Abstract
Finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.) is a calcium-rich, nutritious and resilient crop that thrives even in harsh environmental conditions. In such ecologies, seed longevity and seedling vigor are crucial for sustainable crop production amid climate change. The current study explores the genetics of accelerated aging on seed longevity traits across 221 diverse accessions of finger millet through genome-wide association approach (GWAS). A significant variation was identified in germination percentage, germination rate indices, mean germination time, seedling vigor indices and dry weight upon aging treatment. GWAS model from 11,832 high-quality SNPs identified through Genotyping-by-Sequencing (GBS) approach produced 491 marker-trait associations (MTAs) for 27 traits, of which 54 were FDR-corrected. A pleiotropic SNP, FM_SNP_9478 identified on chromosome 7B was associated with the traits viz., germination after aging, germination index after aging and their relative measures. Functional annotation revealed DET1 and expansin-A2 influenced seed coat integrity, critical for germination and aging resilience. Probable protein phosphatase 2C3 and piezo-type ion channels contributed to mechanical sensing and stress adaptation in seeds. Beta-amylase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 were identified for seed metabolism and stress response. These insights lay the framework for targeted breeding efforts to improve seed quality and resilience under diverse production conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Among the small millets, finger millet (Eleusine coracana L. Gaertn.) stands out due to its significant nutritional value. Rich in calcium, dietary fiber, phytochemicals and essential amino acids1, this allotetraploid crop (2n = 4x = 36, AABB) is mostly grown under rainfed conditions. Although originating in Africa, India is the leading producer of finger millet, with 1.22 million hectares under cultivation, producing 1.7 million tons at a productivity of 1724 kg per hectare, contributing to 60% of global production2. With the increasing impact of climate change, the climate-resilient crops such as finger millet have become indispensable3. The success of finger millet cultivation crucially hinges on seed quality and longevity, necessitating precise methods to assess physiological traits that determine seed quality for propagation and subsequent growth stages4.
Studies on seed longevity traits are important in finger millet, as the crop is primarily grown in rainfed systems. Early seedling vigor and longevity enhance seedling establishment, maintain moisture during grain filling, and ensure long-term viability. Seed longevity, being a quantitative trait, varies within the species and also among different species5. During seed storage, the inevitable aging process results in poor quality of stored seeds that lead to losses to the tune of 25%6,7,8).
Seed longevity and aging directly impact agricultural sustainability, particularly when farmers store seeds for extended periods. Prolonged storage under various traditional conditions can significantly affect seed viability. This reduction in viability leads to decreased germination rates and consequently, lower crop yields. Moreover, with the ongoing challenges of global warming, the decline in seed longevity is expected to become a critical concern for farmers who rely on farm-saved seeds for future planting seasons rather than purchasing new seeds at a higher cost9.
Understanding the genetic mechanisms underlying seed longevity and seedling vigor related traits is essential for developing improved cultivars suitable to diverse environmental conditions. The accelerated aging (AA) test stands out as an efficient method for evaluating seed vigor. AA test provides valuable insights into the storage potential of seed lots and their emergence in the field within a short span10. Studies have shown that results from AA tests provide a more accurate prediction of field emergence under stressful soil conditions compared to standard germination tests11. The process of seed aging, typically involves initial damage to cellular membranes, followed by compromised cellular repair and biosynthetic processes, resulting in a reduced rate of germination, slower seedling growth, heightened susceptibility to environmental stresses, diminished field emergence and ultimately loss of viability6. The AA vigor test finds wide application across different crops, including soybean (Glycine max L. Merrill)12, wheat (Triticum aestivum L. Thell)13 and corn (Zea mays L.)14. Studies on artificial aging mimic the aging process under storage conditions have revealed the intricate genetic and environmental factors influencing seed longevity in wheat15 and barley16.
Advancements in genomics technologies have accelerated the next-generation breeding efforts in crops17. Genomic technologies such as the GBS approach identified 2,977 SNPs across genetically diverse accessions in finger millet and facilitated the mapping of the SNPs associated with seed protein content18. A recent chromosomal-level genome assembly of finger millet, with a genome size of 1.1 Gb, has significantly enhanced the accuracy of genome mapping19 and created an opportunity for a comprehensive understanding of the genetic basis underlying key traits. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) provide the genetic architecture of traits by analyzing historical recombination events in genetically diverse populations, allowing accurate identification of genomic regions linked to specific traits20. GWAS approach has been extensively used in millets and cereals such as sorghum21, foxtail millet22 pearl millet23,24 and maize25,26.
Understanding the genetic basis of traits related to seed germination and seedling growth is limited in finger millet27, but QTLs and genes were identified in several crops using various approaches. In tobacco, overexpression of the heat shock factor A9, has enhanced the seed longevity28. Two stable QTLs, QlgGR.cas-1 A and QlgGR.cas-2B.2, explaining 6.7–11.4% of the phenotypic variation, were identified in wheat and associated with seed longevity. The QTL-linked FAR1-related sequence 6-like protein, along with synthase 3, dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide-protein glycosyltransferase, glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase, and alpha-Amy2/53, were found to be associated to seed longevity29. Eight QTLs for seed vigor were identified in rice from a recombinant inbred line population derived from a cross between ZS97 and MH63. Among these, five QTLs (qSV-1, qSV-5b, qSV-6a, qSV-6b and qSV-11) influenced seedling establishment, while three QTLs (qSV-5a, qSV-5c and qSV-8) specifically influenced germination30.
Considering the importance of understanding the genetics of seed longevity traits, our study aims to develop comprehensive phenotypic data for seed vigor and longevity traits using a genetically diverse panel, to identify SNP associated with traits and the genes responsible for seed vigor and longevity in finger millet. The SNPs and genes associated with the seed traits could contribute to the productivity gain and sustainability of this ancient and nutri-rich grain in rainfed agriculture.
Results
Statistics of seed phenotypic traits
The descriptive statistics for each trait assessed, under both control and accelerated aging conditions, revealed significant insights into seed germination and seedling growth (Supplementary Table S1). The frequency distribution curve exhibited a pattern closely resembling a normal distribution for germination rate index after accelerated aging (GRIAA), relative germination rate index after accelerated aging (GRIAAR), mean germination time (days) after accelerated aging (MGTAA), relative mean germination time after accelerated aging (MGTAAR), Shoot length (cm) after accelerated aging (SLAA), relative shoot length after accelerated aging (SLAAR) and relative seedling dry weight after accelerated aging (SDWAAR) indicating their polygenic nature (Fig. 1). AA had a detrimental effect on seed performance, leading to decreased seed germination percentage, germination rates, seedling growth and vigor across all the traits over the respective control (Fig. 2). These observations indicated that seeds subjected to AA experienced impaired metabolic activity, potentially due to oxidative stress and loss of membrane integrity during the aging process. The reduced seedling growth and lower vigor indices observed under AA further reflect the cumulative impact of aging on seed health, affecting both physiological and morphological aspects.
Frequency distribution of seed traits of the finger millet GWAS panel, the X-axis represents the trait values, and the Y-axis represents frequency. The traits are organized as follows: (a) GC, GAA, GAAR; (b) GIC, GIAA, GIAAR; (c) GRIC, GRIAA, GRIAAR; (d) MGTC, MGTAA, MGTAAR; (e) RLC, RLAA, RLAAR; (f) SLC, SLAA, SLAAR; (g) SVI1C, SVI1AA, SVI1AAR; (h) SDWC, SDWAA, SDWAAR; (i) SVI2C, SVI2AA, SVI2AAR.
