Abstract
Eleocharis dulcis (Burm. f.) Trin. ex Hensch., commonly known as Chinese water chestnut, is a traditional aquatic vegetable in China, and now is widely cultivated throughout the world because of its high nutritional value and unique tastes. Here, we report the assembly of a 493.24 Mb telomere-to-telomere (T2T) genome of E. dulcis accomplished by integrating ONT ultra-long reads, PacBio long reads and Hi-C data. The reference genome was anchored onto 111 gap-free chromosomes, containing 48.31% repeat elements and 33,493 predicted protein-coding genes. Whole genome duplication (WGD) and inter-genomic synteny analyses indicated that chromosome breakage and genome duplication in E. dulcis possibly occurred multiple times during genome evolution after its divergence from a common ancestor with Rhynchospora breviuscula at ca. 35.6 Mya. A comparative time-course transcriptome analysis of corm development revealed different patterns of gene expression between cultivated and wild accessions with the highest number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs, 15,870) at the middle swelling stage and some of the DEGs were significantly enriched for starch metabolic process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background & Summary
Eleocharis dulcis (Cyperaceae), commonly known as Chinese water chestnut, is an aquatic perennial herbaceous plant that grows in shallow waters and is mainly distributed in China, Southeast Asia, the Americas, Europe, and Oceania1,2,3. Eleocharis dulcis is commonly consumed as a vegetable, as its underground corms are rich in starch and have unique tastes. It is also a critical ingredient in traditional Chinese medicine4,5. The cultivated history of Chinese water chestnut in China and India dates back to about two thousand years ago3,6. Now, it is widely cultivated in various counties and regions, including Japan, Australia, the Philippines, Malaysia, Hawaii, and other Pacific islands1.
Similar to other aquatic vegetable (rhizome, tuber, and bulbs), the corm of Chinse water chestnut is an underground stem that serves as a storage organ. The accumulating evidence suggests that the formation of storage organ is regulated by both genetic and environmental factors7,8,9. For example, Cheng et al.10 have identified some up-regulated transcription factors and genes related to organ formation of Chinese water chestnut. However, it remains unclear which genes are likely involved in domestication, and how they regulate corm development. In addition, the lack of an assembled genome has hitherto hindered the studies on the genome structure and evolution of E. dulcis which has a large number of chromosomes (more than 210)11,12. Thus, it is necessary to obtain the whole genome sequences of Chinese water chestnut to deepen our understanding of the mechanisms of the corm development and genome evolution.
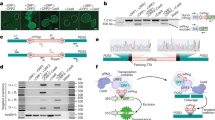
In this study, we reported a telomere-to-telomere (T2T) gap-free genome assembly for E. dulcis. De novo assembly using Oxford Nanopore Technology (ONT) ultra-long reads and PacBio high-fidelity (HiFi) long reads generated 521.12 Mb contigs with a contig N50 length of 4.67 Mb. After scaffolding by Hi-C reads, approximately 94.66% (493.24 Mb) of the assembled sequence were anchored onto pseudochromosomes, resulting in 111 gapless chromosomes (Fig. 1A,B; Tables 2, S1). A total of 33,493 protein-coding genes were predicted, of which 32,646 (97.47%) could be functionally annotated, with an average length of 4,211 bp (Table 3). In addition, we also identified 4,032 non-coding genes, including 225 miRNAs, 590 tRNAs, 2,735 rRNAs and 482 snRNAs (Table 3). Phylogenomic and comparative analyses (Figs. 1C, 2) suggested that chromosome breakage and genome duplication in E. dulcis likely took place multiple times during the evolution of its genome, after its divergence from a common ancestor with Rhynchospora breviuscula at ca. 35.6 million years ago (Mya). To understand the process of corm development, we conducted transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) at four distinct stages of corm development (Stage1–Stage4, Stage1: initial swelling stage, Stage2: middle swelling stage, Stage3: late swelling stage and Stage4: maturity stage) in both cultivated and wild accessions (Fig. 3A). Among these stages, Stage 2 exhibited the highest number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs, 15,870) (Fig. 3B,C). The GO and KEGG enrichment analyses showed that 45 of these upregulated 2,840 in Cluster 2 of reaction norms of those DEGs were significantly enriched for starch metabolic process (Fig. 3D, Tables S2, S3). The complete genomic and transcriptomic resources represent a major step forward in disentangling the complexities of corm development and genome evolution of E. dulcis; and will also facilitate functional genomics and molecular breeding studies in Chinese water chestnut.
