autoimmunity. Nature. 2016;529:532–6.
Oh H, Grinberg-Bleyer Y, Liao W, Maloney D, Wang P, Wu Z, et al. An NF-kappaB transcription-factor-dependent lineage-specific transcriptional program promotes regulatory T cell identity and function. Immunity. 2017;47:450–465 e455.
Vasanthakumar A, Liao Y, Teh P, Pascutti MF, Oja AE, Garnham AL, et al. The TNF Receptor superfamily-NF-kappaB Axis Is critical to maintain effector regulatory T cells in lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues. Cell Rep. 2017;20:2906–20.
Grinberg-Bleyer Y, Oh H, Desrichard A, Bhatt DM, Caron R, Chan TA, et al. NF-kappaB c-Rel is crucial for the regulatory T cell immune checkpoint in cancer. Cell. 2017;170:1096–1108 e1013.
Itahashi K, Irie T, Yuda J, Kumagai S, Tanegashima T, Lin YT, et al. BATF epigenetically and transcriptionally controls the activation program of regulatory T cells in human tumors. Sci Immunol. 2022;7:eabk0957.
Shan F, Cillo AR, Cardello C, Yuan DY, Kunning SR, Cui J, et al. Integrated BATF transcriptional network regulates suppressive intratumoral regulatory T cells. Sci Immunol. 2023;8:eadf6717.
Delacher M, Imbusch CD, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Mallm JP, Bauer K, Simon M, et al. Precursors for nonlymphoid-tissue treg cells reside in secondary lymphoid organs and are programmed by the transcription factor BATF. Immunity. 2020;52:295–312 e211.
Vasanthakumar A, Moro K, Xin A, Liao Y, Gloury R, Kawamoto S, et al. The transcriptional regulators IRF4, BATF and IL-33 orchestrate development and maintenance of adipose tissue-resident regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2015;16:276–85.
Obradovic A, Ager C, Turunen M, Nirschl T, Khosravi-Maharlooei M, Iuga A, et al. Systematic elucidation and pharmacological targeting of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cell master regulators. Cancer Cell. 2023;41:933–949 e911.
Delacher M, Imbusch CD, Weichenhan D, Breiling A, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Trager U, et al. Genome-wide DNA-methylation landscape defines specialization of regulatory T cells in tissues. Nat Immunol. 2017;18:1160–72.
Long X, Zhang S, Wang Y, Chen J, Lu Y, Hou H, et al. Targeting JMJD1C to selectively disrupt tumor T(reg) cell fitness enhances antitumor immunity. Nat Immunol. 2024;25:525–36.
Ren Z, Zhang A, Sun Z, Liang Y, Ye J, Qiao J, et al. Selective delivery of low-affinity IL-2 to PD-1+ T cells rejuvenates antitumor immunity with reduced toxicity. J Clin Investig. 2022;132:e153604.
Wei X, Zhao L, Yang F, Yang Y, Zhang H, Du K, et al. A CD25xTIGIT bispecific antibody induces anti-tumor activity through selective intratumoral Treg cell depletion. Mol Ther. 2024;32:4075–94.
Conde E, Casares N, Mancheno U, Elizalde E, Vercher E, Capozzi R, et al. FOXP3 expression diversifies the metabolic capacity and enhances the efficacy of CD8 T cells in adoptive immunotherapy of melanoma. Mol Ther. 2023;31:48–65.
Guo Y, Xie YQ, Gao M, Zhao Y, Franco F, Wenes M, et al. Metabolic reprogramming of terminally exhausted CD8(+) T cells by IL-10 enhances anti-tumor immunity. Nat Immunol. 2021;22:746–56.
Zhao Y, Chen J, Andreatta M, Feng B, Xie YQ, Wenes M, et al. IL-10-expressing CAR T cells resist dysfunction and mediate durable clearance of solid tumors and metastases. Nat Biotechnol. 2024;42:1693–704.
Postow MA, Sidlow R, Hellmann MD. Immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint blockade. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:158–68.
Hu T, Allam M, Cai S, Henderson W, Yueh B, Garipcan A, et al. Single-cell spatial metabolomics with cell-type specific protein profiling for tissue systems biology. Nat Commun. 2023;14:8260.
Arguello RJ, Combes AJ, Char R, Gigan JP, Baaziz AI, Bousiquot E, et al. SCENITH: a flow cytometry-based method to functionally profile energy metabolism with single-cell resolution. Cell Metab. 2020;32:1063–1075 e1067.
Ma EH, Verway MJ, Johnson RM, Roy DG, Steadman M, Hayes S, et al. Metabolic profiling using stable isotope tracing reveals distinct patterns of glucose utilization by physiologically activated CD8(+) T cells. Immunity. 2019;51:856–870 e855.
Reinfeld BI, Madden MZ, Wolf MM, Chytil A, Bader JE, Patterson AR, et al. Cell-programmed nutrient partitioning in the tumour microenvironment. Nature. 2021;593:282–8.
Shi H, Doench JG, Chi H. CRISPR screens for functional interrogation of immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023;23:363–80.
Manguso RT, Pope HW, Zimmer MD, Brown FD, Yates KB, Miller BC, et al. In vivo CRISPR screening identifies Ptpn2 as a cancer immunotherapy target. Nature. 2017;547:413–8.
Wei J, Long L, Zheng W, Dhungana Y, Lim SA, Guy C, et al. Targeting REGNASE-1 programs long-lived effector T cells for cancer therapy. Nature. 2019;576:471–6.
LaFleur MW, Lemmen AM, Streeter ISL, Nguyen TH, Milling LE, Derosia NM, et al. X-CHIME enables combinatorial, inducible, lineage-specific and sequential knockout of genes in the immune system. Nat Immunol. 2024;25:178–88.
LaFleur MW, Nguyen TH, Coxe MA, Yates KB, Trombley JD, Weiss SA, et al. A CRISPR-Cas9 delivery system for in vivo screening of genes in the immune system. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1668.
Zhou P, Shi H, Huang H, Sun X, Yuan S, Chapman NM, et al. Single-cell CRISPR screens in vivo map T cell fate regulomes in cancer. Nature. 2023;624:154–63.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge N. Chapman for insightful scientific discussions and editing of the manuscript, and H. Shi, J. Raynor, X. Sun, and Z. You for insightful scientific discussions. Research support is provided by ALSAC, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants CA253188, CA281868, AI105887, AI131703, AI140761, AI150241, and AI150514, and the Lupus Research Alliance. This work is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.S. wrote and edited the manuscript. H.C. wrote and edited the manuscript and provided overall scientific direction.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
H.C. consults for Kumquat Biosciences and TCura Biosciences, and is a co-inventor on patents/patent applications in the field of immunotherapy. J.S. has no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Saravia, J., Chi, H. Immunometabolism of regulatory T cells in cancer. Oncogene 44, 2011–2024 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03458-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-025-03458-1