Initial germination of seeds (GC) ranged from 85.33 to 97.53%, with a mean of 93.57%. In comparison, germination after accelerated aging (GAA) showed a broader range of 23.26–95.52%, averaging 80.50%. Relative germination after accelerated aging (GAAR) varied significantly from 25.81 to 103.69%, highlighting the impact of accelerated aging on seed viability at different tolerance levels of genotypes. Germination index (GIC) ranged between 619.11 and 777.26, with an average of 721.01. Germination index after accelerated aging (GIAA) dropped considerably, ranging from 54.08 to 582.01, with a mean of 397.80. This represents nearly a two-fold reduction in germination potential, as reflected in relative germination index after accelerated aging (GIAAR), which averaged 55.13%, with some genotypes experiencing a significant decline (Supplementary Table S1).
Mean germination time (MGTC) averaged 1.29 days, with a range of 1.05 to 1.86 days. Mean germination time significantly increased to an average of 4.12 days, with a range of Germination index after accelerated aging 2.38 to 7.30 days after aging treatment. MGTAAR ranged from 229.29 to 472.63%, indicating that a longer period was needed for germination after the aging process. Root length (RLC) averaged 5.93 cm, with values ranging from 3.99 to 8.09 cm. After aging, root length after accelerated aging (RLAA) decreased to an average of 4.37 cm, with a range of 1.04 to 7.35 cm. Relative root length after accelerated aging (RLAAR) varied broadly, spanning from 18.94 to 130.46%, indicating a substantial decrease in radicle growth post-aging, with some genotypes showing a significant contraction. Shoot length (SLC) averaged 2.83 cm, with a range of 2.03 to 3.47 cm. Post-aging, SLAA dropped to an average of 1.99 cm, with values ranging from 0.44 to 2.87 cm, indicating a substantial reduction in shoot length due to aging.
Seedling vigor index-1 (SVI1C) averaged 818.68, with a range of 597.58 to 1066.41. Following aging, Seedling vigor index-1 (SVI1AA) decreased to an average of 516.17, ranging from 56.06 to 913.01. Relative seedling vigor index-1 after accelerated aging (SVI1AAR) ranged from 7.76 to 115.42%, with an average of 64.32%, indicating a considerable decline in seedling vigour. Seedling dry weight (SDWC) averaged 2.07 mg, ranging from 1.40 to 3.08 mg. Seedling dry weight after accelerated aging (SDWAA) slightly increased to an average of 2.16 mg, with a range of 0.58 to 3.20 mg. Relative seedling dry weight after accelerated aging (SDWAAR) varied from 34.64 to 141.75%, with some genotypes showing a substantial increase in dry weight despite the aging treatment. Seedling vigor index-2 (SVI2C) averaged 193.68, with values ranging from 127.33 to 281.24. Seedling vigor index-2 after aging, (SVI2AA) decreased to an average of 174.52, with a range of 24.97 to 256.89.
These results highlight significant variability in seed germination indices and seedling vigor traits under both control and AA conditions. The germination parameters, such as GC, GAA and GAAR, demonstrated substantial differences, reflecting the impact of AA on seed viability, which will help to predict the seed longevity potential of genotypes. The germination indices GIC, GIAA, GRIC, GRIAA and respective relative values (GIAAR and GRIAAR) revealed the speed of germination. Higher relative values for MGTAAR indicated the delay in the germination process of the genotype that reflects the poor vigor status of aged seeds. Similarly, seedling growth metrics, including root and shoot lengths (RLC and SLC) and their relative measures post-aging (RLAAR and SLAAR), measured the tolerance levels of growth under aging treatment.
The variance components showed significant differences for all the traits under control and AA conditions (Table 1). GC had a heritability of 61.22%, while GAA and GAAR showed heritability of 90.03% and 86.80%, respectively. Traits related to germination indices viz., GIC, GIAA, and GIAAR had a heritability of 78.33%, 93.06%, and 91.73%, respectively. Mean germination time (MGTC, MGTAA, MGTAAR), root and shoot lengths (RLC, SLC) and seedling vigor indices (SVI1C, SVI2C) had heritability ranging from 80.63 to 95.08%. These results explained the significant genetic basis of seed germination and seedling growth traits, indicating the potential for genetic enhancement of seed vigor and longevity.
GIAA showed significant positive correlations with GAA (0.86), GIAAR (0.97), and GRIAA (0.98) (Fig. 3). On the other hand, MGTAA exhibited a negative correlation with traits such as SVI1AA (-0.60) and SVI2AA (-0.28). A significant negative correlation between GAA and MGTAA (-0.55) indicates that seeds with higher germination rates after aging stress tend to germinate early. Similarly, the significant negative correlation between GIAA (-0.87) and GRIAA (-0.86) with MGTAA suggests that early germination is associated with better overall seed performance. These relationships provide valuable insights for breeding strategies focused on improving seed viability, early germination and robust seedling growth under aging conditions. The correlations among multiple traits highlight potential genetic linkages and pathways influencing seed development and viability, which could be critical for breeding programs to enhance finger millet resilience and productivity.
Statistics of SNP calling
A total of 5,63,270 SNPs were identified using the GBS approach from a panel of 221 genotypes. After eliminating SNPs with over 10% missing values, 1,04,907 SNPs were retained. These SNPs were then filtered by removing more than 10% heterozygosity and a minor allele frequency (MAF) below 3%, resulting in the retention of 11,832 high-quality SNPs for the genome-wide association study (Fig. 4).
The SNP density across the chromosomes was analysed and presented in the heatmap (Fig. 5) (Supplementary Table S2). Chromosome 5 A had the highest SNP density (1054), followed by chromosome 5B (1101) and chromosome 6 A (1014). Chromosome 3B had the lowest SNPs (164), while scaffold regions of the genome contained 50 SNPs.
Linkage disequilibrium (LD)
LD was measured across 11,832 SNP markers among 221 finger millet accessions, revealing that the LD block size at LD50 decay was 3.39 Mb (Fig. 6). SNPs within this distance are considered to belong to the same inheritance block.
The linkage disequilibrium (LD) decay plot among 221 diverse finger millet genotypes in GWAS panel, featuring 11,832 SNPs. The X-axis represents the genomic distance in Mb, while the Y-axis displays the r² values. The red line marks the threshold where linkage LD decayed to 50% of its maximum value.
Principle Component Analysis (PCA)
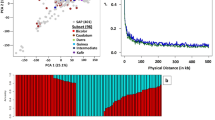
PCA revealed a relatively uniform distribution of genotypes across regions, with some overlap between populations. African and Asian genotypes are grouped separately, suggesting the presence of subpopulation structure. (Fig. 7a). The PCA based on races showed uniform distribution and wider spread across the first three principal components (Fig. 7b).
Marker trait associations (MTAs)
The GAPIT model selection feature, which integrates both the kinship matrix and PCA, was employed to identify the associations with the traits in a panel of 221 genotypes using 11,832 high-quality SNPs.
A total of 491 MTAs was discovered with a significance -log10(p) value greater than 3. Among traits, SVI2AA had the highest number of significant MTAs (32) and RLAAR had the fewest (4). The SNP associations for each trait under different treatments, along with their p-values are presented in Supplementary Table S3. MTAs were further filtered using a Bonferroni threshold of -log10(p) greater than 5.37, which narrowed down to 54 SNPs across 13 chromosomes. Table 2 provides detailed information on those Bonferroni-corrected MTAs. Furthermore, Manhattan plots displaying the MTAs and Q-Q plots showing the observed versus expected associations of various seed traits, adjusted for population structure, are presented in Figs. 8, 9 and 10.
FM_SNP_10872 was identified as the most significant marker associated with the trait SDWC. The pleiotropic quantitative trait loci (QTL), FM_SNP_9478 on chromosome 7B, exhibited associations with multiple traits, including GAA, GAAR, GIAA and GIAAR. GAAR, SDWAAR and SVI2AAR shared a common association with FM_SNP_235 on chromosome 2A. Another pleiotropic locus, FM_SNP_9403 explained 41.94% of phenotypic variance (PV) for SVI2C, 19.79% for SDWC and 17.99% for SDWAA. Comprehensive statistics for the significant SNPs identified are provided in Table 2.