(A) The Hi-C heatmap of chromosome interactions in E. dulcis genome. (B) The characteristics of the assembled E. dulcis genome. The tracks from outer to inner represent the gene density, repeat sequence density and GC content according to 50kbp windows. (C) A phylogenetic tree was constructed based on 634 single copy orthologues retrieved from 11 species. Arabidopsis thaliana and Vitis vinifera were chosen as outgroups. The red and green numbers on the branches represent the contracted and expanded gene families, respectively. Numbers at each node represent the inferred divergence times between species (millions of years). Red dots represent calibration ages between Rhynchospora breviuscula and Juncus effusus; R. breviuscula and Oryza sativa; R. breviuscula and Asparagus officinalis; A. officinalis and Vitis vinifera; V. vinifera and Arabidopsis thaliana. Calibration ages were obtained from the Timetree database (http://www.timetree.org/).
(A) Four developmental stages of corms of cultivated (‘Xuanci’)/wild accessions (S1: initial swelling stage; S2: middle swelling stage; S3: late swelling stage and S4: maturity stage) used for RNA sequencing. (B) Principal components analysis (PCA) of the transcriptomes of all samples. (C) Numbers of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in cultivated and wild corms. (D) Changes in gene expression in terms of four reaction norms for cultivar (‘Xuanci’) at the four stages (S1 to S4).
Methods
Plant materials and genome sequencing
We obtained the wild sample of E. dulcis from field in Baojiakan Village, Haishu District, Ningbo City, China (121.37° E, 29.76° N) and extracted the genomic DNA from mature leaves using the DNAsecure Plant Kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China). A hybrid approach, which combined ONT ultra-long sequencing, PacBio HiFi sequencing and a Hi-C chromatin interaction map, was employed to generate the genome assembly. For ONT ultra-long sequencing, as described by ONT Community’s protocol, genomic DNAs with long fragment were selected using Short Read Eliminator XL (Circulomics, MD, USA). After preparing the library using the SQK-LSK109 kit (Oxford Nanopore Technologies; Oxford, UK), Oxford Nanopore sequencing was performed on a PromethION flow cell (ONT, Oxford, UK). For PacBio HiFi sequencing, the genomic DNA was fragmented into 15 kb segments to construct a standard SMRTbell library, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, this library was sequenced on a PacBio Sequel IIe platform (Pacifc Biosciences, Menlo Park, USA). Hi-C library was constructed using NEBNext Ultra II DNA library preparation kit and DpnII enzyme (Ipswich, MA, USA). The Hi-C and Illumina short-insert libraries were sequenced on a DNBSEQ-T7 platform.
Estimation of genomic characteristics
llumina short reads were used to estimate genomic characteristics using a k-mer-based statistical analysis implemented in JELLYFISH v2.2.113 with the following parameters: ‘count -m 19 -C -c 7 -s 1 G -F 2’. Genome heterozygosity and genome size were estimated using GenomeScope v2.0 with default parameters14. Based on 19-mer depth analysis, genome size and heterozygosity were estimated to be 517.78 Mb and 0.77%, respectively (Fig. S1).
Quality assessment, genome assembly and gap filling
For ONT ultra-long data, FILTLONG v0.2.4 (https://github.com/rrwick/Filtlong) and PORECHOP v0.2.4 (https://github.com/rrwick/Porechop) were employed to remove low quality reads and trim primer sequences. The PacBio HiFi original sequencing data (subreads) were filtered by CCS v6.0 (–min-passes 3 –min-snr 2.5 –top-passes 60, https://github.com/PacificBiosciences/ccs). For Hi-C data, FASTP v0.2115 was used to remove the joint sequences and low-quality reads from raw data. Then, clean data were aligned to the reference genome with HICUP v0.816. After quality controlling, 36.98 Gb of ONT ultra-long data, 29.19 Gb of PacBio HiFi data and 58 Gb of Hi-C data (Table 1) were used for de novo genome assembly. The initial assembly of the ONT Ultra-long sequencing data was performed using NextDenovo v2.5 (read_cutoff = 1k, blocksize = 1 g, nextgraph_options = -a 1, https://github.com/Nextomics/NextDenovo). Additionally, we employed HIFIASM v0.16.117 to perform genome assembly with the HiFi sequencing data. To obtain a more comprehensive and accurate genome assembly, we also conducted a hybrid assembly combining HiFi and ONT data using HIFIASM v0.16.1. The mitochondrial and chloroplast sequences were removed from the alignments using MINIMAP2 v2.1718. The complete chloroplast sequence of E. dulcis (NC_047447) and complete mitochondrial sequence of Liriodendron tulipifera (NC_012152) were used as references. A BLAST RefSeq library was used to remove bacterial contamination and contigs with low read counts.
To achieve a telomere-to-telomere genome assembly, the contig sequences were clustered into various chromosome groups using a bottom-up hierarchical clustering algorithm with ALLHIC v0.9.819. The resulting assembly was further refined through adjustment of chromosome construction using the JUICEBOX tool v2.1220 (Fig. 1A). To fill the gaps in the assembled genome, WINNOWMAP v1.1121 was used for sequence alignment, including the assemblies derived from nextDenovo and Hifiasm, HiFi reads and ONT ultra-long reads. The longest and the most consensus sequences were applied to replace the corresponding gap-tied sequence. Subsequently, error correction was conducted using RACON v1.622, resulting in the attainment of a high-quality gap-free genome assembly. In total, 493.27 Mb reads were successfully anchored to 111 gapless chromosomes, with a contig N50 of 4.7 Mb (Table 2). Telomeres and centromeres were predicted employing quarTeT23 with recommended parameters (Table S1).
Genome annotation
Annotations of transposable elements (TEs) were obtained from homology-based searching in known repeat databases and de novo predictions. As part of homology-based detection, RepeatMasker v4.0.9 (http://www.repeatmasker.org) was used to identify TEs against the Repbase database at the DNA level. De novo TEs were detected by RepeatMasker v4.0.9 based on a de novo repeat library constructed by RepeatModeler v1.0.4. (http://www.repeatmasker.org/RepeatModeler.html), LTR_FINDER v1.0.524, and REPEATSCOUT v1.0.525. The tandem repeat sequences in the genome were identified using TANDEM REPEATS FINDER v4.0.926. A total of 238.28 Mb (48.31%) repetitive sequences were annotated in E. dulcis (Table 3), with long terminal repeat (LTR) accompanied for the largest proportion (24.32%).
To predict the gene structure of E. dulcis, three approaches were used: homology-based prediction, ab initio gene prediction and transcriptome-assisted annotation. For the homology-based gene prediction, the protein-coding sequences from Rhynchospora pubera27, R. breviuscula27, R. tenuis27, Brachypodium distachyon28, Carex cristatella29, and Oryza sativa30 were mapped to the assembled genome using TBLASTN v2.2.26 (E-value ≤ 1e−5)31 to obtain high-quality protein structures. The ab initio gene prediction was performed using AUGUSTUS v3.2.332, GENSCAN v1.033, GLIMMERHMM v3.0.434, GENEID v1.4.435 and SNAP v2013.11.2936. Besides, the RNA-seq reads separately derived from different tissues (i.e., root, stem, leaf) were aligned to the genome sequence using TOPHAT v2.0.1137 in transcriptome-assisted prediction. Subsequently, the mapped reads were assembled into longer transcripts using CUFFINKS v2.2.138. The transcripts from all tissues were merged and subjected to TransDecoder in PASA v2.4.139 for protein-coding sequence prediction and quality filtering. Only complete transcripts were retained for further analysis. All genes predicted by the above methods were integrated into a non-redundant gene set using EvidenceModeler (EVM) v1.1.140. The EVM-predicted genes were further corrected with PASA v2.4.139 to predict the untranslated regions and alternative splicings. The resulting protein models were functionally annotated according to the best matches with proteins deposited in GeneOntology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), Swiss-Prot, TREMBL and NCBI non-redundant protein database (Nr) using BLASTP (E-value = 1e−5). We identified tRNA genes, rRNA genes and ncRNA genes using TRNASCAN-SE v1.2341, INFERNAL v1.1.242 and RFAM database (https://rfam.org/), respectively. Finally, we employed MCSCANX43 and ‘CIRCLIZE’ R package44 to detect and visualize collinear blocks (Fig. 1B).