Seed germination percentage
Nine significant markers were identified for QTLs associated with seed germination percentage, with three linked to GAA and six to GAAR. FM_SNP_11315 on chromosome 6B was observed in both treated seeds and relative germination after accelerated aging. For GAA, three SNPs on chromosomes 5B, 6B and 7B were identified, with FM_SNP_9478 on 7B being highly significant and explaining 31.52% of PV. For GAAR, six SNPs on chromosomes 1 A, 1B, 2A, 5B, 6B and 7B were identified, with FM_SNP_235 on 2A and FM_SNP_9478 on 7B explaining 28.36% and 18.63% of PV, respectively.
Manhattan plot of genome-wide SNPs of (a) GC, GAA, GAAR (b) GIC, GIAA, GIAAR (c) GRIC, GRIAA, GRIAAR. The X-axis shows genomic positions, and the Y-axis shows − log10(p-values). The grey horizontal line indicates the Bonferroni correction threshold. The corresponding Q–Q plot displays observed versus expected − log10(p-values).
Germination indices
The loci, FM_SNP_9478 and FM_SNP_9582 on chromosome 7B were observed in both treated seeds and the relative germination index after AA treatment. The locus FM_SNP_3796 on chromosome 8A in treated seeds showed the strongest association, explaining 31.12% of PV. For GRIC, only one SNP, FM_SNP_3303 on chromosome 6A, was linked, explaining 46.07% of PV. No significant associations were detected for GRIAA and GRIAAR.
Mean germination time
Significant SNPs associated with mean germination time were identified for control and relative mean germination time under AA treatment. For MGTC, FM_SNP_3303 and FM_SNP_10858 located on chromosomes 6A and 6B explained a PV of 31.86% and 30.14%, respectively. Similarly, FM_SNP_8722 on chromosome 9B showed a significant association and explained 12.03% of PV. For MGTAAR, FM_SNP_9852 on chromosome 5B explained 32.17% of PV.
Manhattan plot of genome-wide SNPs of (a) MGTC, MGTAA, MGTAAR (b) RLC, RLAA, RLAAR (c) SDWC, SDWAA, SDWAAR. X-axis showing genomic positions and the Y-axis showing − log10(p-values). The grey horizontal line indicates the Bonferroni threshold. The corresponding Q–Q plot displays observed versus expected − log10(p-values).
Root and shoot length
FM_SNP_8168 on chromosome 7B was associated with RLC, explaining 27.08% of PV. While, FM_SNP_3851 on chromosome 8 A showed a strong association, accounting for 39.58% of PV. No significant SNP associations were found for RLAA and RLAAR. FM_SNP_3696 on chromosome 3A was identified for SLC, accounted for 32.48% of PV. No significant SNPs were observed for SLAA and SLAAR.
Seedling dry weight
Among all the traits, seed germination percentage revealed the highest number of MTAs, with eight SNPs identified for SDWC and three for SDWAA. Additionally, four SNPs were identified for SDWAAR. The locus FM_SNP_9403 on chromosome 1B was consistently detected in control and treated seeds after the Bonferroni correction. For SDWC, FM_SNP_9403 on chromosome 1B and FM_SNP_10872 on chromosome 6B showed strong statistical significance explaining 19.79% and 21.56% of PV, respectively. Similarly, SDWAA showed significant associations with FM_SNP_4948 on chromosome 3A and FM_SNP_483 on chromosome 5A. These SNPs explained a PV of 37.48% and 30.75%, respectively. FM_SNP_1517 on chromosome 1A as a significant SNP with 70.19% of PV was identified for SDWAAR, highlighting its substantial role in influencing seedling response under AA condition over the control.
Manhattan plot of genome-wide SNPs of (a) SLC, SLAA, SLAAR (b) SVI1C, SVI1AA, SVI1AAR (c) SVI2C, SVI2AA, SVI2AAR. X-axis showing genomic positions and the Y-axis showing − log10(p-values). The grey horizontal line indicates the Bonferroni correction threshold. The corresponding Q-Q plot displays observed versus expected − log10(p-values).
Seedling vigor indices
GWAS model identified three significant SNPs associated with SVI1C, but did not find any significant associations for SVI1AA and SVI1AAR. FM_SNP_6503, located on chromosome 1A, explained 34.31% of PV, while FM_SNP_3851 on chromosome 8A explained 25.99% of PV. Significant SNPs associated with SVI2C, SVI2AA and SVI2AAR were primarily identified under control conditions. FM_SNP_9403 on chromosome 1B explained 41.94% of PV, whereas FM_SNP_8521 on chromosome 9B accounted for 23.58% of PV in SVI2C highlighting their significant influence on the trait. In contrast, SVI2AAR was linked to FM_SNP_235 on chromosome 2A and FM_SNP_9246 on chromosome 6B, explained 46.17% and 10.97% of PV, respectively, under rapid aging.
Several pleiotropic loci, namely, FM_SNP_9403, FM_SNP_9478, FM_SNP_3851, FM_SNP_9852 and FM_SNP_235, were detected for multiple traits. The SNP, FM_SNP_9478 on chromosome 7B was significantly associated with GAA, GAAR, GIAA and GIAAR, suggesting a common genetic basis in predicting seed longevity. The correlation study further confirmed that these four traits were significantly and positively associated. FM_SNP_7145 on chromosome 5B and the SNP FM_SNP_11315 on chromosome 6B were both linked to both GAA and GAAR, indicating the genetic relationship between these traits. These findings explained a strong correlation between the seed traits and the presence of common SNPs, suggesting potential pleiotropy or closely linked genes influencing multiple phenotypic characteristics in finger millet. These hotspots could serve as valuable markers for improving multiple traits through marker-assisted selection.
The high heritability values for traits viz., GIAA (93.06%), GAAR (86.80%) and GAA (90.03%) indicated a strong genetic control of these seed longevity characteristics. Notably, the SNPs associated with these high heritability traits also explained a significant portion of the phenotypic variation for seed storability potential. SNP FM_SNP_9478 on chromosome 7B accounted for 31.52% of the variation in GAA and 19.19% in GIAA. Similarly, FM_SNP_7145 on chromosome 5B explained 22.67% of the variation in GAA and 9.89% in GAAR, while FM_SNP_11315 on chromosome 6B explained 15.15% of the PV in GAA and 7.54% in GAAR. These findings suggested that the traits with high heritability are also those explaining a high degree of phenotypic variance for seed longevity.
In-silico comparative genomics
Significant SNPs associated with seed quality traits were functionally annotated across different monocot species viz., rice (Oryza sativa), maize (Zea mays), foxtail millet (Setaria italica), sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) to determine their roles in seed development, metabolism and adaptation. Considering the LD span of 3.39 Mb, genes within a 2 Mb region around the significant SNPs in finger millet were annotated. Among the SNPs identified as significantly associated through GWAS, annotations were obtained for 24 SNPs linked to crucial seed traits across various monocot species (Supplementary Table S4). FM_SNP_6503 and FM_SNP_6470 in sorghum were associated with the light-mediated development protein DET1 and probable protein phosphatase 2C3, respectively. FM_SNP_1517 and FM_SNP_9403 were associated with expansin-A2 and piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channels, indicating their roles in root mechanotransduction. Respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein F in sorghum for FM_SNP_51 and auxin transport protein BIG-like in switchgrass for FM_SNP_6154 were identified. DP-dependent glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase for FM_SNP_3881, beta-amylase for FM_SNP_9582, and auxin transport protein BIG for FM_SNP_6154 were identified as other important genes. This highlights their potential roles in mitigating accelerated aging effects through regulatory mechanisms in seed development.