Gene family evolution analyses
We employed ORTHOFINDER v2.3.1245 to identify orthologous groups for 11 species, including Arabidopsis thaliana46, Vitis vinifera47, Eleocharis dulcis, Ananas comosus48, Rhynchospora breviuscula27, Phoenix dactylifera49, Juncus effusus27, Asparagus officinalis50, Musa acuminata51, Sorghum bicolor52 and Oryza sativa30. A total of 634 single copy orthologues were obtained and subsequently aligned using MUSCLE v3.853. All these genes were finally concatenated into one sequence as a ‘supergene’. Based on the ‘supergene’, we used RAXML v8.2.154 to construct a maximum likelihood (ML) tree, with the PROTGAMMAWAG model. Additionally, MCMCtree program implemented in PAML v4.955 was employed to estimate divergence times among species. According to the time-calibrated phylogeny, the genus Eleocharis was estimated to diverge from Rhynchospora ca. 20 million years ago (Fig. 1C). Subsequently, according to the species phylogenetic tree and gene family clustering results (Fig. 1C), gene family expansions and contractions analysis was performed using CAFE v3.156. GO enrichment analysis of gene families (P-value < 0.05) was performed using AGRIGO v2.057 with default parameters. The results revealed that 5,463 and 620 gene families had undergone significant expansions and contractions in E. dulcis (Fig. 1C), respectively. These expanded families were mostly enriched for essential functions, e.g. DNA binding, flavonoid biosynthetic process, nucleic acid binding (Fig. 1D).
The Ks method was employed to identify whole-genome duplication (WGD) events. The yn00 module implemented in PAML v4.955 was used to calculate the synonymous mutation frequency (Ks), nonsynonymous mutation frequency (Ka), and the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous mutation rates (Ka/Ks) for collinear gene pairs. The analysis of the Ks distribution showed that, except for a common whole-genome duplication (WGD) event shared by all monocots, E. dulcis underwent a recent WGD event which occurred after its divergence from R. breviuscula (Fig. 2A). Additionally, the synteny blocks generated by JCVI v0.9.1358 showed collinearity between a single chromosome of R. breviuscula and multiple chromosomes of E. dulcis and high self-collinearity among chromosomes of E. dulcis. Both suggest multiple occurrences of chromosome breakage and duplication during genomic evolution (Fig. 2B).
Transcriptome analysis
Wild individuals and a traditional cultivar ‘Xuanci’ of Chinese water chestnut were chosen for differential expression analysis of corm development. Our sampling strategy encompassed four distinct stages of corm development, i.e. Stage 1 (S1, initial swelling stage), Stage 2 (S2, middle swelling stage), Stage 3 (S3, late swelling stage), and Stage 4 (S4, maturity stage) (Fig. 3A). The samples of each stage included three biological replicates. Raw reads were generated by the DNBSEQ-T7 platform. Adapters and low-quality reads were filtered using FASTP v0.2115. Clean reads of each tissue were mapped to the reference genome using HISAT2 v2.0.459. The read counting of the annotated genes was performed using STRINGTIE v2.1.660. R package ‘DESeq2’61 was used to analyze differential gene expression. PCA showed that transcriptomes of three biological replicates within each time point group clustered together (Fig. 3B). The DEGs between various tissues were defined according to the following criteria:|log2FC| ≥ 1 and the false discovery rate (FDR) corrected P-value < 0.05.
RNAseq generated a total of 1,345,118,694 reads, with an average of 56,046,612 reads per sample
Among these stages, Stage 4 (maturity stage) exhibited the lowest number of DEGs, with 5,949 down-regulated genes and 5,965 up-regulated genes between cultivated and wild accessions (Fig. 3C). In contrast, Stage 2 (the middle swelling stage) had the highest number of DEGs, with 9,121 down-regulated genes and 6,749 up-regulated genes (Fig. 3C). Fuzzy c-means clustering implemented in the ‘MFUZZ’ R package62 revealed four major expression reaction norms in cultivated accessions (Fig. 3D). Genes in Cluster 1 were down-regulated after S1, while genes in Cluster 2 and Cluster 3 were up-regulated, reaching expression peak at S2 and S3, respectively. In Cluster 4, genes showed bimodal expression patterns (Fig. 3D). GO (Table S2) and KEGG enrichment (Table S3) analyses further demonstrated that the up-regulated genes in Cluster 2 were significantly (P < 0.05) enriched for starch metabolic process.