GO analysis highlighted enrichment in key biological processes such as embryo development ending in seed dormancy and ribosome biogenesis (Fig. 11a). KEGG pathway analysis identified significant pathways such as ribosome, endocytosis, phagosome and proteosome, emphasizing their importance in maintaining seed vigor and longevity, especially under conditions of accelerated aging (Fig. 11b). This comprehensive analysis enhances our understanding of the genetic basis of seed vigor and longevity traits in finger millet and reveals conserved molecular mechanisms shared with related cereal crops.
(a) GO analysis illustrating finger millet’s molecular landscape: Cellular components, biological processes and molecular functions. The Y-axis shows the fold enrichment and the X-axis shows highly enriched GO categories. (b) Dot plot visualization of KEGG pathway enrichment: Fold enrichment (x-axis) vs. pathway name (y-axis). Dot size represents gene count and color indicates p-value threshold.
Discussion
Finger millet, known for its climate resilience and nutritional value, plays a vital role in food security, especially in regions facing challenges such as drought and poor soil conditions31. Seed vigor and longevity are the critical traits that determine the success of crop establishment and yield. These traits are influenced by a complex interplay of genetic, environmental and physiological factors32. High temperatures, humidity and other external conditions can accelerate the seed aging, thereby affecting seed vigor and viability33.
The AA test is designed to simulate long-term storage conditions, allowing us to assess the seed longevity. Seeds with better longevity tend to deteriorate less, while those with poor longevity deteriorate more quickly. Studies across various crops such as rice, maize and Arabidopsis have revealed that seed vigor is controlled by multiple genes, with several QTLs identified that govern traits like germination rate, seedling length and dry weight34. Thirteen novel loci for seed longevity traits were identified using SNP whole genome mapping in wheat5. Advances in functional genomics have shed light on specific genes and pathways involving heat shock proteins, lectin-like receptor kinases and oxidative repair mechanisms that enhance seed vigor under stress conditions34. Despite significant progress, understanding the molecular mechanisms of seed vigor, particularly in finger millet, remains a challenge.
The phenotypic data of the seed longevity and seedling vigor-related traits revealed that the majority of these traits followed a normal distribution pattern, suggesting that they are influenced by genetic and environmental factors. The normal distribution pattern for the traits GIAA, GIAAR, GRIAA, GRIAAR, RLC, RLAA, RLAAR, SLC, SLAA, SLAAR, SVI1C, SVI1AA, SVI1AAR, SVI2C, SVI2AA and SVI2AARsuggests polygenic inheritance, where trait variation arises from the cumulative effects of multiple genes. Each of these genes contributes small, additive effects without displaying dominance, highlighting a complex genetic architecture governing these traits. In contrast, MGTC and GRIC exhibited skewed distributions, indicating a different genetic control, often characterized by the influence of polygenes with a dominance effect35.
The impact of rapid aging on seed germination and seedling growth across multiple traits indicated a consistent decrease in germination percentage, germination rate indices, seedling growth and vigor metrics, highlighting the vulnerability of seeds to stress conditions36,37. These results align with the general understanding that aging induces oxidative stress, leading to cellular damage and reduced metabolic activity in seeds38.
Seed viability status at the time of sowing is the crucial factor in determining crop establishment39. Among all the traits, seed germination percentage indicates the life span potential of a genotype after passing through a certain period of aging during storage. The significant variability observed in germination parameters under control and accelerated aging conditions highlights the sensitivity of seed viability to environmental stress40,41,42. Post aging, the sharp decline in GAA and its relative measure GAAR revealed the pronounced differences in seed longevity potential among the finger millet accessions, as the key factor that contributes to seed vigor during germination and emergence. Furthermore, the post aging reduction in GIAA and GRIAA and their relative values GIAAR and GIAAR indicated poor seed performance in terms of both speed and uniformity of germination which are essential for uniform crop stand and productivity41,43.
The decline in root and shoot lengths after aging emphasized the impaired seedling establishment capacity under stress conditions, limiting nutrient uptake and overall performance44,45,46. The vigor of a seed refers to its ability to quickly and evenly emerge and develop into healthy seedlings. This includes factors such as germination percentage, germination rate, germination index, root length, shoot length, and dry weight during the seedling growth process47,48. The significant decrease in seedling vigor indices (SVI1AA, SVI2AA) after aging reaffirmed the cumulative impact of oxidative stress on metabolic processes critical for seedling growth and development49. The vigorous seeds under artificial aging maintained rapid and homogenous germination whereas, the non-vigorous seeds had a marked decline40,50.
The genome-wide SNP distribution revealed higher SNP densities in the telomeric regions compared to the pericentromeric regions suggesting that the telomeric regions are potential hotspots for gene diversity. While, SNP density was lower in the pericentromeric regions, likely due to reduced recombination rates51. Chromosome 8B exhibited high SNP density in its telomeric regions among other chromosomes. The longer chromosomes, such as 5B, 6A, 6B, and 9B exhibited proportionately higher SNP counts. Chromosome 5B, the largest chromosome with a length of 80.35 Mb19, had the highest number of SNPs (1101), whereas, chromosome 4A, the smallest chromosome with a length of 41.34 Mb19, had fewer SNPs (609).
LD among populations can be influenced by multiple factors, such as population size, non-random mating, genetic drift, selection pressures, mutation rates, pollination type and recombination frequency. Self-pollinating species wheat and rice tend to have longer LD blocks (up to 20 Mb)52. However, limited information on LD decay is available in finger millet53. In finger millet, the LD decayed over a distance of 3.39 Mb, indicating the conservation of alleles. A similar trend of high LD has been observed in other self-pollinated polyploid species, such as wheat (5 Mb54, 9.04 Mb55) and peanut (3.78 Mb56). The slow LD decay suggests that breeding strategies need to focus on haplotypes or larger genetic regions, potentially requiring low-density markers for trait mapping and genomic selection approaches for effective trait improvement in finger millet. On the other hand, the high LD region linked to target traits is helpful for the selection of multiple genes in marker-assisted selection (MAS)57.
The SNP markers and their associated genes provide valuable insights into the complex regulatory networks governing seed longevity. In-silico comparative study of significant SNPs identified through GWAS, with Oryza sativa, Zea mays, Sorghum bicolor, Panicum virgatum and Setaria italica (Fig. 12, Supplementary Table S4) highlights the conserved genetic mechanisms involved in seed aging and stress response across these cereal crops. The orthologous genes across the monocot species suggested that a high degree of evolutionary conservation in maintaining seed longevity and viability under stress conditions58,59,60.
The annotation of the significant SNPs identified by the GWAS model in finger millet indicated that several of them were associated with functional genes. Light-mediated development protein DET1 (FM_SNP_6503) is the key one, which is involved in seedling development and showed to play important roles in seed dormancy61 and shade avoidance. Probable protein phosphatase 2C3 (FM_SNP_6503) is known to regulate seed dormancy by interacting with key signaling pathways involved in the inhibition of germination. Probable protein phosphatase 2C3 interacts with ANAC060 transcription factor, forming a regulatory network between seed dormancy and germination, ensuring optimal timing for seedling establishment62. The expansin-A2 gene (FM_SNP_1517) is vital for cell wall modification, enhancing seed coat integrity and water uptake during germination63. This is critical for combating seed aging, as maintaining seed coat structure and permeability preserves seed viability and vigor over extended storage periods. Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel homologs (FM_SNP_9403) sense mechanical cues that signal seed maturation and response to environmental stresses64. Their presence across cereal species highlights their importance in maintaining seed quality and longevity.
Metabolic regulators like peroxisome biogenesis protein 12 (FM_SNP_90) and malate dehydrogenase (FM_SNP_90) play roles in energy metabolism during seed development and storage65,66, their activities in managing oxidative stress and maintaining metabolic homeostasis are essential for mitigating aging-related imbalances and preserving seed viability. The respiratory burst oxidase homolog protein F (FM_SNP_51) and antioxidant enzymes like glutathione reductase 1 (FM_SNP_4948) safeguard cellular integrity against oxidative stress, a primary contributor to seed aging67. Their roles in detoxifying reactive oxygen species (ROS) and maintaining redox homeostasis are crucial for preserving seed vigor over extended storage periods.
Actin-related proteins (FM_SNP_1366) and auxin transporters (FM_SNP_1366) are regulators of cellular dynamics and hormone transport, influencing seed growth and development7,68. Regulatory proteins, CBL-interacting protein kinase 32 (FM_SNP_7145) and calcium-dependent protein kinase 27 (FM_SNP_11328), regulate seed germination and early seedling development through stress-responsive pathways to ensure adaptive responses during seed aging, enhancing seed quality and storage potential69,70. Protein HIRA (FM_SNP_2924), a positive regulator of seed germination71 and serine/threonine-protein kinase STY46 (FM_SNP_2840), contributes to stress adaptation and early seedling growth69, which is crucial for seed aging resilience.
Spermine synthases (FM_SNP_2799), regulate seed germination, grain size and yield72 and heat shock proteins (FM_SNP_2799); play an important role in metabolic regulation; and stress tolerance mechanisms73, ensuring seeds are primed for optimal growth under diverse conditions and during prolonged storage. Enzymes such as beta-amylases (FM_SNP_9582) and acetyl-CoA carboxylases (FM_SNP_9478) contribute to starch and lipid metabolism, respectively, supporting energy reserves and membrane integrity for seed germination and early seedling growth74. Their roles in energy metabolism and nutrient mobilization are vital for sustaining seed viability and performance during aging processes.
Acetyl-CoA carboxylases associated with pleiotropic SNP, FM_SNP_9478 involved in fatty acid biosynthesis and hormonal signaling pathways, which regulate seed dormancy and influence germination75. These processes are essential for energy storage and membrane integrity in seeds. CBL-interacting protein kinase 32 (FM_SNP_7145) is involved in calcium signaling, crucial for regulating physiological processes, including germination. It interacts with MAP kinase pathways and ABA signaling, key regulators of seed dormancy and stress responses76.
The GO terms and KEGG pathways provide significant insights into the molecular and cellular processes associated with seed aging traits. Enriched GO terms related to biological processes such as embryo development ending in seed dormancy and response to light stimulus highlight critical developmental and environmental response mechanisms essential for seed viability77. The involvement of ribosome biogenesis and protein refolding indicates a strong emphasis on protein synthesis and stress response, which are crucial during seed aging78. The significant enrichment of the proteasomal protein catabolic process suggests active protein turnover and degradation, vital for maintaining cellular homeostasis in aged seeds79. KEGG pathway analysis supports these findings, with significant pathways such as ribosome, endocytosis and proteasome indicating robust protein synthesis, trafficking and degradation activities. These pathways are essential for maintaining seed vigor and longevity80,81). The role of the antioxidant system in seed priming and aging emphasize the importance of redox homeostasis and stress responses in seed longevity and germination82.
Conclusion
The study provides valuable insights into the genetic basis of seed vigor and longevity traits in finger millet, which are crucial for crop establishment and productivity, especially in harsh environments. Accelerated aging experiments revealed significant impacts on seed viability and seedling vigor highlighting the importance of addressing oxidative stress during seed storage. GWAS approach identified key SNPs and genes linked to important seed longevity and seedling vigor traits. GO and KEGG pathway analysis further elucidated the biological processes and metabolic pathways involved, highlighting the roles of genes related to seed vigor and longevity. The identification of MTAs and key genes related to seed longevity offers avenues for improving seed performance in terms of seed vigor and longevity, ensuring high-quality seeds for sustainable production systems. This is particularly important for improving quality seed production and storability potential, as seeds with better germination efficiency and vigor are more likely to withstand the challenges posed by environmental stresses. Integrating genomic insights into breeding can expedite finger millet variety development suited to diverse environmental conditions, enhancing global food and nutritional security and sustainability.
Materials and methods
GWAS panel
A panel consists of 221 genetically diverse finger millet accessions, selected from the mini-core collection of the gene bank at ICRISAT, spanning across four continents namely, Africa (116), Asia (93), Europe (4), North America (2) and unknown origin (6) were selected for the GWAS experiment. The panel encompasses all finger millet races and subraces: vulgaris (143 accessions), plana (40 accessions), elongata (14 accessions), compacta (23 accessions) and one unclassified accession. The panel also includes representations of traditional landraces (191 accessions) and advanced breeding lines (30 accessions). Supplementary Table S5 provides detailed information on these accessions, including sample locations, as well as race and subrace classifications.
Phenotyping
GWAS accessions were phenotyped for nine seed traits under two experimental conditions: control and accelerated aging (AA) treatment with three replications. Seed germination (%), germination index, germination rate index, mean germination time (days), root length (cm), shoot length (cm), seedling vigor index (1), seedling dry weight (mg) and seedling vigor index (2) were phenotyped. For each trait, measurements were recorded for the control, accelerated aging treatment and their relative values (Table 3). As per prior standardization of the AA test for finger millet diverse panel, the test conditions involved a 17-day period in an ‘accelerated aging chamber (Memmert-HPP 108/749, Germany)’ maintained at a humidity of 90% or above and a temperature of 44 ± 1 °C. The control (fresh) seeds and the AA seeds of these 221 accessions were evaluated for seed quality traits following standard seed germination test83.
Phenotypic data was collected for nine traits under control and treatment conditions and their relative values were estimated (Table 3). The germination percentage (G) represents the total number of seedlings at the end of the test on the 8th day. Germination index (GI) was calculated as GI = (8 × n1) + (7 × n2) + . (1 × n8). Where, n1, n2 …. n8 is the number of germinated seeds on the first, second, and subsequent days until the 8th day; 8, 7. and 1 are the weights given to the number of germinated seeds on the first, second and subsequent days, respectively84. Germination Rate Index (GRI) was computed using the formula GRI = G1 / 1 + G2 / 2 + G3 / 3 +…. + Gn / n (%/day)85, where, G1 = Germination percentage × 100 at the first day after sowing, G2 = Germination percentage × 100 at the second day after sowing until the 8th day; 1, 2… and n are the days of first, second … and final count, respectively. Mean Germination Time (MGT) was worked out using the formula MGT = ∑ n.D / n (day)86, where n is the number of seeds germinated the day D. Mean root length (RL) (cm) of five normal seedlings was measured from the collar region to the tip of the primary root. Mean shoot length (SL) (cm) of five normal seedlings was measured from the collar region to the tip of the first leaf. Seedling dry weight (SDW) (mg) was measured after drying the 10 normal seedlings in a hot air oven maintained at 80 °C for 24 h. After completion of drying, immediately, seedlings were transferred to desiccator for half an hour for cooling and then mean dry weight of normal seedlings was noted. The seedling vigor index 1 (SVI1) was calculated multiplying final germination percentage by mean seedling length (root + shoot). The seedling vigor index 2 (SVI2) was calculated multiplying mean germination percentage by mean seedling dry weight (SVI2).
Genotyping
DNA extraction
The genomic DNA from 15 to 20 seeds of 221 finger millet genotypes was isolated using the CTAB (Cetyl Trimethyl Ammonium Bromide) extraction method, as described by Murray and Thompson87, with some modifications. Quantification of DNA was performed using Nanodrop 1000 (Thermo Scientific), measuring absorbance at 260 and 280 nm to assess both quality and quantity. Qualitative analysis of the DNA was carried out by agarose gel electrophoresis, where isolated products were resolved on a 1% agarose gel at 80 V for 30 min. Post-electrophoresis, DNA bands were visualized and documented using a gel documentation system and checks for RNA and protein contamination were conducted.