Data Records
The whole genome sequencing datasets have been stored in the National Genomics Data Center (NGDC). The raw data can be located using the GSA number CRA01314763, the genome sequence and annotation data were under accession number GWHEQVU0000000064, which corresponds to the BioProject accession number PRJCA01861365. Additionally, the RNA-seq data for both cultivated and wild accessions at four different stages can be found under the BioProject accession number PRJCA02068266, with the corresponding GSA number being CRA01313467. The genome sequence data were also deposited in the SRA (Sequence Read Archive) database with accession number SRX22848329–SRX2284833368,69,70,71,72 under the BioProject accession number PRJNA1033537. The assembled genome was deposited in the GeneBank in NCBI under accession number GCA_040741935.173. The RNA-seq data were submitted under PRJNA1033533. All expression data were uploaded to the the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) public database under Accession No. GSE26413274.
Technical Validation
The evaluation of the contig and chromosome levels of the assemblies was conducted through four methods: N50 for assessing continuity (contig N50 = 4.7 Mb), QV scores calculated by MERQURY75 v1.3 for measuring accuracy (QV = 49.2) and the paired-end (Illumina) reads mapping rate for ensuring consistency with the raw data (Mapping rate = 98.9%, read coverage (20X) = 99.0%). The verification of protein-coding genes was performed using BUSCO76. The BUSCO analysis showed 94.4% of complete BUSCO genes at the “genome mode” and 94.0% at the “protein mode”. The latter comprised 1,036 (64.8%) single-copy BUSCOs and 472 (29.2%) duplicated BUSCOs.
Code availability
No custom code was developed in this work. Software and pipelines were implemented according to the manuals and protocols of published bioinformatics tools. Software version and parameters were described in Methods.
References
Morton, J. F., Sanchez, C. A. & Snyder, G. H. Chinese water chestnuts in Florida: past, present, and future. Proc. Fla. State. Hort. Soc. 101, 139–144 (1988).
Wu, Z. Y., P. H. Raven & D. Y. Hong. Cyperaceae. In Flora of China. Vol. 23 188–200. (Science Press, Beijing, and Missouri Botanical Garden Press, St. Louis., 2010).
Li, M. & Midmore, D. J. Estimating the genetic relationships of Chinese water chestnut (Eleocharis dulcis (Burm. f.) Hensch) cultivated in Australia, using random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPDs). J. Horticult. Sci. Biotechnol. 74, 224–231 (2015).
Zhan, G. et al. Study on antibacterial properties and major bioactive constituents of Chinese water chestnut (Eleocharis dulcis) peels extracts/fractions. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 238, 789–796 (2014).
Zhang, Y. et al. Eleocharis dulcis corm: phytochemicals, health benefits, processing and food products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 102, 19–40 (2022).
Chen, Q. Y. Chinese water chestnuts. (Chinese Agricultural Publishing House, Beijing, China; 1995).
Jing, S. et al. Long-distance control of potato storage organ formation by SELF PRUNING 3D and FLOWERING LOCUS T-like 1. Plant Commun. 4, 100547 (2023).
Navarro, C. et al. Control of flowering and storage organ formation in potato by FLOWERING LOCUS T. Nature. 478, 119–122 (2011).
Zhang, X. et al. Pangenome of water caltrop reveals structural variations and asymmetric subgenome divergence after allopolyploidization. Horticulture Research. 10, uhad203 (2023).
Cheng, L. et al. Transcriptome analysis of gene expression during Chinese water chestnut storage organ formation. PLoS One 11, e164223 (2016).
Uchiyama, H., Matoba, H., Aizawa, T., Sumida, H. & Do, M. N. Chromosome counts of some wetland cyperaceous species from the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Cytologia. 75, 335–339 (2010).
Roalson, E. H. A synopsis of chromosome number variation in the Cyperaceae. Bot. Rev. 74, 209–393 (2008).
Marçais, G. & Kingsford, C. A fast, lock-free approach for efficient parallel counting of occurrences of k-mers. Bioinformatics 27, 764–770 (2011).
Vurture, G. W. et al. GenomeScope: fast reference-free genome profiling from short reads. Bioinformatics 33, 2202–2204 (2017).
Chen, S., Zhou, Y., Chen, Y. & Gu, J. fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, 884–890 (2018).
Wingett, S. et al. HiCUP: pipeline for mapping and processing Hi-C data. F1000Res 4, 1310 (2015).
Cheng, H., Concepcion, G. T., Feng, X., Zhang, H. & Li, H. Haplotype-resolved de novo assembly using phased assembly graphs with hifiasm. Nat. Methods. 18, 170–175 (2021).
Li, H. Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 34, 3094–3100 (2018).
Zhang, X., Zhang, S., Zhao, Q., Ming, R. & Tang, H. Assembly of allele-aware, chromosomal-scale autopolyploid genomes based on Hi-C data. Nat. Plants. 5, 833–845 (2019).
Durand, N. C. et al. Juicebox provides a visualization system for Hi-C contact maps with unlimited zoom. Cell Syst 3, 99–101 (2016).
Jain, C. et al. Weighted minimizer sampling improves long read mapping. Bioinformatics 36, 111–118 (2020).
Vaser, R., Sović, I., Nagarajan, N. & Šikić, M. Fast and accurate de novo genome assembly from long uncorrected reads. Genome Res 27, 737–746 (2017).
Lin, Y. et al. quarTeT: a telomere-to-telomere toolkit for gap-free genome assembly and centromeric repeat identification. Horticulture Research 10, uhad127 (2023).
Xu, Z. & Wang, H. LTR_FINDER: an efficient tool for the prediction of full-length LTR retrotransposons. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 265–268 (2007).
Price, A. L., Jones, N. C. & Pevzner, P. A. De novo identification of repeat families in large genomes. Bioinformatics 21, 351–358 (2005).
Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 573–580 (1999).
Hofstatter, P. G. et al. Repeat-based holocentromeres influence genome architecture and karyotype evolution. Cell 185, 3153–3168 (2022).
The International Brachypodium Initiative. Genome sequencing and analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon. Nature 463, 763–768 (2010).
Planta, J. et al. Chromosome-scale genome assemblies and annotations for Poales species Carex cristatella, Carex scoparia, Juncus effusus, and Juncus inflexus. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genet. 12, jkac211 (2022).
Ouyang, S. et al. The TIGR Rice Genome Annotation Resource: improvements and new features. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 883–887 (2007).
Gertz, E. M., Yu, Y., Agarwala, R., Schäffer, A. A. & Altschul, S. F. Composition-based statistics and translated nucleotide searches: improving the TBLASTN module of BLAST. BMC Biol. 4, 1–14 (2006).
Stanke, M., Schoffmann, O., Morgenstern, B. & Waack, S. Gene prediction in eukaryotes with a generalized hidden Markov model that uses hints from external sources. BMC Bioinf. 7, 62 (2006).
Burge, C. & Karlin, S. Prediction of complete gene structures in human genomic DNA. J. Mol. Biol. 268, 78–94 (1997).
Majoros, W. H., Pertea, M. & Salzberg, S. L. TigrScan and GlimmerHMM: two open source ab initio eukaryotic gene-finders. Bioinformatics 20, 2878–2879 (2004).
Blanco, E., Parra, G. & Guigo, R. Using geneid to identify genes. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. Chapter 4, 3–4 (2007).
Korf, I. Gene finding in novel genomes. BMC Bioinf. 5, 59 (2004).
Trapnell, C., Pachter, L. & Salzberg, S. L. TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25, 1105–1111 (2009).
Trapnell, C. et al. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 7, 562–578 (2012).
Haas, B. J. et al. Improving the Arabidopsis genome annotation using maximal transcript alignment assemblies. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 5654–5666 (2003).
Haas, B. J. et al. Automated eukaryotic gene structure annotation using EVidenceModeler and the Program to Assemble Spliced Alignments. Genome Biol. 9, R7 (2008).
Schattner, P., Brooks, A. N. & Lowe, T. M. The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 686–689 (2005).