The DNA samples were normalized for GBS to a final concentration of 50 µg. GBS analysis was conducted on lyophilized DNA samples. The resulting GBS libraries were sequenced using Illumina NovaSeq 6000 version paired-end sequencing technology with 150 bp read lengths from 221 samples. Sequence reads from the sequencer were preprocessed with FASTP to obtain high-quality reads filtered based on the Q20 parameter. These high-quality reads were then aligned against the reference genome Eleusine_coracana_v1.0 (GCA_032690845.1)19 using the Bowtie2 genome assembler. This process generated a SAM file containing valuable mapping information for the variant calling of the aligned reads with the average mapping percentage of 94.9%.
SNP filtering
To call variants, stacks were utilized, and all BAM files were used with the default stacks parameters. The Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) was employed to refine the SNP dataset, utilizing its advanced tools for variant analysis to identify biallelic SNPs specifically. A total of 5,63,270 SNPs passed the selection criteria after biallelic filtration. Vcftools tool was used to calculate missing percentages and to identify SNPs with high missing values. After removing SNPs with over 10% missing data and 10% heterozygosity, a minor allele frequency (MAF) threshold of 3% was applied, resulting in the retention of 11,832 high-quality SNPs for GWAS analysis.
Phenotypic data analysis
The adjusted means of replicates were obtained by fitting mixed linear models (MLM). The adjusted means were calculated as best linear unbiased predictions (BLUPs), considering replication and genotypes as random effects. MLM is chosen to estimate BLUPs as they effectively account for fixed and random effects and improve the accuracy of factors. It is useful in field experiments for handling complex data structures, repeated measurements and variance components, providing more reliable and precise estimates than simpler models88. The BLUPs for each genotype and the analysis of variance (ANOVA) were estimated using the R package “lme4”89. The BLUPs were obtained using the following formula90.
where Yik is the trait of interest; µ is the mean effect; Ri is the effect of the ith replicate; Gk is the effect of the kth genotype; εik is the error associated with the ith replication and the kth genotype, which is assumed to be normally and independently distributed, with mean zero and homoscedastic variance σ2. The broad sense heritability (h2) was estimated using the formula.
Where, σ2g is the genotypic variance; σ2e is the error variance and nreps is the number of replications.
Genome-wide association mapping (GWAS)
Genome-wide linkage disequilibrium was calculated using TASSEL v5.091 from the filtered SNP markers. Pairwise comparisons of markers with a sliding window size of 50 markers were used to estimate for linkage disequilibrium (LD) statistic r2. The LD block size was estimated by plotting the r2 value against the distance in base pairs and noting the distance at the half LD decay point. A smoothened LD decay curve was fit to the TASSEL output data using the R script.
The filtered 11,832 high-quality SNPs and BLUPs for each trait were used for the GWAS using the “BLINK” (Bayesian-information and Linkage-disequilibrium Iteratively Nested Keyway) model available in GAPIT v392 with kinship and PCA (https://zzlab.net/GAPIT/gapit_help_document.pdf). The BLINK model is considered superior for identifying marker-trait associations (MTAs) and minimizing false positives to uncover true associations93. This model excels in efficiently managing large-scale genomic data and accurately detecting significant associations by integrating Bayesian and frequentist approaches.
The quality of the association model fitting was assessed using a Q-Q plot, which was drawn by comparing expected versus observed − log10(p) values. MTAs were filtered based on a significance threshold of p-value cut-off at 0.05. To avoid false positives, a stringent selection of MTAs was performed using the Bonferroni correction (p-value cut-off at 0.05/ total number of markers). A Manhattan plot was drawn to represent the MTAs. Additionally, pleiotropic SNPs associated with more than one trait were also identified.
In-silico comparative analysis
In-silico comparative analysis was conducted for the significant SNPs identified through GWAS in finger millet. Cross-species validation was performed using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). For each SNP, the genomic region spanning 1 Mb upstream and downstream was extracted and formatted into FASTA files, which were then queried against the well-annotated monocot species viz., rice (Oryza sativa), maize (Zea mays), foxtail millet (Setaria italica), sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and switchgrass (Panicum virgatum). The regions displaying sequence similarity on the chromosomes of monocot species were analysed to identify candidate gene(s). Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis was conducted on these candidate genes to assess their potential roles in seed traits. Subsequently, the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)94 pathway database was utilized to investigate the biological pathways potentially involved in finger millet seed development. Significant GO and KEGG pathways were identified with the criterion of FDR corrected p value < 0.05. The GO and KEGG analyses were done using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) Version 6.8.
Data availability
The raw sequence data are available in NCBI’s sequence read archive under BioProject ID PRJNA1178163. All other supporting data are included in the manuscript and its supplementary files.
Change history
20 May 2025
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-02029-4
References
Nakarani, U. M. et al. Nutritional and phytochemical profiling of nutracereal finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) genotypes. Food Chem. 341 (2), 128271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128271 (2021).
Ministry of Consumer Affairs. Food & Public Distribution. Title of the press release. Press Information Bureau. (2023)., March 15 Retrieved from https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1907194
Wilson, M. L. & VanBuren, R. Leveraging millets for developing climate resilient agriculture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 75, 102683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2022.102683 (2022).
Sundareswaran, S., Ray Choudhury, P., Vanitha, C. & Yadava, D. K. Seed Quality: Variety development to planting-An overview. In M. Dadlani & D. K. Yadava (Eds.), Seed Sci. Technol. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5888-5_1
Arif, M. A. R., Borner, A. & An SNP based GWAS analysis of seed longevity in wheat. Cereal Res. Commun. 48, 149–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-021-00196-4 (2021).
McDonald, M. B. Seed deterioration: physiology, repair and assessment. Seed Sci. Technol. 27 (1), 177–237 (1999).
Rajjou, L. et al. Proteome-wide characterization of seed aging in Arabidopsis: a comparison between artificial and natural aging protocols. Plant. Physiol. 148 (1), 620–641. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.12314 (2008).
Schwember, A. R. & Bradford, K. J. Quantitative trait loci associated with longevity of lettuce seeds under conventional and controlled deterioration storage conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 61, 4423–4436. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq248 (2010).
Rehmani, M. S. et al. Seedling establishment: the neglected trait in the seed longevity field. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 200, 107765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107765 (2023).
Marcos Filho, J. Seed vigor testing: an overview of the past, present and future perspective. Sci. Agric. 73 (1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1590/0103-9016-2015-0007 (2016).
Dennis, M. Jan., T. Accelerated Aging Test: Principles and Procedures. Seed Technology, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 135–46. JSTOR, (2025). http://www.jstor.org/stable/23433228. Accessed 6 (2005).
Torres, R. M., Roberval, D. V., Panobianco, M. & & Accelerated aging and seedling field emergence in soybean. Scientia Agricola. 61. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162004000500002 (2004).
Ghahfarokhi, M. G., Ghasemi, E., Saeidi, M. & Heidari Kazafi, Z. The effect of accelerated aging on germination characteristics, seed reserve utilization and malondialdehyde content of two wheat cultivars. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 10 (2), 15–23 (2014). https://www.jspb.ru/issues/2014/N2/JSPB_2014_2_15-23.pdf
Kavitha, S., Menaka, C., Srinivasan, S. & Yuvaraja, A. Accelerated aging test in maize: pattern of seed deterioration. Madras Agric. J. 104 (1–3), 41–44. https://doi.org/10.29321/MAJ.01.000395 (2017).
Arif, M. A. R., Nagel, M. & Neumann, K. Genetic studies of seed longevity in hexaploid wheat using segregation and association mapping approaches. Euphytica DOI. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0471-5 (2011).
Nagel, M. et al. Genome-wide association mapping and biochemical markers reveal that seed aging and longevity are intricately affected by genetic background and developmental and environmental conditions in barley. Plant. Cell. Environ. 38 (6), 1011–1022. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12474 (2015).