Nawrocki, E. P. & Eddy, S. R. Infernal 1.1: 100-fold faster RNA homology searches. Bioinformatics 29, 2933–2935 (2013).
Wang, Y. et al. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 49 (2012).
Gu, Z., Gu, L., Eils, R., Schlesner, M. & Brors, B. circlize implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics. 19, 2811 (2014).
Emms, D. M. & Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: solving fundamental biases in whole genome comparisons dramatically improves orthogroup inference accuracy. Genome Biol. 16, 157 (2015).
The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408, 796–815 (2000).
Massonnet, M. et al. The genetic basis of sex determination in grapes. Nat. Commun. 11, 2902 (2020).
Ming, R. et al. The pineapple genome and the evolution of CAM photosynthesis. Nature Genet. 47, 1435–1442 (2015).
Al-Dous, E. K. et al. De novo genome sequencing and comparative genomics of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera). Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 521–527 (2011).
Harkess, A. et al. The asparagus genome sheds light on the origin and evolution of a young Y chromosome. Nat. Commun. 8, 1279 (2017).
D Hont, A. et al. The banana (Musa acuminata) genome and the evolution of monocotyledonous plants. Nature 488, 213–217 (2012).
Paterson, A. H. et al. The Sorghum bicolor genome and the diversification of grasses. Nature 457, 551–556 (2009).
Edgar, R. C. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1792–1797 (2004).
Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30, 1312–1313 (2014).
Yang, Z. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1586–1591 (2007).
Han, M. V., Thomas, G. W., Lugo-Martinez, J. & Hahn, M. W. Estimating gene gain and loss rates in the presence of error in genome assembly and annotation using CAFE 3. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 1987–1997 (2013).
Tian, T. et al. agriGO v2.0: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 122–129 (2017).
Tang, H. et al. Synteny and collinearity in plant genomes. Science. 320, 486–488 (2008).
Kim, D., Langmead, B. & Salzberg, S. L. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods. 12, 357–360 (2015).
Pertea, M. et al. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 290–295 (2015).
Love, M. I., Huber, W. & Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq 2. Genome Biol. 15 (2014).
Kumar, L. & E, F. M. Mfuzz: a software package for soft clustering of microarray data. Bioinformation. 2, 5–7 (2007).
NGDC Genome Sequence Archive. https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa/browse/CRA013147 (2024).
NGDC Genome Warehouse. https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gwh/Assembly/83530/show (2024).
NGDC BioProject. https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/bioproject/browse/PRJCA018613 (2024).
NGDC BioProject. https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/bioproject/browse/PRJCA020682 (2024).
NGDC Genome Sequence Archive. https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa/browse/CRA013134 (2024).
NCBI Sequence Read Archive. https://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.sra:SRX22848329 (2024).
NCBI Sequence Read Archive. https://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.sra:SRX22848330 (2024).
NCBI Sequence Read Archive. https://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.sra:SRX22848331 (2024).
NCBI Sequence Read Archive. https://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.sra:SRX22848332 (2024).
NCBI Sequence Read Archive. https://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.sra:SRX22848333 (2024).
NCBI GeneBank. https://identifiers.org/ncbi/insdc.gca:GCA_040741935.1 (2024).
NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus. https://identifiers.org/geo/GSE264132 (2024).
Rhie A. et al. Merqury: reference-free quality, completeness, and phasing assessment for genome assemblies. Genome biology, 21 (2020).
Simão, F. A., Waterhouse, R. M., Ioannidis, P., Kriventseva, E. V. & Zdobnov, E. M. BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics. 31, 3210–3212 (2015).
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to the colleagues in BENAGEN company for their assistance with data analyses. This work was supported by the Program on the Collection, Conservation, and Utilization of Germplasm Resources of Aquatic Vegetables in Zhejiang Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Q. and Z.Z. conceived the project. Y.C., X.Z. and L.W. performed experiments and coordinated research activities. Y.C., X.Z., L.W., Y. H., M.F., X. C., W. S., and M.F. collected the samples. Y.C. and X.Z. analyzed data. Y.C. drafted the manuscript. Y.Q., Y.M., X.Z. and R. L. revised and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhang, X., Wang, L. et al. Telomere-to-telomere genome assembly of Eleocharis dulcis and expression profiles during corm development. Sci Data 11, 869 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03717-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03717-y