Nepolean, T., Kaul, J. & Mukri, G. Mittal. Genomics-enabled next-generation breeding approaches in Maize. Front. Plant. Sci. 9, 361. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00361 (2018).
Tiwari, A. et al. Genome-wide association mapping for seed protein content in finger millet (Eleusine coracana) global collection through genotyping by sequencing. J. Cereal Sci. 91, 102888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2019.102888 (2020).
Devos, K. M. et al. Genome analyses reveal population structure and a purple stigma color gene candidate in finger millet. Nat. Commun. 14, 3694. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38915-6 (2023).
Uffelmann, E. et al. Genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers. 1, 59. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-021-00056-9 (2021).
Ahn, E. et al. Genome wide association study of seed morphology traits in Senegalese sorghum cultivars. Plants (Basel). 12 (12), 2344. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12122344 (2023).
Gupta, S., Kumari, K., Muthamilarasan, M., Parida, S. K. & Prasad, M. Population structure and association mapping of yield contributing agronomic traits in foxtail millet. Plant. Cell. Rep. 33 (6), 881–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1564-0 (2014).
Sehgal, D. et al. Integration of gene-based markers in a pearl millet genetic map for identification of candidate genes underlying drought tolerance quantitative trait loci. BMC Plant. Biol. 2229. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-9 (2012). 12 – 9.
Serba, D. D. & Yadav, R. S. Genomic tools in pearl millet breeding for drought tolerance: Status and prospects. Front. Plant. Sci. 7, 1724. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01724 (2016).
Nepolean, T. et al. Functional mechanisms of drought tolerance identified in subtropical maize using genome-wide association mapping. BMC Genom. 15, 1182. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-1182 (2014).
Nepolean, T. et al. Unraveling the genetic architecture of subtropical maize (Zea mays L.) lines and their utility in breeding programs. BMC Genom. 14, 877. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-877 (2013).
Ajeeshkrishna, T. P., Maharajan, T. & Ceasar, S. A. Improvement of millets in the post genomic era. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants. 28 (3), 669–685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-022-01158-8 (2022).
Wang, X. et al. Arabidopsis HSFA9 acts as a regulator of heat response gene expression and the acquisition of thermotolerance and seed longevity. Plant. Cell. Physiol. 65 (3), 372–389. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcad164 (2024).
Zuo, J. H. et al. Genome-wide association study reveals loci associated with seed longevity in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Plant. Breed. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12784 (2020).
Xie, L. et al. Identification and fine mapping of quantitative trait loci for seed vigor in germination and seedling establishment in rice. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 56 (3), 288–299. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12190 (2014).
Kumar, A. et al. Nutraceutical value of finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.), and their improvement using omics approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 7, 934. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00934 (2016).
Finch-Savage, W. E. & Bassel, G. W. Seed vigour and crop establishment: extending performance beyond adaptation. J. Exp. Bot. 67 (3), 567–591. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv490 (2016).
Corbineau, F. The effects of Storage conditions on seed deterioration and ageing: how to improve seed longevity. Seeds 3, 56–75. https://doi.org/10.3390/seeds3010005 (2024).
Arif, M. A. R., Afzal, I. & Borner, A. Genetic aspects and molecular causes of seed longevity in plants-A review. Plants 11 (5), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11050598 (2022).
Allard, R. W. Principles of Plant Breeding (Wiley, 1960).
Rastegar, Z., Sedghi, M. & Khomari, S. Effects of accelerated aging on soybean seed germination indexes at laboratory conditions. Not Sci. Biol. 3, 126. https://doi.org/10.15835/nsb336075 (2011).
Waterworth, W. M. & West, C. E. Genome damage accumulated in seed aging leads to plant genome instability and growth inhibition. Biochem. J. 480 (7), 461–470. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20230006 (2023).
Tonguç, M., Guler, M. & Onder, S. Germination, reserve metabolism, and antioxidant enzyme activities in safflower as affected by seed treatments after accelerated aging. South. Afr. J. Bot. 153, 209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2022.12.021 (2023).
Gayathri, M., Jerlin, R., Eevera, T. & Amuthaselvi, G. Effect of acceleratedly aged groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seeds on physiological and biochemical properties. J. Seed Sci. 2 (1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.18805/LR-5161 (2023).
Landjeva, S., Lohwasser, U. & Borner, A. Genetic mapping within the wheat D genome reveals QTL for germination, seed vigor and longevity, and early seedling growth. Euphytica 171, 129–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-009-0016-3 (2010).
Zuo, J. et al. Genome-wide linkage mapping reveals QTLs for seed Vigor-related traits under Artificial Aging in Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum). Front. Plant. Sci. 9, 1101. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01101 (2018).
Pirredda, M., Fananas-Pueyo, I., Onate-Sanchez, L. & Mira, S. Seed longevity and aging: a review on physiological and genetic factors with an emphasis on hormonal regulation. Plants 13 (1), 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13010041 (2023).
Delouche, J. C. & Baskin, C. C. Accelerated aging techniques for predicting the relative storability of seed lots. Seed Sci. Technol. 1, 427–452 (1973).
Ivana, D. & Slavoljub, L. Seed priming with antioxidants improves sunflower seed germination and seedling growth under unfavorable germination conditions. Turk. J. Agric. For. 36 (1), 87–95. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1110-16 (2012).
Ehsan, B., Ruhollah, N., Kazem, N., Todd, P. & Egan Effects of accelerated aging on germination and biochemistry of eight rice cultivars. J. Plant. Nutr. 40 (14), 1942–1951. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2016.1201502 (2017).
Chopra, R., Burow, G., Buke, J. J., Gladman, N. & Xin, Z. Genome-wide association analysis of seedling traits in diverse sorghum germplasm under thermal stress. BMC Plant Biol. 17:12, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-016-0966-2 (2017).
Redona, E. D. & Mackill, D. J. Mapping quantitative trait loci for seedling vigor in rice using RFLPs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 92, 395–402 (1996).
Regan, K. L., Siddique, K. H. M., Turner, N. C. & Whan, B. R. Potential for increasing early vigour and total biomass in spring wheat. II. Characteristics associated with early vigour. Aust J. Agric. Res. 43, 541–553 (1992).
Ademola, E. A., Tomi, L. A., Boby, V., Sershen, N. W. & Pammenter Oxidative stress, aging and methods of seed in vigoration: an overview and perspectives. Agronomy 11 (12), 2369–2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122369 (2021).
Han, Z. P. et al. QTLs for seed vigor-related traits identified in maize seeds germinated under artificial aging conditions. PLoS One. 9, e92535. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092535 (2014).
Bancic, J. et al. Genomic and phenotypic characterization of finger millet indicates a complex diversification history. Plant. Genome. 17 (1). https://doi.org/10.1002/tpg2.20392 (2023).
Vos, P. G. et al. Evaluation of LD decay and various LD-decay estimators in simulated and SNP array data of tetraploid potato. Theor. Appl. Genet. 130 (1), 123–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2798-8 (2017).
KalyanaBabu, B. & Rashmi, C. Genomic designing for biotic stress resistance in finger millet. In Bhattacharya, S. (Ed.), Biotic Stress Resistance in Millets 313–323. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-75879-0_8
Tyrka, M. et al. Evaluation of genetic structure in European wheat cultivars and advanced breeding lines using a high-density genotyping-by-sequencing approach. BMC Genom. 22, 81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-020-07351-x (2021).
Dharmateja, P. et al. Genome-wide association studies reveal putative QTLs for physiological traits under contrasting phosphorus conditions in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Front. Genet. 13, 984720. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.984720 (2022).
Otyama, P. I. et al. Evaluation of linkage disequilibrium, population structure, and genetic diversity in the U.S. peanut mini core collection. BMC Genom. 20, 481. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-5824-9 (2019).
Remington, D. L. et al. Buckler ES 4th. Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 98, 20:11479–11484. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.201394398 (2001).
Gale, M. D. & Devos, K. M. Comparative genetics in the grasses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 95 (5), 1971–1974. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.5.1971 (1998).
Mittal, S. et al. Comparative analysis of CDPK Family in Maize, Arabidopsis, Rice, and Sorghum revealed potential targets for Drought Tolerance Improvement. Front. Chem. 5, 115. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00115 (2017).
Chakraborty, A., Viswanath, A., Malipatil, R., Rathore, A. & Thirunavukkarasu, T. Structural and functional characteristics of miRNAs in five Strategic Millet species and their utility in Drought Tolerance. Front. Genet. 11, 608421. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.608421.s (2020).
Dong, J. et al. Arabidopsis DE-ETIOLATED1 represses photomorphogenesis by positively regulating phytochrome-interacting factors in the dark. Plant. Cell. 26, 3630–3645. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.130666 (2014).
Song, S. et al. DE-ETIOLATED1 represses photomorphogenesis by positively regulating phytochrome-interacting factors in the dark. bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.05.03.442418 (2021).
Chen, F. & Bradford, K. J. Expression of an expansin is associated with endosperm weakening during tomato seed germination. Plant. Physiol. 124 (3), 1265–1274. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.124.3.1265 (2000).
Mousavi, S. et al. PIEZO ion channel is required for root mechanotransduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 118 (e2102188118). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2102188118 (2021).
Pan, R., Liu, J. & Hu, J. Peroxisomes in plant reproduction and seed-related development. J. Integr. Plant. Biol. 61, 1211–1233. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12765 (2018).
Sew, Y. S., Ströher, E., Fenske, R. & Millar, A. H. Loss of mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase activity alters seed metabolism impairing seed maturation and post-germination growth in Arabidopsis. Plant. Physiol. 171 (3), 849–863. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00039 (2016).
Zhang, H. et al. Evolutionary analysis of Respiratory Burst Oxidase Homolog (RBOH) genes in plants and characterization of ZmRBOHs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 3858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24043858 (2023).
Peer, W. A., Blakeslee, J. J., Yang, H. & Murphy, A. S. Seven things we think we know about auxin transport. Mol. Plant. 4, 487–504. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr034 (2011).
Shi, S. et al. The CBL-Interacting protein kinase NtCIPK23 positively regulates seed germination and early Seedling Development in Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L). Plants 10, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10020323 (2021).
Dekomah, S. D. et al. The role of CDPKs in plant development, nutrient and stress signaling. Front. Genet. 13, 996203. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.996203 (2022).
Layat, E. et al. The histone chaperone HIRA is a positive regulator of seed germination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22084031 (2021).
Yajun, T. et al. The Spermine synthase OsSPMS1 regulates seed germination, grain size, and yield. Plant. Physiol. 178, 1522–1536. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00877 (2018).
Kaur, H. et al. Differentially expressed seed aging responsive heat shock protein OsHSP18.2 implicates in seed vigor, longevity and improves germination and seedling establishment under abiotic stress. Front. Plant. Sci. 6, 713. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00713 (2015).
Hayashi, O. & Satoh, K. Determination of Acetyl-CoA and Malonyl-CoA in Germinating Rice seeds using the LC-MS/MS technique. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 70, 2676–2681. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.60269 (2006).
Nautiyal, P. C., Sivasubramaniam, K. & Dadlani, M. Seed dormancy and regulation of Germination. In: (eds Dadlani, M. & Yadava, D. K.) Seed Sci. Techn. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5888-5_3 (2023).
Poddar, N., Deepika, D., Chitkara, P., Singh, A. & Kumar, S. Molecular and expression analysis indicate the role of CBL interacting protein kinases (CIPKs) in abiotic stress signaling and development in chickpea. Sci. Rep. 12, 16862. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-20750-2 (2022).
Bentsink, L. & Koornneef, M. Seed dormancy and germination. Arabidopsis Book. https://doi.org/10.1199/tab.0119 (2008).
Ninoles, R. et al. Comparative analysis of wild-type accessions reveals novel determinants of Arabidopsis seed longevity. Plant. Cell. Environ. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.14374 (2022).
Rajjou, L. et al. Proteomic investigation of the effect of salicylic acid on Arabidopsis seed germination and establishment of early defense mechanisms. Plant. Physiol. 141, 910–923. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.082057 (2006).
Wang, B. et al. Integration of miRNA and mRNA analysis reveals the role of ribosome in anti-artificial aging in sweetcorn. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 240, 124434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124434 (2023).
Song, X. et al. Proteomic analysis of the Effect of Accelerated Aging on Allium Mongolicum Seeds. Horticulturae 9, 1155. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9101155 (2023).
Chen, K. & Arora, R. Dynamics of the antioxidant system during seed osmopriming, post-priming germination, and seedling establishment in spinach (Spinacia oleracea). Plant. Sci. 180, 212–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.08.007 (2011).
International Rules for Seed Testing. International Seed Testing Association (ISTA), full issue i–19 – 8 (300). Online ISSN 2310–3655 (2021).
Kader, M. A. A comparison of seed germination calculation formulae and the associated interpretation of resulting data. Journal & Proceedings of the Royal Society of New South Wales, 138, 65–75 (2005).
Esechie, H. Interaction of salinity and temperature on the germination of sorghum. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 172, 194–199 (1994). (1994).
Ellis, R. A. & Roberts, E. H. The quantification of aging and survival in orthodox seeds. Seed Sci. Technol. 9, 373–409 (1981).
Murray, M. & Thompson, W. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 8, 4321–4326 (1980).
Piepho, H. P., Möhring, J., Melchinger, A. E. & Büchse, A. BLUP for phenotypic selection in plant breeding and variety testing. Euphytica 161 (1), 209–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9449-8 (2008).
Bates, D., Mächler, M., Bolker, B. & Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 67 (1), 1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01 (2015).
Henderson, C. R. Best linear unbiased estimation and prediction under a selection model. Biometrics 31 (2), 423–447. https://doi.org/10.2307/2529430 (1975).
Bradbury, P. J. et al. Tassel: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23, 2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308 (2007).
Wang, J. & Zhang, Z. GAPIT version 3: boosting power and accuracy for genomic association and prediction. Genomics Proteom. Bioinf. 19, 629–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2021.08.001 (2021).
Huang, M., Liu, X., Zhou, Y., Summers, R. M. & Zhang, Z. Blink: a package for the next level of genome-wide association studies with both individuals and markers in the millions. GigaScience 8, giy154. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giy154 (2019).
Kanehisa, M., Furumichi, M., Sato, Y., Matsuura, Y. & Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG: biological systems database as a model of the real world. Nucleic Acids Res. 53 (D1), D672–D677. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae909 (2025).
Acknowledgements
The experiment was funded by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology, Government of India under the project CRG/2021/000477, the ICAR-Indian Institute of Millets Research project (IIMR/SS/2020-2025/126) and the Global Centre of Excellence on Millets (Shree Anna) project. The seed material of the finger millet diverse panel was supplied by the Gene Bank, International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT), Hyderabad, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NT, NK and TS conceptualized the research program. NK, RV, RM, IKD and AS conducted phenotyping experiments. MV contributed seeds. SN, NN and SS performed NGS data analysis. NT and AV performed genotyping. SN, NN, NK, TS and NT wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this Article was revised: In the original version of this Article, Netyam Kannababu was omitted as a corresponding author. Correspondence and requests for materials should also be addressed to [email protected]
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Kannababu, N., Nanjundappa, S., Narayanan, N. et al. Role of functional genes for seed vigor related traits through genome-wide association mapping in finger millet (Eleusine coracana L. Gaertn.). Sci Rep 15, 5569 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-89315-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-89315-3